Windows Kimlik Bilgileri Korumaları
Tip
AWS Hacking’i öğrenin ve pratik yapın:
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
GCP Hacking’i öğrenin ve pratik yapın:HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Azure Hacking’i öğrenin ve pratik yapın:
HackTricks Training Azure Red Team Expert (AzRTE)
HackTricks'i Destekleyin
- abonelik planlarını kontrol edin!
- 💬 Discord grubuna veya telegram grubuna katılın ya da Twitter’da bizi takip edin 🐦 @hacktricks_live.**
- Hacking ipuçlarını paylaşmak için HackTricks ve HackTricks Cloud github reposuna PR gönderin.
WDigest
WDigest protokolü, Windows XP ile tanıtılmış olup HTTP Protocolü üzerinden kimlik doğrulama için tasarlanmıştır ve Windows XP’den Windows 8.0’a ve Windows Server 2003’ten Windows Server 2012’ye kadar varsayılan olarak etkinleştirilmiştir. Bu varsayılan ayar, LSASS içinde düz metin parola depolanmasına yol açar (Yerel Güvenlik Yetkilisi Alt Sistem Hizmeti). Bir saldırgan, Mimikatz kullanarak bu kimlik bilgilerini çıkarabilir; şu komutu çalıştırarak:
sekurlsa::wdigest
bu özelliği kapatmak veya açmak için, UseLogonCredential ve Negotiate kayıt defteri anahtarlarının HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\WDigest altında “1” olarak ayarlanması gerekir. Bu anahtarlar yoksa veya “0” olarak ayarlanmışsa, WDigest devre dışıdır:
reg query HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\WDigest /v UseLogonCredential
LSA Koruması (PP & PPL korumalı süreçler)
Protected Process (PP) ve Protected Process Light (PPL), LSASS gibi hassas süreçlere yetkisiz erişimi önlemek için tasarlanmış Windows çekirdek düzeyi korumalarıdır. Windows Vista’da tanıtılan PP modeli, başlangıçta DRM uygulaması için oluşturulmuştu ve yalnızca özel bir medya sertifikasıyla imzalanmış ikili dosyaların korunmasına izin veriyordu. PP olarak işaretlenmiş bir sürece yalnızca ayrıca PP olan ve eşit veya daha yüksek koruma düzeyine sahip diğer süreçler erişebilir; üstelik izin verilmediği sürece erişim hakları sınırlıdır.
PPL, Windows 8.1’de tanıtıldı ve PP’nin daha esnek bir sürümüdür. LSASS, Defender gibi daha geniş kullanım senaryolarına izin vermek için dijital imzanın EKU (Enhanced Key Usage) alanına dayalı “koruma seviyeleri” getirir. Koruma düzeyi EPROCESS.Protection alanında saklanır; bu alan PS_PROTECTION yapısıdır ve şunları içerir:
- Type (
ProtectedveyaProtectedLight) - Signer (ör.
WinTcb,Lsa,Antimalware, vb.)
Bu yapı tek bir bayta paketlenmiştir ve kimin kime erişebileceğini belirler:
- Daha yüksek signer değerleri daha düşük olanlara erişebilir
- PPL’ler PP’lere erişemez
- Korumasız süreçler hiçbir PPL/PP’ye erişemez
Saldırgan bakış açısından bilmeniz gerekenler
- LSASS PPL olarak çalıştığında, normal bir admin bağlamından
OpenProcess(PROCESS_VM_READ | QUERY_INFORMATION)ile açma girişimleri,SeDebugPrivilegeetkin olsa bile0x5 (Access Denied)ile başarısız olur. EPROCESS.Protectiondeğerini okuyarak veya Process Hacker gibi araçlarla LSASS koruma düzeyini kontrol edebilirsiniz.- LSASS genellikle
PsProtectedSignerLsa-Light(0x41) olur; bu yalnızcaWinTcb(0x61veya0x62) gibi daha yüksek düzeyli bir signer ile imzalanmış süreçler tarafından erişilebilir. - PPL, yalnızca userland seviyesinde bir kısıtlamadır; çekirdek düzeyi kodu bunu tamamen aşabilir.
- LSASS’in PPL olması, eğer kernel shellcode çalıştırabiliyor veya uygun erişime sahip yüksek yetkili bir süreci kullanabiliyorsanız credential dumping’i engellemez.
- PPL’in ayarlanması veya kaldırılması genellikle yeniden başlatma veya Secure Boot/UEFI ayarları gerektirir; bu, kayıt defteri değişiklikleri geri alınsa bile PPL ayarının kalıcı olmasına neden olabilir.
Başlangıçta PPL süreci oluşturma (belgelendirilmiş API)
Windows, genişletilmiş startup attribute listesi kullanarak çocuk süreç oluşturulurken Protected Process Light seviyesi talep etmek için belgelendirilmiş bir yol sunar. Bu, imzalama gereksinimlerini baypas etmez — hedef imaj, istenen signer sınıfı için imzalanmış olmalıdır.
C/C++ için minimal akış:
// Request a PPL protection level for the child process at creation time
// Requires Windows 8.1+ and a properly signed image for the selected level
#include <windows.h>
int wmain(int argc, wchar_t **argv) {
STARTUPINFOEXW si = {0};
PROCESS_INFORMATION pi = {0};
si.StartupInfo.cb = sizeof(si);
SIZE_T attrSize = 0;
InitializeProcThreadAttributeList(NULL, 1, 0, &attrSize);
si.lpAttributeList = (PPROC_THREAD_ATTRIBUTE_LIST)HeapAlloc(GetProcessHeap(), 0, attrSize);
if (!si.lpAttributeList) return 1;
if (!InitializeProcThreadAttributeList(si.lpAttributeList, 1, 0, &attrSize)) return 1;
DWORD level = PROTECTION_LEVEL_ANTIMALWARE_LIGHT; // or WINDOWS_LIGHT/LSA_LIGHT/WINTCB_LIGHT
if (!UpdateProcThreadAttribute(
si.lpAttributeList, 0,
PROC_THREAD_ATTRIBUTE_PROTECTION_LEVEL,
&level, sizeof(level), NULL, NULL)) {
return 1;
}
DWORD flags = EXTENDED_STARTUPINFO_PRESENT;
if (!CreateProcessW(L"C\\Windows\\System32\\notepad.exe", NULL, NULL, NULL, FALSE,
flags, NULL, NULL, &si.StartupInfo, &pi)) {
// If the image isn't signed appropriately for the requested level,
// CreateProcess will fail with ERROR_INVALID_IMAGE_HASH (577).
return 1;
}
// cleanup
DeleteProcThreadAttributeList(si.lpAttributeList);
HeapFree(GetProcessHeap(), 0, si.lpAttributeList);
CloseHandle(pi.hThread);
CloseHandle(pi.hProcess);
return 0;
}
Notes and constraints:
STARTUPINFOEXileInitializeProcThreadAttributeListveUpdateProcThreadAttribute(PROC_THREAD_ATTRIBUTE_PROTECTION_LEVEL, ...)kullanın, sonraCreateProcess*’eEXTENDED_STARTUPINFO_PRESENTiletiniz.- Koruma
DWORD’uPROTECTION_LEVEL_WINTCB_LIGHT,PROTECTION_LEVEL_WINDOWS,PROTECTION_LEVEL_WINDOWS_LIGHT,PROTECTION_LEVEL_ANTIMALWARE_LIGHTveyaPROTECTION_LEVEL_LSA_LIGHTgibi sabitlere ayarlanabilir. - Child ancak imajı o signer sınıfı için imzalıysa PPL olarak başlar; aksi takdirde process oluşturma başarısız olur, genelde
ERROR_INVALID_IMAGE_HASH (577)/STATUS_INVALID_IMAGE_HASH (0xC0000428)ile. - Bu bir bypass değil — uygun şekilde imzalanmış imajlar için tasarlanmış desteklenen bir API’dir. Araçları güçlendirmek veya PPL korumalı yapılandırmaları doğrulamak için faydalıdır.
Example CLI using a minimal loader:
- Antimalware signer:
CreateProcessAsPPL.exe 3 C:\Tools\agent.exe --svc - LSA-light signer:
CreateProcessAsPPL.exe 4 C:\Windows\System32\notepad.exe
Bypass PPL protections options:
If you want to dump LSASS despite PPL, you have 3 main options:
- Use a signed kernel driver (e.g., Mimikatz + mimidrv.sys) to remove LSASS’s protection flag:

- Bring Your Own Vulnerable Driver (BYOVD) to run custom kernel code and disable the protection. Tools like PPLKiller, gdrv-loader, or kdmapper make this feasible.
- Steal an existing LSASS handle from another process that has it open (e.g., an AV process), then duplicate it into your process. This is the basis of the
pypykatz live lsa --method handleduptechnique. - Abuse some privileged process that will allow you to load arbitrary code into its address space or inside another privileged process, effectively bypassing the PPL restrictions. You can check an example of this in bypassing-lsa-protection-in-userland or https://github.com/itm4n/PPLdump.
Check current status of LSA protection (PPL/PP) for LSASS:
reg query HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\LSA /v RunAsPPL
When you running mimikatz privilege::debug sekurlsa::logonpasswords it’ll probably fail with the error code 0x00000005 because of this.
- Bu kontrol hakkında daha fazla bilgi için https://itm4n.github.io/lsass-runasppl/
Credential Guard
Credential Guard, a feature exclusive to Windows 10 (Enterprise and Education editions), makine kimlik bilgilerini Virtual Secure Mode (VSM) ve Virtualization Based Security (VBS) kullanarak daha güvenli hale getirir. CPU sanallaştırma uzantılarını kullanarak, ana işletim sisteminin erişim alanının dışında korumalı bir bellek alanında kritik süreçleri izole eder. Bu izolasyon, kernel’in bile VSM içindeki belleğe erişememesini sağlar ve böylece kimlik bilgilerini pass-the-hash gibi saldırılardan etkin şekilde korur. Local Security Authority (LSA) bu güvenli ortam içinde bir trustlet olarak çalışırken, ana OS içindeki LSASS süreci yalnızca VSM’deki LSA ile iletişim kuran bir aracıdır.
Varsayılan olarak Credential Guard etkin değildir ve kurum içi olarak manuel etkinleştirme gerektirir. Mimikatz gibi araçlara karşı güvenliği artırmada kritik öneme sahiptir; bu araçların kimlik bilgilerini çıkarması büyük ölçüde zorlaşır. Ancak, oturum açma sırasında kimlik bilgilerini açık metin olarak yakalamak için özel Security Support Providers (SSP) eklenmesi yoluyla hâlâ zafiyetler kullanılabilir.
Credential Guard’ın etkinlik durumunu doğrulamak için LsaCfgFlags anahtarına ve HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\LSA altındaki değere bakılabilir. “1” değeri UEFI lock ile etkinleştirildiğini, “2” kilit olmadan etkinleştirildiğini ve “0” ise etkin olmadığını gösterir. Bu kayıt kontrolü güçlü bir gösterge olmasına rağmen, Credential Guard’ı etkinleştirmek için tek adım değildir. Bu özelliği etkinleştirmeye yönelik ayrıntılı rehberlik ve bir PowerShell script’i çevrimiçi olarak mevcuttur.
reg query HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\LSA /v LsaCfgFlags
For a comprehensive understanding and instructions on enabling Credential Guard in Windows 10 and its automatic activation in compatible systems of Windows 11 Enterprise and Education (version 22H2), visit Microsoft’s documentation.
Further details on implementing custom SSPs for credential capture are provided in this guide.
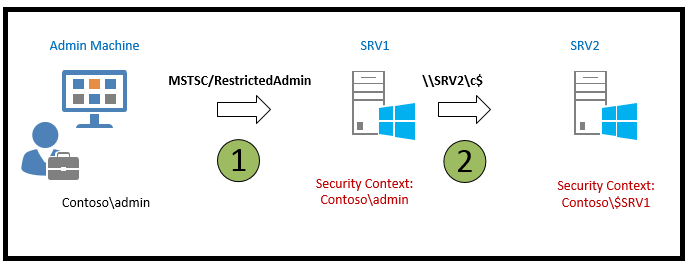
RDP RestrictedAdmin Mode
Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2 introduced several new security features, including the Restricted Admin mode for RDP. This mode was designed to enhance security by mitigating the risks associated with pass the hash attacks.
Traditionally, when connecting to a remote computer via RDP, your credentials are stored on the target machine. This poses a significant security risk, especially when using accounts with elevated privileges. However, with the introduction of Restricted Admin mode, this risk is substantially reduced.
When initiating an RDP connection using the command mstsc.exe /RestrictedAdmin, authentication to the remote computer is performed without storing your credentials on it. This approach ensures that, in the event of a malware infection or if a malicious user gains access to the remote server, your credentials are not compromised, as they are not stored on the server.
It’s important to note that in Restricted Admin mode, attempts to access network resources from the RDP session will not use your personal credentials; instead, the machine’s identity is used.
This feature marks a significant step forward in securing remote desktop connections and protecting sensitive information from being exposed in case of a security breach.
For more detailed information on visit this resource.
Cached Credentials
Windows secures domain credentials through the Local Security Authority (LSA), supporting logon processes with security protocols like Kerberos and NTLM. A key feature of Windows is its capability to cache the last ten domain logins to ensure users can still access their computers even if the domain controller is offline—a boon for laptop users often away from their company’s network.
The number of cached logins is adjustable via a specific registry key or group policy. To view or change this setting, the following command is utilized:
reg query "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\MICROSOFT\WINDOWS NT\CURRENTVERSION\WINLOGON" /v CACHEDLOGONSCOUNT
Access to these cached credentials is tightly controlled, with only the SYSTEM account having the necessary permissions to view them. Administrators needing to access this information must do so with SYSTEM user privileges. The credentials are stored at: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SECURITY\Cache
Mimikatz can be employed to extract these cached credentials using the command lsadump::cache.
For further details, the original source provides comprehensive information.
Protected Users
Membership in the Protected Users group introduces several security enhancements for users, ensuring higher levels of protection against credential theft and misuse:
- Credential Delegation (CredSSP): Even if the Group Policy setting for Allow delegating default credentials is enabled, plain text credentials of Protected Users will not be cached.
- Windows Digest: Starting from Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2, the system will not cache plain text credentials of Protected Users, regardless of the Windows Digest status.
- NTLM: The system will not cache Protected Users’ plain text credentials or NT one-way functions (NTOWF).
- Kerberos: For Protected Users, Kerberos authentication will not generate DES or RC4 keys, nor will it cache plain text credentials or long-term keys beyond the initial Ticket-Granting Ticket (TGT) acquisition.
- Offline Sign-In: Protected Users will not have a cached verifier created at sign-in or unlock, meaning offline sign-in is not supported for these accounts.
These protections are activated the moment a user, who is a member of the Protected Users group, signs into the device. This ensures that critical security measures are in place to safeguard against various methods of credential compromise.
For more detailed information, consult the official documentation.
Table from the docs.
| Windows Server 2003 RTM | Windows Server 2003 SP1+ |
Windows Server 2012, | Windows Server 2016 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Account Operators | Account Operators | Account Operators | Account Operators |
| Administrator | Administrator | Administrator | Administrator |
| Administrators | Administrators | Administrators | Administrators |
| Backup Operators | Backup Operators | Backup Operators | Backup Operators |
| Cert Publishers | |||
| Domain Admins | Domain Admins | Domain Admins | Domain Admins |
| Domain Controllers | Domain Controllers | Domain Controllers | Domain Controllers |
| Enterprise Admins | Enterprise Admins | Enterprise Admins | Enterprise Admins |
| Enterprise Key Admins | |||
| Key Admins | |||
| Krbtgt | Krbtgt | Krbtgt | Krbtgt |
| Print Operators | Print Operators | Print Operators | Print Operators |
| Read-only Domain Controllers | Read-only Domain Controllers | ||
| Replicator | Replicator | Replicator | Replicator |
| Schema Admins | Schema Admins | Schema Admins | Schema Admins |
| Server Operators | Server Operators | Server Operators | Server Operators |
Kaynaklar
- CreateProcessAsPPL – minimal PPL process launcher
- STARTUPINFOEX structure (Win32 API)
- InitializeProcThreadAttributeList (Win32 API)
- UpdateProcThreadAttribute (Win32 API)
- LSASS RunAsPPL – background and internals
Tip
AWS Hacking’i öğrenin ve pratik yapın:
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
GCP Hacking’i öğrenin ve pratik yapın:HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Azure Hacking’i öğrenin ve pratik yapın:
HackTricks Training Azure Red Team Expert (AzRTE)
HackTricks'i Destekleyin
- abonelik planlarını kontrol edin!
- 💬 Discord grubuna veya telegram grubuna katılın ya da Twitter’da bizi takip edin 🐦 @hacktricks_live.**
- Hacking ipuçlarını paylaşmak için HackTricks ve HackTricks Cloud github reposuna PR gönderin.
 HackTricks
HackTricks